今天根据斯坦福大学的在线课程复习链表和二叉树
上面对于二叉树的递归定义非常简洁:
a binary tree is either empty (represented by a null pointer), or is made of a single node, where the left and right pointers (recursive definition ahead) each point to a binary tree.
二叉树的一个分支:二叉搜索树(binary search tree,BST),是所有左节点的值 <= 中间节点 ,右节点的值 > 中间节点。
这就是一棵二叉搜索树
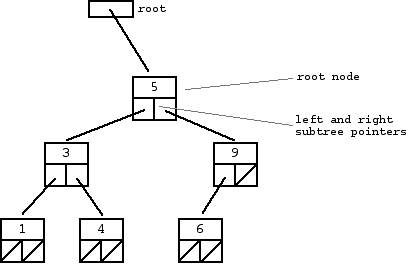
BST的优点是便于插入和查找,在一棵数量为N的BST中插入和查找的算法复杂度是O(lgN),类似二分查找。
下面使用Java描述的二叉树,包括插入和查找的基本方法。另外说一点,面向对象的好处就是对外屏蔽不需要显示的细节,封装。
// BinaryTree.java public class BinaryTree { // Root node pointer. Will be null for an empty tree. private Node root; /* --Node-- The binary tree is built using this nested node class. Each node stores one data element, and has left and right sub-tree pointer which may be null. The node is a "dumb" nested class -- we just use it for storage; it does not have any methods. */ private static class Node { Node left; Node right; int data; Node(int newData) { left = null; right = null; data = newData; } } /** Creates an empty binary tree -- a null root pointer. */ public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } /** Returns true if the given target is in the binary tree. Uses a recursive helper. */ public boolean lookup(int data) { return(lookup(root, data)); } /** Recursive lookup -- given a node, recur down searching for the given data. */ private boolean lookup(Node node, int data) { if (node==null) { return(false); } if (data==node.data) { return(true); } else if (data<node.data) { return(lookup(node.left, data)); } else { return(lookup(node.right, data)); } } /** Inserts the given data into the binary tree. Uses a recursive helper. */ public void insert(int data) { root = insert(root, data); } /** Recursive insert -- given a node pointer, recur down and insert the given data into the tree. Returns the new node pointer (the standard way to communicate a changed pointer back to the caller). */ private Node insert(Node node, int data) { if (node==null) { node = new Node(data); } else { if (data <= node.data) { node.left = insert(node.left, data); } else { node.right = insert(node.right, data); } } return(node); // in any case, return the new pointer to the caller }
另外还有获得树的高度以及最小值的方法
//获得树的高度
/** Returns the max root-to-leaf depth of the tree. Uses a recursive helper that recurs down to find the max depth. */ public int maxDepth() { return(maxDepth(root)); } private int maxDepth(Node node) { if (node==null) { return(0); } else { int lDepth = maxDepth(node.left); int rDepth = maxDepth(node.right); // use the larger + 1 return(Math.max(lDepth, rDepth) + 1); } } //获得最小值 /** Returns the min value in a non-empty binary search tree. Uses a helper method that iterates to the left to find the min value. */ public int minValue() { return( minValue(root) ); } /** Finds the min value in a non-empty binary search tree. */ private int minValue(Node node) { Node current = node; while (current.left != null) { current = current.left; } return(current.data); }
关于链表
记得大学还没毕业的时候有一次面试,面试官问我把一个链表倒置需要几个指针?当时没答出来,印象特别深刻,所以这次就把这个知识点复习下。
使用C代码写的,但思路是一样的
/* Iterative list reverse. Iterate through the list left-right. Move/insert each node to the front of the result list -- like a Push of the node. */ static void Reverse(struct node**headRef){ struct node*result=NULL; struct node*current=*headRef; struct node*next; while(current!=NULL){ next=current->next; // tricky: note the next node current->next=result; // move the node onto the result result=current; current=next; } *headRef=result; }
需要三个指针,一个指向需要倒置的链表,一个保存next节点,一个指向倒置后返回的链表。