bean的生命周期
bean的生命周期:
bean创建---初始化----销毁的过程
容器管理bean的生命周期;
我们可以自定义初始化和销毁方法;容器在bean进行到当前生命周期的时候来调用我们自定义的初始化和销毁方法-----一共四种方式
构造(对象创建)
单实例:在容器启动的时候创建对象
多实例:在每次获取的时候创建对象

初始化:
对象创建完成,并赋值好,调用初始化方法。。。
销毁:
单实例:容器关闭的时候
多实例:容器不会管理这个bean;容器不会调用销毁方法;
指定方式
1、指定初始化和销毁方法;
通过@Bean指定init-method和destroy-method;
MainConfigOfLifeCycle:
package com.atguigu.config; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import com.atguigu.bean.Car; @Configuration public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle { @Bean(initMethod="init",destroyMethod="detory") public Car car(){ return new Car(); } }
car:
package com.atguigu.bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Car { public Car(){ System.out.println("car constructor..."); } public void init(){ System.out.println("car ... init..."); } public void detory(){ System.out.println("car ... detory..."); } }
2、通过让Bean实现InitializingBean(定义初始化逻辑),DisposableBean(定义销毁逻辑);
Cat:
package com.atguigu.bean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Cat implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean { public Cat(){ System.out.println("cat constructor..."); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("cat...destroy..."); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("cat...afterPropertiesSet..."); } }
MainConfigOfLifeCycle
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.bean")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
}
3、可以使用JSR250;
@PostConstruct:在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成;来执行初始化方法
@PreDestroy:在容器销毁bean之前通知我们进行清理工作
Dog:
package com.atguigu.bean; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Dog { public Dog(){ System.out.println("dog constructor..."); } //对象创建并赋值之后调用 @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("Dog....@PostConstruct..."); } //容器移除对象之前 @PreDestroy public void detory(){ System.out.println("Dog....@PreDestroy..."); } }
MainConfigOfLifeCycle:
@ComponentScan("com.atguigu.bean")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
}
4、BeanPostProcessor【interface】:bean的后置处理器;
在bean初始化前后进行一些处理工作;
postProcessBeforeInitialization:在初始化之前工作
postProcessAfterInitialization:在初始化之后工作
MyBeanPostProcessor:
package com.atguigu.bean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作 * 将后置处理器加入到容器中 * @author lfy */ @Component public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean); return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean); return bean; } }
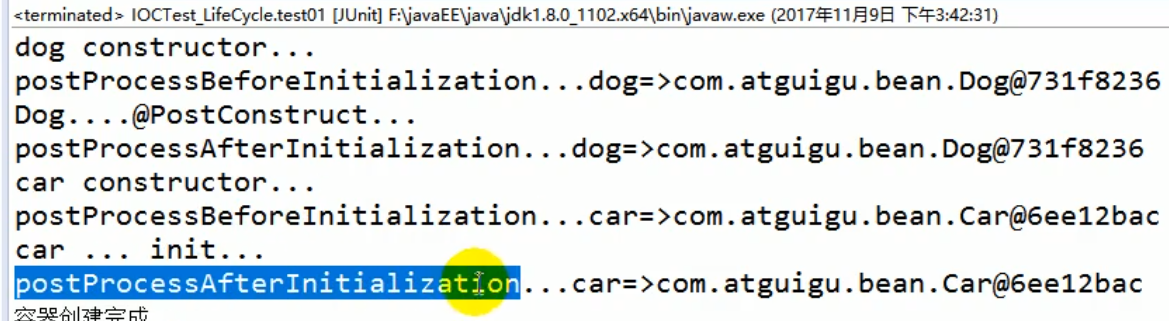
在bean初始化(调用构造方法)之后----->调用postProcessBeforeInitialization()----->@PostConstruct -----> InitializingBean -----> init-methodinit()方法----->postProcessAfterInitialization()
BeanPostProcessor原理
执行顺序
-----BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
|-----初始化:对象创建完成,并赋值好,调用初始化方法。。。
-----BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
执行流程(BeanPostProcessor原理)
1、populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);-----给bean进行属性赋值
2、initializeBean
{
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);-----执行自定义初始化
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
注:遍历得到容器中所有的BeanPostProcessor;挨个执行beforeInitialization,
一但返回null,跳出for循环,不会执行后面的BeanPostProcessor.postProcessorsBeforeInitialization
spring底层对BeanPostProcessor的使用
1、ApplicationContextAware-----实现ApplicationContextAware接口后,就可以将ApplicationContext对象通过setApplicationContext()注入。
package com.atguigu.bean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Dog implements ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } }
属性赋值
@Value赋值
1、MainConfigOfPropertyValues
package com.atguigu.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource; import com.atguigu.bean.Person; //使用@PropertySource读取外部配置文件中的k/v保存到运行的环境变量中;加载完外部的配置文件以后使用${}取出配置文件的值 @PropertySource(value={"classpath:/person.properties"}) @Configuration public class MainConfigOfPropertyValues { @Bean public Person person(){ return new Person(); } }
2、Person
package com.atguigu.bean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; public class Person { //使用@Value赋值; //1、基本数值 //2、可以写SpEL; #{} //3、可以写${};取出配置文件【properties】中的值(在运行环境变量里面的值) @Value("张三") private String name; @Value("#{20-2}") private Integer age; @Value("${person.nickName}") private String nickName; public String getNickName() { return nickName; } public void setNickName(String nickName) { this.nickName = nickName; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public Person(String name, Integer age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Person() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", nickName=" + nickName + "]"; } }
3、person.properties
person.nickName=李四
注:对于在classpath路径下的配置文件,也可以通过如下方式获取属性。配置文件的值都会加载到environment环境变量中,可以直接从环境变量中取值。
