1.先来看sdk中的介绍:
A Handler allows you to send and process {@link Message} and Runnable objects associated with a thread's {@link MessageQueue}. Each Handler instance is associated with a single thread and that thread's message queue. When you create a new Handler, it is bound to the thread /message queue of the thread that is creating it -- from that point on,it will deliver messages and runnables to that message queue and execute them as they come out of the message queue.
翻译:一个Handler可以发送或处理和一个线程相关的任务对象。每个Handler实例都关联一个单线程及其消息队列。每当你创造一个新的Handler,它必然对应产生一个线程/消息队列,从此刻开始,它将发送消息和任务到消息队列并且当它们从消息队列出来时去处理它们。
There are two main uses for a Handler: (1) to schedule messages and runnables to be executed as some point in the future; and (2) to enqueue an action to be performed on a different thread than your own.
翻译:Handler有两个主要用途:(1)预先排队将要处理的线程(2)将一个动作异步优先处理
When posting or sending to a Handler, you can either allow the item to be processed as soon as the message queue is ready to do so, or specify a delay before it gets processed or absolute time for it to be processed. The latter two allow you to implement timeouts, ticks, and other timing-based behavior.
翻译:这句讲Handler既可以立刻处理,也可以延时处理
When a process is created for your application, its main thread is dedicated to running a message queue that takes care of managing the top-level application objects (activities, broadcast receivers, etc) and any windows they create. You can create your own threads, and communicate back with the main application thread through a Handler. This is done by calling the same <em>post</em> or <em>sendMessage</em> methods as before, but from your new thread. The given Runnable or Message will then be scheduled in the Handler's message queue and processed when appropriate.
翻译:这句讲的是通过sendMessage方法实现异步线程和主线程的通信
2.Handler构造函数
public Handler() { this(null, false); } public Handler(Callback callback) { this(callback, false); } public Handler(Looper looper) { this(looper, null, false); } public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback) { this(looper, callback, false); } public Handler(boolean async) { this(null, async); } public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) { final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass(); if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) && (klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) { Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " + klass.getCanonicalName()); } } mLooper = Looper.myLooper(); if (mLooper == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); } mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async; } public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) { mLooper = looper; mQueue = looper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async; }
这几个构造函数最终要做的都是这几句
mLooper = looper; //或Looper.myLooper() mQueue = looper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async;
3.Looper
Looper构造函数
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
创建了一个MessageQueue对象。
这里有个需要注意的地方:
ActivityThread的主线程中执行了如下方法:
public static void main(String[] args) { ... Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ... Looper.loop(); ... }
来看Looper执行了哪些:
prepareMainLooper()
public static void prepareMainLooper() { prepare(false); synchronized (Looper.class) { if (sMainLooper != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared."); } sMainLooper = myLooper(); } }
其中prepare()向sThreadLocal中塞了一个Looper对象(一个线程中只能有一个Looper)
public static void prepare() { prepare(true); } private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); }
前面Handler的构造函数中执行Looper.myLooper()
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() { return sThreadLocal.get(); }
这样就能获取当前线程保存的Looper实例。而且在Handler构造函数中执行了下面这句
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
这样就保证了handler的实例与我们Looper实例中MessageQueue关联上了。
执行loop()
public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper(); final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; ... for (;;) { Message msg = queue.next(); // might block if (msg == null) { return; } ... msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
... msg.recycleUnchecked(); } }
msg.target就是Handler自身
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { if (msg.callback != null) { handleCallback(msg); } else { if (mCallback != null) { if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { return; } } handleMessage(msg); } }
因为再往回看,发现我们一开始msg.callback其实是null,所以最终执行的是handleMessage(msg);
public void handleMessage(Message msg) { }
方法体是空的,所以需要去复写处理Message
4.Message
构造函数
public Message() { }
获取Message
public static Message obtain() { synchronized (sPoolSync) { if (sPool != null) { Message m = sPool; sPool = m.next; m.next = null; m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag sPoolSize--; return m; } } return new Message(); } public static Message obtain(Message orig) { Message m = obtain(); m.what = orig.what; m.arg1 = orig.arg1; m.arg2 = orig.arg2; m.obj = orig.obj; m.replyTo = orig.replyTo; m.sendingUid = orig.sendingUid; if (orig.data != null) { m.data = new Bundle(orig.data); } m.target = orig.target; m.callback = orig.callback; return m; } public static Message obtain(Handler h) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; return m; } public static Message obtain(Handler h, int what) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; m.what = what; return m; } public static Message obtain(Handler h, int what, Object obj) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; m.what = what; m.obj = obj; return m; } public static Message obtain(Handler h, int what, int arg1, int arg2) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; m.what = what; m.arg1 = arg1; m.arg2 = arg2; return m; } public static Message obtain(Handler h, int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj) { Message m = obtain(); m.target = h; m.what = what; m.arg1 = arg1; m.arg2 = arg2; m.obj = obj; return m; }
其中obtain()最重要
Message m = sPool; sPool = m.next; m.next = null; m.flags = 0; // clear in-use flag sPoolSize--; return m;
显而易见,是一个链表结构,分析如下:

