基本分类
官网示例:https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/basic_classification
主要步骤:
- 加载Fashion MNIST数据集
- 探索数据:了解数据集格式
- 预处理数据
- 构建模型:设置层、编译模型
- 训练模型
- 评估准确率
- 做出预测:可视化
Fashion MNIST数据集
- 经典 MNIST 数据集(常用作计算机视觉机器学习程序的“Hello, World”入门数据集)的简易替换
- 包含训练数据60000个,测试数据10000个,每个图片是28x28像素的灰度图像,涵盖10个类别
- https://keras.io/datasets/#fashion-mnist-database-of-fashion-articles
- TensorFlow:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist
- GitHub:https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist
tf.keras
- Keras是一个用于构建和训练深度学习模型的高级API
- TensorFlow中的tf.keras是Keras API规范的TensorFlow实现,可以运行任何与Keras兼容的代码,保留了一些细微的差别
- 最新版TensorFlow中的tf.keras版本可能与PyPI中的最新Keras版本不同
- https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/
过拟合
如果机器学习模型在新数据上的表现不如在训练数据上的表现,就表示出现过拟合
示例
脚本内容
GitHub:https://github.com/anliven/Hello-AI/blob/master/Google-Learn-and-use-ML/1_basic_classification.py
1 # coding=utf-8 2 import tensorflow as tf 3 from tensorflow import keras 4 import numpy as np 5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 6 import os 7 8 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' 9 print("TensorFlow version: {} - tf.keras version: {}".format(tf.VERSION, tf.keras.__version__)) # 查看版本 10 11 # ### 加载数据集 12 # 网络畅通的情况下,可以从 TensorFlow 直接访问 Fashion MNIST,只需导入和加载数据即可 13 # 或者手工下载文件,并存放在“~/.keras/datasets”下的fashion-mnist目录 14 fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist 15 (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data() 16 # 训练集:train_images 和 train_labels 数组,用于学习的数据 17 # 测试集:test_images 和 test_labels 数组,用于测试模型 18 # 图像images为28x28的NumPy数组,像素值介于0到255之间 19 # 标签labels是整数数组,介于0到9之间,对应于图像代表的服饰所属的类别,每张图像都映射到一个标签 20 21 class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat', 22 'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] # 类别名称 23 24 # ### 探索数据:了解数据格式 25 print("train_images.shape: {}".format(train_images.shape)) # 训练集中有60000张图像,每张图像都为28x28像素 26 print("train_labels len: {}".format(len(train_labels))) # 训练集中有60000个标签 27 print("train_labels: {}".format(train_labels)) # 每个标签都是一个介于 0 到 9 之间的整数 28 print("test_images.shape: {}".format(test_images.shape)) # 测试集中有10000张图像,每张图像都为28x28像素 29 print("test_labels len: {}".format(len(test_labels))) # 测试集中有10000个标签 30 print("test_labels: {}".format(test_labels)) 31 32 # ### 预处理数据 33 # 必须先对数据进行预处理,然后再训练网络 34 plt.figure(num=1) # 创建图形窗口,参数num是图像编号 35 plt.imshow(train_images[0]) # 绘制图片 36 plt.colorbar() # 渐变色度条 37 plt.grid(False) # 显示网格 38 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-1.png", dpi=200, format='png') # 保存文件,必须在plt.show()前使用,否则将是空白内容 39 plt.show() # 显示 40 plt.close() # 关闭figure实例,如果要创建多个figure实例,必须显示调用close方法来释放不再使用的figure实例 41 42 # 值缩小为0到1之间的浮点数 43 train_images = train_images / 255.0 44 test_images = test_images / 255.0 45 46 # 显示训练集中的前25张图像,并在每张图像下显示类别名称 47 plt.figure(num=2, figsize=(10, 10)) # 参数figsize指定宽和高,单位为英寸 48 for i in range(25): # 前25张图像 49 plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1) 50 plt.xticks([]) # x坐标轴刻度 51 plt.yticks([]) # y坐标轴刻度 52 plt.grid(False) 53 plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) 54 plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]]) # x坐标轴名称 55 