一. flask依赖wsgi,实现wsgi的模块:wsgiref(django),werkzeug(flask),uwsgi
1. werkzeug示例
from werkzeug.wrappers import Request, Response
@Request.application
def hello(request):
return Response('Hello World!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
run_simple('localhost', 4000, hello)
2. wsgiref示例:
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
def runserver(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return [bytes('<h1>Hello, web!</h1>', encoding='utf-8'), ]
if __name__ == '__main__':
# obj = WSGIHandler()
httpd = make_server('', 8000, runserver)
httpd.serve_forever()
3. 本质的本质 -- socket
import socket
def handle_request(client):
buf = client.recv(1024)
client.send("HTTP/1.1 200 OK
")
client.send("Hello, Seven")
def main():
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.bind(('localhost', 8000))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
connection, address = sock.accept()
handle_request(connection)
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
4. app.run()中的run方法源码
def run(self, host=None, port=None, debug=None, **options):
"""Runs the application on a local development server.
Do not use ``run()`` in a production setting. It is not intended to
meet security and performance requirements for a production server.
Instead, see :ref:`deployment` for WSGI server recommendations.
If the :attr:`debug` flag is set the server will automatically reload
for code changes and show a debugger in case an exception happened.
If you want to run the application in debug mode, but disable the
code execution on the interactive debugger, you can pass
``use_evalex=False`` as parameter. This will keep the debugger's
traceback screen active, but disable code execution.
It is not recommended to use this function for development with
automatic reloading as this is badly supported. Instead you should
be using the :command:`flask` command line script's ``run`` support.
.. admonition:: Keep in Mind
Flask will suppress any server error with a generic error page
unless it is in debug mode. As such to enable just the
interactive debugger without the code reloading, you have to
invoke :meth:`run` with ``debug=True`` and ``use_reloader=False``.
Setting ``use_debugger`` to ``True`` without being in debug mode
won't catch any exceptions because there won't be any to
catch.
.. versionchanged:: 0.10
The default port is now picked from the ``SERVER_NAME`` variable.
:param host: the hostname to listen on. Set this to ``'0.0.0.0'`` to
have the server available externally as well. Defaults to
``'127.0.0.1'``.
:param port: the port of the webserver. Defaults to ``5000`` or the
port defined in the ``SERVER_NAME`` config variable if
present.
:param debug: if given, enable or disable debug mode.
See :attr:`debug`.
:param options: the options to be forwarded to the underlying
Werkzeug server. See
:func:`werkzeug.serving.run_simple` for more
information.
"""
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
if host is None:
host = '127.0.0.1'
if port is None:
server_name = self.config['SERVER_NAME']
if server_name and ':' in server_name:
port = int(server_name.rsplit(':', 1)[1])
else:
port = 5000
if debug is not None:
self.debug = bool(debug)
options.setdefault('use_reloader', self.debug)
options.setdefault('use_debugger', self.debug)
try:
run_simple(host, port, self, **options)
finally:
# reset the first request information if the development server
# reset normally. This makes it possible to restart the server
# without reloader and that stuff from an interactive shell.
self._got_first_request = False
基本流程
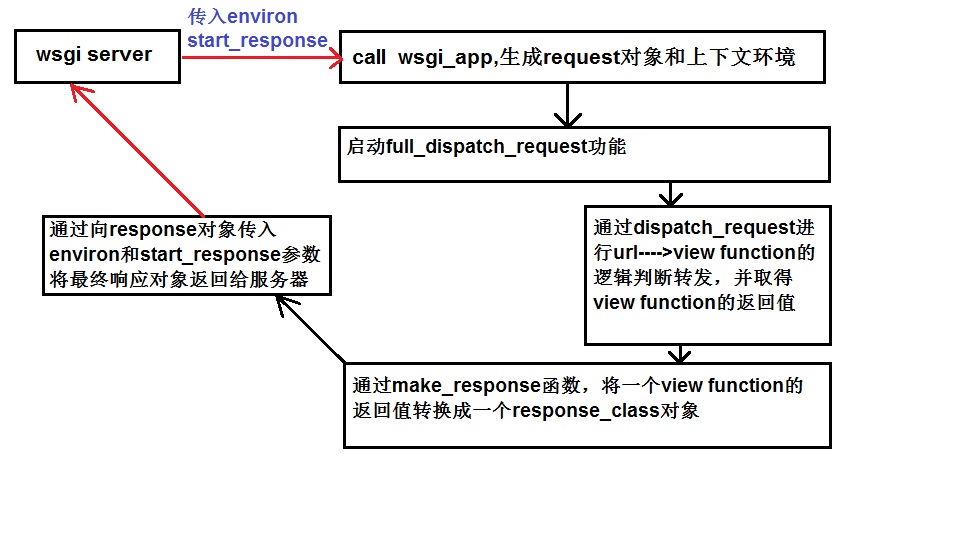
图片来源:https://blog.csdn.net/bestallen/article/details/54342120