AOP概述
aop其实就是面向切面编程,举个例子,比如项目中有n个方法是对外提供http服务的,那么如果我需要对这些http服务进行响应时间的监控,按照传统的方式就是每个方法中添加相应的逻辑,但是这些逻辑是重复的,我无非是需要记录请求的时间以及响应时间,另外可能需要加上请求入参以及响应出参。这时候就可以把这些http服务看成切面,通过aop的方式在方法前和方法后去做点什么操作。
aop的实现者有很多,包括AspectJ、Spring AOP等等,当然我们重点就放在Spring aop上了。
在spring中,aop可以由jdk动态代理或cglib实现,这地方的示例可以看下本人之前的文章了动态代理
jdk动态代理跟cglib有个重要的区别就是jdk动态代理的类必须要实现了某个接口,但是cglib则没这个要求。
针对cglib,举例如下:
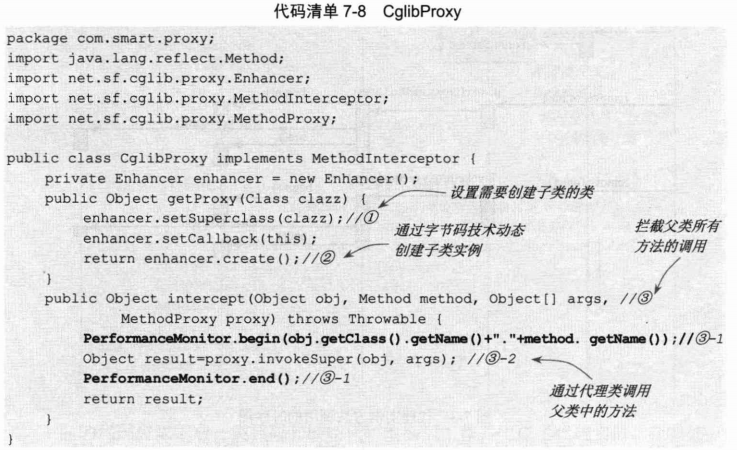
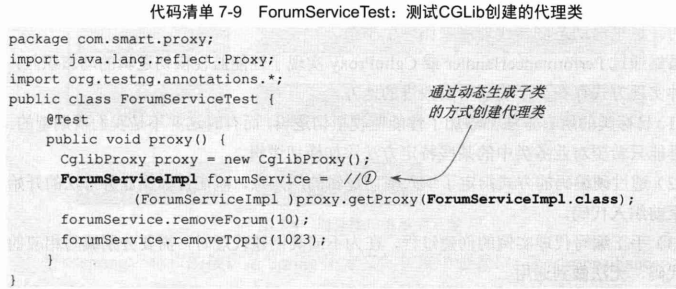
spring aop简单示例
业务代码
@Component("knight")
public class BraveKnight {
public void saying(){
System.out.println("我是骑士..(切点方法)");
}
}
package com.cjh.aop2; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 注解方式声明aop * 1.用@Aspect注解将类声明为切面(如果用@Component("")注解注释为一个bean对象,那么就要在spring配置文件中开启注解扫描,<context:component-scan base-package="com.cjh.aop2"/> * 否则要在spring配置文件中声明一个bean对象) * 2.在切面需要实现相应方法的前面加上相应的注释,也就是通知类型。 * 3.此处有环绕通知,环绕通知方法一定要有ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数传入,然后执行对应的proceed()方法,环绕才能实现。 */ @Component("annotationTest") @Aspect public class AnnotationTest { //定义切点 @Pointcut("execution(* *.saying(..))") public void sayings(){} /** * 前置通知(注解中的sayings()方法,其实就是上面定义pointcut切点注解所修饰的方法名,那只是个代理对象,不需要写具体方法, * 相当于xml声明切面的id名,如下,相当于id="embark",用于供其他通知类型引用) * <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="mistrel"> <!-- 定义切点 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *.saying(..))" id="embark"/> <!-- 声明前置通知 (在切点方法被执行前调用) --> <aop:before method="beforSay" pointcut-ref="embark"/> <!-- 声明后置通知 (在切点方法被执行后调用) --> <aop:after method="afterSay" pointcut-ref="embark"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> */ @Before("sayings()") public void sayHello(){ System.out.println("注解类型前置通知"); } //后置通知 @After("sayings()") public void sayGoodbey(){ System.out.println("注解类型后置通知"); } //环绕通知。注意要有ProceedingJoinPoint参数传入。 @Around("sayings()") public void sayAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("注解类型环绕通知..环绕前"); pjp.proceed();//执行方法 System.out.println("注解类型环绕通知..环绕后"); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 开启注解扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.cjh.aop2"/> <!-- 开启aop注解方式,此步骤不能少,这样java类中的aop注解才会生效 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> </beans>
测试:
package com.cjh.aop2; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/cjh/aop2/beans.xml"); BraveKnight br = (BraveKnight) ac.getBean("knight"); br.saying(); } }
自动创建代理
1、BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
通过名字就可以看出来是干嘛的,可以根据bean的名字来创建自动代理,示例如下:
业务类:
public interface UserService { void print(); } public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void print(){ System.out.println(getClass()+"#print"); } }
拦截器:
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println(getClass()+"调用方法前"); Object ret=invocation.proceed(); System.out.println(getClass()+"调用方法后"); return ret; } }
配置类:
@Configuration public class AppConfig { //要创建代理的目标Bean @Bean public UserService userService(){ return new UserServiceImpl(); } //创建Advice或Advisor @Bean public Advice myMethodInterceptor(){ return new MyMethodInterceptor(); } //使用BeanNameAutoProxyCreator来创建代理 @Bean public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator(){ BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator=new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator(); //设置要创建代理的那些Bean的名字 beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setBeanNames("userSer*"); //设置拦截链名字(这些拦截器是有先后顺序的) beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setInterceptorNames("myMethodInterceptor"); return beanNameAutoProxyCreator; } }
测试:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); UserService userService= applicationContext.getBean(UserService.class); userService.print(); } }
自定义注解+BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
基于上面说的,对一些http接口做个响应时间监控,先以一个接口为例吧!