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-2.png", dpi=200, format='png') 56 plt.show() 57 plt.close() 58 59 # ### 构建模型 60 # 构建神经网络需要先配置模型的层,然后再编译模型 61 # 设置层 62 model = keras.Sequential([ 63 keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), # 将图像格式从二维数组(28x28像素)转换成一维数组(784 像素) 64 keras.layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), # 全连接神经层,具有128个节点(或神经元) 65 keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax)]) # 全连接神经层,具有10个节点的softmax层 66 # 编译模型 67 model.compile(optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(), # 优化器:根据模型看到的数据及其损失函数更新模型的方式 68 loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', # 损失函数:衡量模型在训练期间的准确率。 69 metrics=['accuracy']) # 指标:用于监控训练和测试步骤;这里使用准确率(图像被正确分类的比例) 70 71 # ### 训练模型 72 # 将训练数据馈送到模型中,模型学习将图像与标签相关联 73 model.fit(train_images, # 训练数据 74 train_labels, # 训练数据 75 epochs=5, # 训练周期(训练模型迭代轮次) 76 verbose=2 # 日志显示模式:0为安静模式, 1为进度条(默认), 2为每轮一行 77 ) # 调用model.fit 方法开始训练,使模型与训练数据“拟合 78 79 # ### 评估准确率 80 # 比较模型在测试数据集上的表现 81 test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels) 82 print('Test loss: {} - Test accuracy: {}'.format(test_loss, test_acc)) 83 84 # ### 做出预测 85 predictions = model.predict(test_images) # 使用predict()方法进行预测 86 print("The first prediction: {}".format(predictions[0])) # 查看第一个预测结果(包含10个数字的数组,分别对应10种服饰的“置信度” 87 label_number = np.argmax(predictions[0]) # 置信度值最大的标签 88 print("label: {} - class name: {}".format(label_number, class_names[label_number])) 89 print("Result true or false: {}".format(test_labels[0] == label_number)) # 对比测试标签,查看该预测是否正确 90 91 92 # 可视化:将该预测绘制成图来查看全部10个通道 93 def plot_image(m, predictions_array, true_label, img): 94 predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array[m], true_label[m], img[m] 95 plt.grid(False) 96 plt.xticks([]) 97 plt.yticks([]) 98 plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary) 99 predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array) 100 if predicted_label == true_label: 101 color = 'blue' # 正确的预测标签为蓝色 102 else: 103 color = 'red' # 错误的预测标签为红色 104 plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label], 105 100 * np.max(predictions_array), 106 class_names[true_label]), 107 color=color) 108 109 110 def plot_value_array(n, predictions_array, true_label): 111 predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array[n], true_label[n] 112 plt.grid(False) 113 plt.xticks([]) 114 plt.yticks([]) 115 thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777") 116 plt.ylim([0, 1]) 117 predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array) 118 thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red') 119 thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue') 120 121 122 # 查看第0张图像、预测和预测数组 123 i = 0 124 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) 125 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) 126 plot_image(i, predictions, test_labels, test_images) 127 plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) 128 plot_value_array(i, predictions, test_labels) 129 plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45) # x坐标轴刻度,参数rotation表示label旋转显示角度 130 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-3.png", dpi=200, format='png') 131 plt.show() 132 plt.close() 133 134 # 查看第12张图像、预测和预测数组 135 i = 12 136 plt.figure(num=4, figsize=(8, 5)) 137 plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) 138 plot_image(i, predictions, test_labels, test_images) 139 plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) 140 plot_value_array(i, predictions, test_labels) 141 plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45) # range(10)作为x轴的刻度,class_names作为对应的标签 142 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-4.png", dpi=200, format='png') 143 plt.show() 144 plt.close() 145 146 # 绘制图像:正确的预测标签为蓝色,错误的预测标签为红色,数字表示预测标签的百分比(总计为 100) 147 num_rows = 5 148 num_cols = 3 149 num_images = num_rows * num_cols 150 plt.figure(num=5, figsize=(2 * 2 * num_cols, 2 * num_rows)) 151 for i in range(num_images): 152 plt.subplot(num_rows, 2 * num_cols, 2 * i + 1) 153 plot_image(i, predictions, test_labels, test_images) 154 plt.subplot(num_rows, 2 * num_cols, 2 * i + 2) 155 plot_value_array(i, predictions, test_labels) 156 plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45) 157 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-5.png", dpi=200, format='png') 158 plt.show() 159 plt.close() 160 161 # 使用经过训练的模型对单个图像进行预测 162 image = test_images[0] # 从测试数据集获得一个图像 163 print("img shape: {}".format(image.shape)) # 图像的shape信息 164 image = (np.expand_dims(image, 0)) # 添加到列表中 165 print("img shape: {}".format(image.shape)) 166 predictions_single = model.predict(image) # model.predict返回一组列表,每个列表对应批次数据中的每张图像 167 print("prediction_single: {}".format(predictions_single)) # 查看预测,预测结果是一个具有10个数字的数组,分别对应10种不同服饰的“置信度” 168 169 plt.figure(num=6) 170 plot_value_array(0, predictions_single, test_labels) 171 plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45) 172 plt.savefig("./outputs/sample-1-figure-6.png", dpi=200, format='png') 173 plt.show() 174 plt.close() 175 176 prediction_result = np.argmax(predictions_single[0]) # 获取批次数据中相应图像的预测结果(置信度值最大的标签) 177 print("prediction_result: {}".format(prediction_result))
运行结果
common line
C:UsersanlivenAppDataLocalcondacondaenvsmlccpython.exe D:/Anliven/Anliven-Code/PycharmProjects/TempTest/TempTest.py TensorFlow version: 1.12.0 train_images.shape: (60000, 28, 28) train_labels len: 60000 train_labels: [9 0 0 ... 3 0 5] test_images.shape: (10000, 28, 28) test_labels len: 10000 test_labels: [9 2 1 ... 8 1 5] Epoch 1/5 - 3s - loss: 0.5077 - acc: 0.8211 Epoch 2/5 - 3s - loss: 0.3790 - acc: 0.8632 Epoch 3/5 - 3s - loss: 0.3377 - acc: 0.8755 Epoch 4/5 - 3s - loss: 0.3120 - acc: 0.8855 Epoch 5/5 - 3s - loss: 0.2953 - acc: 0.8914 32/10000 [..............................] - ETA: 15s 2208/10000 [=====>........................] - ETA: 0s 4576/10000 [============>.................] - ETA: 0s 7008/10000 [====================>.........] - ETA: 0s 9344/10000 [===========================>..] - ETA: 0s 10000/10000 [==============================] - 0s 30us/step Test loss: 0.3584352566242218 - Test accuracy: 0.8711 The first prediction: [4.9706377e-06 2.2675355e-09 1.3649772e-07 3.6149192e-08 4.7982059e-08 8.5262489e-03 1.5245891e-05 3.2628113e-03 1.6874857e-05 9.8817366e-01] label: 9 - class name: Ankle boot Result true or false: True img shape: (28, 28) img shape: (1, 28, 28) prediction_single: [[4.9706327e-06 2.2675313e-09 1.3649785e-07 3.6149192e-08 4.7982059e-08 8.5262526e-03 1.5245891e-05 3.2628146e-03 1.6874827e-05 9.8817366e-01]] prediction_result: 9 Process finished with exit code 0
