布尔型数组方法
在数组的一些计算中布尔值会被强制转换为1(True)和0(False)。因此,sum经常被用来对布尔型数组中的True值计数:
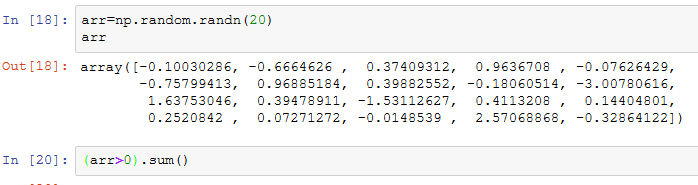
另外还有两个方法any和all,它们对布尔型数组非常有用。any用于测试数组中是否存在一个或多个True,而all则检查数组中所有值是否都是True:
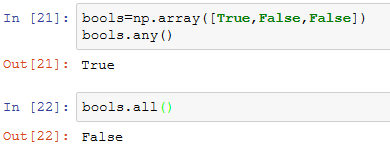
这两个方法也能用于非布尔型数组,所有非0元素将会被当做True。

排序
跟Python内置的列表类型一样,NumPy数组也可以通过sort方法就地排序:
官方描述:
Parameters
----------
a:array_like
Arraytobesorted.
axis:intorNone,optional
Axisalongwhichtosort.IfNone,thearrayisflattenedbefore
sorting.Thedefaultis-1,whichsortsalongthelastaxis.
kind:{'quicksort','mergesort','heapsort'},optional
Sortingalgorithm.Defaultis'quicksort'.
order:strorlistofstr,optional
When`a`isanarraywithfieldsdefined,thisargumentspecifies
whichfieldstocomparefirst,second,etc.Asinglefieldcan
bespecifiedasastring,andnotallfieldsneedbespecified,
butunspecifiedfieldswillstillbeused,intheorderinwhich
theycomeupinthedtype,tobreakties.
关于axis的取值,多次对比,真没发现有什么区别,有知道的可以评论区告知。

可以发现上述的sort方法是直接对ran进行了排序而并没有创建一个副本。
但是np.sort()这个顶级的方法,会返回一个副本:

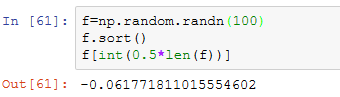
就地排序则会修改数组本身。计算数组分位数最简单的办法是对其进行排序,然后选取特定位置的值:
求中分位数
唯一化以及其他的集合逻辑
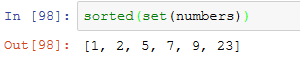
NumPy提供了一些针对一维ndarray的基本集合运算。最常用的可能要数np.unique了,它用于找出数组中的唯一值并返回已排序的结果:
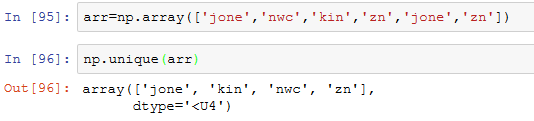
同样适合于数字类型

拿跟np.unique等价的纯Python代码来对比一下:
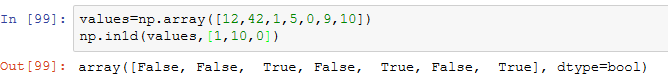
另一个函数np.in1d用于测试一个数组中的值在另一个数组中的成员资格,返回一个布尔型数组:
NumPy中的集合函数请参见表4-6。

译注2:简单点说,就是“异或”。