注解(PerformanceMonitor):
package com.ty.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; //代表此注解是运行过程中生效 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //此注解作用于方法上 @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface PerformanceMonitor { String value() default ""; }
AnnotationController:
package com.ty.controller; import com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller public class AnnotationController { @PerformanceMonitor public String testServer() { System.out.println("do someThing"); return "test"; } }
BeanNameAutoProxyConfig:
package com.ty.configuration; import org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class BeanNameAutoProxyConfig { @Bean public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator create() { BeanNameAutoProxyCreator beanNameAutoProxyCreator = new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator(); //为所有的controller创建自动动态代理 beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setBeanNames("*Controller"); //代理的具体的业务逻辑交给bean-----performanceInterceptor beanNameAutoProxyCreator.setInterceptorNames("performanceInterceptor"); return beanNameAutoProxyCreator; } }
PerformanceInterceptor:
package com.ty.interceptor; import com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor; import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation; import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.lang.reflect.Method; @Service public class PerformanceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { Object result = null; //判断被代理类的方法上是否使用了@PerformanceMonitor注解 PerformanceMonitor performanceMonitor = methodInvocation.getMethod().getAnnotation(PerformanceMonitor.class); if(performanceMonitor != null) { //具体的代理逻辑,实现aop的效果 System.out.println("----------before----" + methodInvocation.getMethod().getName()); result = methodInvocation.proceed(); System.out.println("----------after----" + methodInvocation.getMethod().getName() + ";该笔调用耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - t1) + "ms");
}else { //不使用该注解,则走原方法的调用逻辑 result = methodInvocation.proceed(); } return result; } }
applicationContext.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--自动扫描包配置--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ty"/> <bean id="student" class="com.ty.beans.Student"> <!-- property代表的是set方法注入--> <property name="age" value="27"></property> <property name="name" value="马云"></property> </bean> <bean id="school" class="com.ty.beans.School"> <!-- constructor代表的是构造器注入--> <constructor-arg ref="student"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
测试类:
package com.ty.beans; import com.ty.controller.AnnotationController; import javafx.application.Application; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.AbstractJUnit4SpringContextTests; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:applicationContext.xml" }) @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) public class IOCTest { @Test public void testAnnotation() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); AnnotationController annotationController = (AnnotationController) context.getBean("annotationController"); annotationController.testServer(); } }
运行结果:
----------before----testServer
do someThing
----------after----testServer;该笔调用耗时:8ms
这样也就实现了性能监控的目的,并且以后项目中所有的controller的接口,只要需要这个功能,加个注解即可。
@AspectJ
基于@AspectJ实现aop是相对简单的方式,上面也有类似的案例,下面详细的说说这个玩意。
aop主要包括切面、切入点、增强方法等核心组成部分。
1、切面
//用来声明这是一个AspectJ @Aspect //在此处声明一个Component 是因为Spring扫描注解并不能识别AspectJ 因此在此处声明,不必在applicationContext.xml配置bean标签了 @Component public class ServiceLog { 。。。 }
2、切入点
@Pointcut("execution(* com.sample.service.impl..*.*(..))")
public void pc() {}
a、execution()是最常用的切点函数,整个表达式可以分为五个部分,其语法如下所示:
- execution(): 表达式主体。
- 第一个*号:表示返回类型,*号表示所有的类型。
- 包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,com.sample.service.impl包、子孙包下所有类的方法。
- 第二个*号:表示类名,*号表示所有的类。
- *(..):最后这个星号表示方法名,*号表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。
b、@annotation
另外切入点中的execution()也可以用@Annotation代替,如下:
@AfterReturning("@annotation(com.ty.annotation.PerformanceMonitor)")
public void needTestFun() {
System.out.println("可以对注明@PerformanceMonitor的方法进行增强");
}
对于所有注明@PerformanceMonitor的方法进行增强。
或者还有一种用法,可以方便拿到注解上的信息
@Around(value = "@annotation(apiOperation)") public Object logApiCallInfo(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, ApiOperation apiOperation) { //TODO 1、这里方便拿到注解的信息。不过注意@annotation(apiOperation)名称要与参数名称一致 String apiCode = apiOperation.value(); //TODO 调用业务接口 result = joinPoint.proceed(); //TODO 获取接口请求参数,并拼装成json,格式化输出 Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); String[] parameterNames = methodSignature.getParameterNames(); JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(); if(parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length > 0 && args != null && args.length > 0) { for(int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; i++) { jsonObject.put(parameterNames[i], args[i]); } //标准化输出 jsonObject.toJsonString(); } }
3、增强方法
//环绕通知注解,pc()则是上面的pointcut切入点 @Around("pc()") //环绕通知会多ProceedingJoinPoint这个参数 public Object log(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { 。。。 }
- @Before
- @AfterReturning
- @Around
- @AfterThrowing
- @After
4、applicationContext.xml
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>