Figure1

Figure2

Figure3
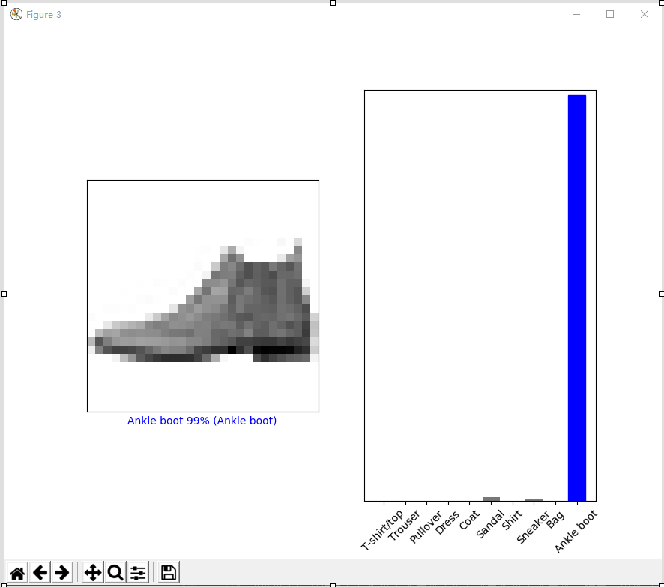
Figure4

Figure5

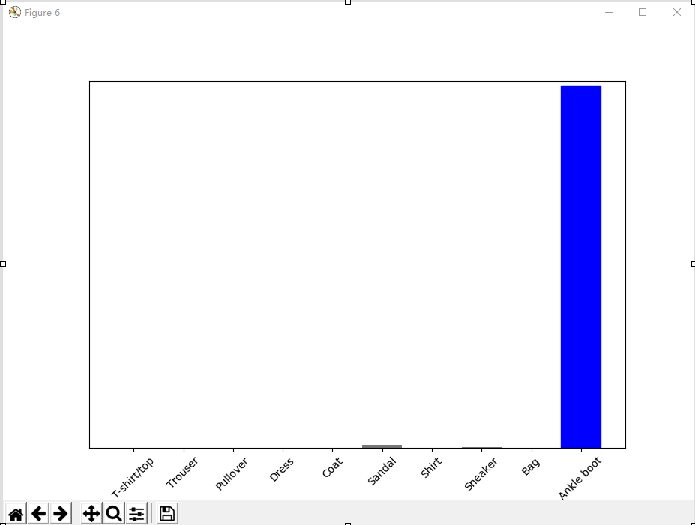
Figure6
问题处理
问题1:执行fashion_mnist.load_data()失败
错误提示
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
......
Exception: URL fetch failure on https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz: None -- [WinError 10060] A connection attempt failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time, or established connection failed because connected host has failed to respond
处理方法1
选择一个链接,
- https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist/tree/master/data/fashion
- https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/
手工下载下面四个文件,并存放在“~/.keras/datasets”下的fashion-mnist目录。
- train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
- train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
- t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
- t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
guowli@5CG450158J MINGW64 ~/.keras/datasets $ pwd /c/Users/guowli/.keras/datasets guowli@5CG450158J MINGW64 ~/.keras/datasets $ ls -l total 0 drwxr-xr-x 1 guowli 1049089 0 Mar 27 14:44 fashion-mnist/ guowli@5CG450158J MINGW64 ~/.keras/datasets $ ls -l fashion-mnist/ total 30164 -rw-r--r-- 1 guowli 1049089 4422102 Mar 27 15:47 t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 guowli 1049089 5148 Mar 27 15:47 t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 guowli 1049089 26421880 Mar 27 15:47 train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz -rw-r--r-- 1 guowli 1049089 29515 Mar 27 15:47 train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
处理方法2
手工下载文件,存放在指定目录。
改写“tensorflowpythonkerasdatasetsfashion_mnist.py”定义的load_data()函数。
from tensorflow.python.keras.utils import get_file import numpy as np import pathlib import gzip def load_data(): # 改写“tensorflowpythonkerasdatasetsfashion_mnist.py”定义的load_data()函数 base = "file:///" + str(pathlib.Path.cwd()) + "\" # 当前目录 files = [ 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz', 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz', 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz' ] paths = [] for fname in files: paths.append(get_file(fname, origin=base + fname)) with gzip.open(paths[0], 'rb') as lbpath: y_train = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=8) with gzip.open(paths[1], 'rb') as imgpath: x_train = np.frombuffer( imgpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(len(y_train), 28, 28) with gzip.open(paths[2], 'rb') as lbpath: y_test = np.frombuffer(lbpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=8) with gzip.open(paths[3], 'rb') as imgpath: x_test = np.frombuffer( imgpath.read(), np.uint8, offset=16).reshape(len(y_test), 28, 28) return (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) (train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = load_data()
问题2:使用gzip.open()打开.gz文件失败
错误提示
“OSError: Not a gzipped file (b' ')”
处理方法
对于损坏的、不完整的.gz文件,zip.open()将无法打开。检查.gz文件是否完整无损。
参考信息