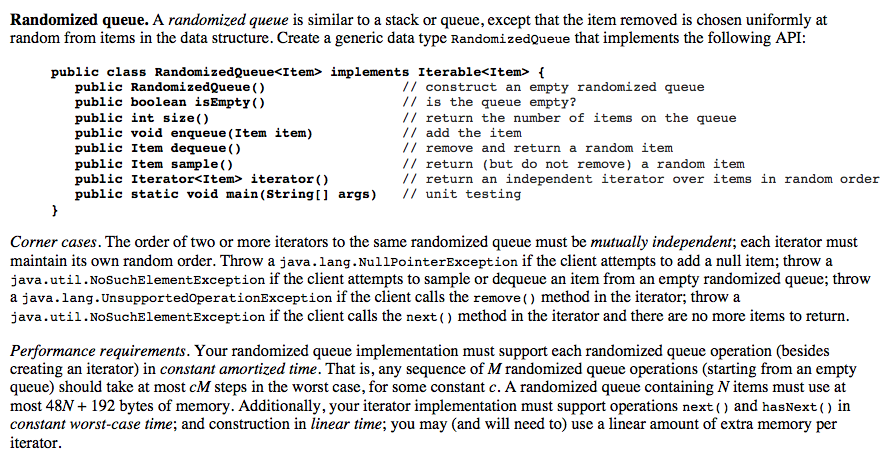
RandomizedQueue 有几个关键点:
1. 选择合适的数据结构,因为需要任意位置删除元素,Linked list 做不到,必须使用resizing arrays.
2. resizing 的技巧。
Q. How to grow array?
A. If array is full, create a new array of twice the size, and copy items.
Q. How to shrink array?
Java code:
A: halve size of array when array is one-quarter full
3. 正确使用StdRandom.shuffle. 要能实现并行使用Iterator,洗牌不是洗array 本身,而是生成一个乱序的index.
Java code:
//RandomizedQueue - should be implemented using resizing arrays import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut; import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.NoSuchElementException; public class RandomizedQueue<Item> implements Iterable<Item> { private Item[] q; // array of items private int N; // number of elements // construct an empty randomized queue public RandomizedQueue() { q = (Item[]) new Object[1]; N = 0; } // is the queue empty? public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; } // return the number of items on the queue public int size() { return N; } // resize the underlying array holding the elements private void resize(int capacity) { assert capacity >= N; Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[capacity]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { temp[i] = q[i]; } q = temp; } // add the item //Throw a java.lang.NullPointerException if the client attempts to add a null item public void enqueue(Item item) { if(item == null) { throw new NullPointerException("add a null item"); } if(N == q.length) { resize(2 * q.length); // double size of array if necessary } q[N++] = item; // add item } /*when deleting random element you can just simply switch it with the last element in array * and decrease the array size counter. So deletion will take constant time. *throw a java.util.NoSuchElementException if the client attempts to sample or dequeue an item *from an empty randomized queue; */ // remove and return a random item public Item dequeue() { if (isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("No element"); } int x = StdRandom.uniform(N); Item item = q[x]; q[x] = q[--N]; q[N] = null; if (N == q.length / 4 && N > 0) { resize(q.length / 2); } return item; } // return (but do not remove) a random item public Item sample() { if(isEmpty()) { throw new NoSuchElementException("No element"); } int x = StdRandom.uniform(N); return q[x]; } // return an independent iterator over items in random order public Iterator<Item> iterator() { return new ArrayIterator(); } private class ArrayIterator implements Iterator<Item> { private int i; private int[] indexSequence; public ArrayIterator() { i = 0; indexSequence = new int[N]; for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { indexSequence[j] = j; } StdRandom.shuffle(indexSequence); } public boolean hasNext() { return i < N ; } public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public Item next() { if (!hasNext()) { throw new NoSuchElementException(); } return q[indexSequence[i++]]; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // unit testing } }