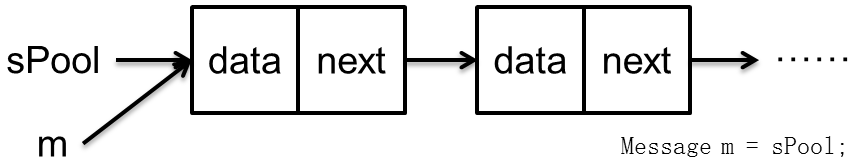
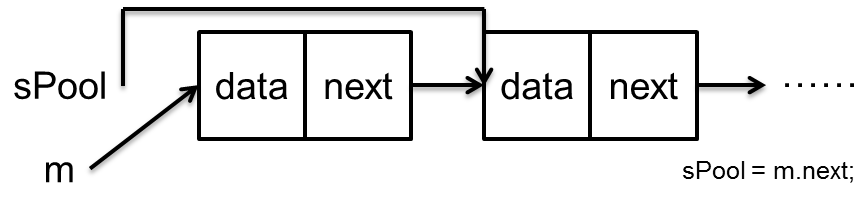

这样,就能从sPool中得到一个Message,体现了重复回收利用的特点。
可能有人会问,得到Message不是通过Handler.obtainMessage方法吗,其实原因很简单,Handler.obtainMessage调用的就是Message.obtain
public final Message obtainMessage(){ return Message.obtain(this); } public final Message obtainMessage(int what){ return Message.obtain(this, what); } public final Message obtainMessage(int what, Object obj){ return Message.obtain(this, what, obj); } public final Message obtainMessage(int what, int arg1, int arg2){ return Message.obtain(this, what, arg1, arg2); } public final Message obtainMessage(int what, int arg1, int arg2, Object obj){ return Message.obtain(this, what, arg1, arg2, obj); }
前面Looper中调用了msg.recycleUnchecked()
void recycleUnchecked() { // Mark the message as in use while it remains in the recycled object pool. // Clear out all other details. flags = FLAG_IN_USE; what = 0; arg1 = 0; arg2 = 0; obj = null; replyTo = null; sendingUid = -1; when = 0; target = null; callback = null; data = null; synchronized (sPoolSync) { if (sPoolSize < MAX_POOL_SIZE) { next = sPool; sPool = this; sPoolSize++; } } }
即回收Message


5.发送消息
public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg){ return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0); } public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what){ return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0); } public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) { Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what = what; return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis); } public final boolean sendEmptyMessageAtTime(int what, long uptimeMillis) { Message msg = Message.obtain(); msg.what = what; return sendMessageAtTime(msg, uptimeMillis); } public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis){ if (delayMillis < 0) { delayMillis = 0; } return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis); } public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue; if (queue == null) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); } public final boolean sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(Message msg) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue; if (queue == null) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, 0); } private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { msg.target = this; if (mAsynchronous) { msg.setAsynchronous(true); } return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis); }
方法这么多,最后执行的都是enqueueMessage
queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
6.MessageQueue.enqueueMessage()
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) { ... synchronized (this) { ... msg.markInUse(); msg.when = when; Message p = mMessages; boolean needWake; if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) { msg.next = p; mMessages = msg; needWake = mBlocked; } else { ... Message prev; for (;;) { prev = p; p = p.next; ... } msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next prev.next = msg; } ... } return true; }
MessageQueue也是一个链表,msg会插入到p的前面
发送消息还有另一种方式post,但其实最终调用的都是sendMessageXXX
public final boolean post(Runnable r){ return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0); } public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, long uptimeMillis){ return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r), uptimeMillis); } public final boolean postAtTime(Runnable r, Object token, long uptimeMillis){ return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r, token), uptimeMillis); } public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis){ return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), delayMillis); } public final boolean postAtFrontOfQueue(Runnable r){ return sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(getPostMessage(r)); }
不一样的是,需要传一个参数Runnable,并且需要getPostMessage(runnable)
private static Message getPostMessage(Runnable r) { Message m = Message.obtain(); m.callback = r; return m; }
总结:
1、首先Looper.prepare()在本线程中保存一个Looper实例,然后该实例中保存一个MessageQueue对象;因为Looper.prepare()在一个线程中只能调用一次,所以MessageQueue在一个线程中只会存在一个。
2、Looper.loop()会让当前线程进入一个无限循环,不端从MessageQueue的实例中读取消息,然后回调msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)方法。
3、Handler的构造方法,会首先得到当前线程中保存的Looper实例,进而与Looper实例中的MessageQueue想关联。
4、Handler的sendMessage方法,会给msg的target赋值为handler自身,然后加入MessageQueue中。
5、在构造Handler实例时,我们会重写handleMessage方法,也就是msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)最终调用的方法。
ps:纯原创,参考文章如下