Shiro认证流程
在学习认证流程之前,你应该先了解Shiro的基本使用流程
认证
- 身份认证: 证明用户是谁。用户需要提供相关的凭证principals(身份标识)和Credentials (凭证,证明你是这个用户,可以理解成密码)
- Principals: 用户的属性,可以有多个。但是至少有一个属性能唯一用户
- Credentials: 证明信息,密码或者证书之类的
认证流程
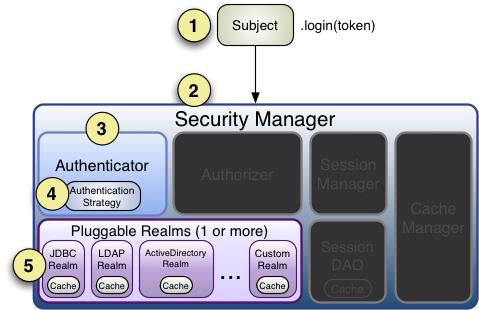
- token传给Subject.login(Token)。在调用login方法时候,内部完成了认证和授权
- 实际上的认证是由SecurityManager调用Authenticator认证器
- Authenticator认证器在调用实际的Realms的时候根据配置的Authentication Strategy认证策略规则判断是否认证成功
详细的认证流程
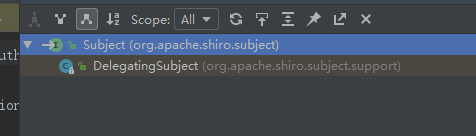
Subject是个接口,实际上的
login(AuthenticationToken var1)是由子类DelegatingSubject实现的
1 public void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { 2 this.clearRunAsIdentitiesInternal(); 3 Subject subject = this.securityManager.login(this, token); 4 String host = null; 5 PrincipalCollection principals; 6 if (subject instanceof DelegatingSubject) { 7 DelegatingSubject delegating = (DelegatingSubject)subject; 8 principals = delegating.principals; 9 host = delegating.host; 10 } else { 11 principals = subject.getPrincipals(); 12 } 13 14 if (principals != null && !principals.isEmpty()) { 15 this.principals = principals; 16 this.authenticated = true; 17 if (token instanceof HostAuthenticationToken) { 18 host = ((HostAuthenticationToken)token).getHost(); 19 } 20 21 if (host != null) { 22 this.host = host; 23 } 24 25 Session session = subject.getSession(false); 26 if (session != null) { 27 this.session = this.decorate(session); 28 } else { 29 this.session = null; 30 } 31 32 } else { 33 String msg = "Principals returned from securityManager.login( token ) returned a null or empty value. This value must be non null and populated with one or more elements."; 34 throw new IllegalStateException(msg); 35 } 36 }
可以看到在第三行中
调用了ScurityManager.login
因此可以证明subject只是存储用户信息,用户的认证和授权其实是通过SecurityManager调用认证器和授权器实现的。可以把SecurityManager理解成一个中央调度器。
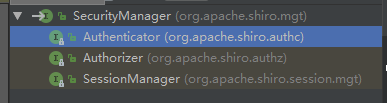
SecurityManager是一个接口,集成Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager
public interface SecurityManager extends Authenticator, Authorizer, SessionManager { Subject login(Subject var1, AuthenticationToken var2) throws AuthenticationException; void logout(Subject var1); Subject createSubject(SubjectContext var1); }
SecurityManager有login方法,因此我们可以找找SecurityManager的实现类
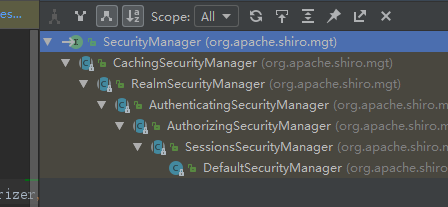
我们可以在DefaultSecurityManager中找到Login()方法
1 public Subject login(Subject subject, AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { 2 AuthenticationInfo info;//存储用户的认证信息和授权信息 3 try { 4 info = this.authenticate(token);//划重点 5 } catch (AuthenticationException var7) { 6 AuthenticationException ae = var7; 7 8 try { 9 this.onFailedLogin(token, ae, subject); 10 } catch (Exception var6) { 11 if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { 12 log.info("onFailedLogin method threw an exception. Logging and propagating original AuthenticationException.", var6); 13 } 14 } 15 16 throw var7; 17 } 18 19 Subject loggedIn = this.createSubject(token, info, subject); 20 this.onSuccessfulLogin(token, info, loggedIn); 21 return loggedIn; 22 }
第四行调用了authenticate(token).这个方法是SecurityManager的一个实现类AuthenticatingSecurityManager.java实现的,也是DefaultSecurityManager的父类
1 private Authenticator authenticator = new ModularRealmAuthenticator();//认证器 2 3 public AuthenticationInfo authenticate(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { 4 return this.authenticator.authenticate(token); 5 }
可以看到最终认证器的实现是 ModularRealmAuthenticator
总结: Shiro通过调用Subject的子类DelegatingSubject 的login(AuthenticationToken token)完成用户的认证和授权。实际上的认证是由SecurityManager的默认子类DefaultSecurityManager中的Login方法调用SecurityManager的另外一个子类AuthenticatingSecurityManager也同时是DefaultSecurityManager的父类authenticate(AuthenticationToken token)完成认证。并且最终的认证器类型是ModualRealmAuthenticator