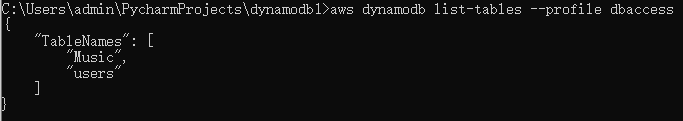
aws configure --profile dbaccess
pip install boto3
import boto3 import pprint session = boto3.Session( aws_access_key_id = '你的access_key', aws_secret_access_key='你的secret_key' ) dynamodb = session.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-2' ) table = dynamodb.Table('users') def table_scan(): result = table.scan() for i in result['Items']: print(i) table_scan()
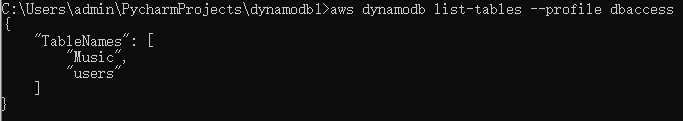
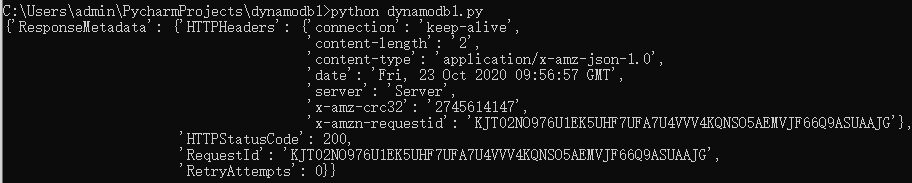
python dynamodb1.py

import boto3 import pprint session = boto3.Session( aws_access_key_id = '你的access_key', aws_secret_access_key='你的secret_key' ) dynamodb = session.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-2' ) table = dynamodb.Table('users') # def table_scan(): # result = table.scan() # for i in result['Items']: # print(i) # # table_scan() def insert_item_db(): response = table.put_item( Item={ 'username': 'janedoe', 'first_name': 'Jane', 'last_name': 'Doe', 'age': 25, 'hobbies':['badminton', 'foodball','singing'], 'account_type': 'standard_user' } ) pprint.pprint (response)//注意,这里不能用pprint(response),否则会报错 insert_item_db()
import pprint
pprint.pprint(people)
from pprint import * pprint(people)
def get_db_item(): #retrieve an item using primary key response = table.get_item( Key={ 'username': 'janedoe' } ) item = response['Item'] print(item) get_db_item()
python dynamodb1.py

import boto3 session = boto3.Session( aws_access_key_id = '你的access_key', aws_secret_access_key='你的secret_key' ) dynamodb = session.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-2' ) def create_movie_table(): table = dynamodb.create_table( TableName='Movies', KeySchema=[ { 'AttributeName': 'year', 'KeyType': 'HASH' # Partition key }, { 'AttributeName': 'title', 'KeyType': 'RANGE' # Sort key } ], AttributeDefinitions=[ { 'AttributeName': 'year', 'AttributeType': 'N' }, { 'AttributeName': 'title', 'AttributeType': 'S' }, ], ProvisionedThroughput={ 'ReadCapacityUnits': 5, 'WriteCapacityUnits': 5 } ) return table movie_table = create_movie_table() print("Table status:", movie_table.table_status)
2.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/samples/moviedata.zip
import boto3 import json from decimal import Decimal session = boto3.Session( aws_access_key_id = '你的access_key', aws_secret_access_key='你的secret_key' ) dynamodb = session.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-2' ) def load_movies(movies): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') for movie in movies: year = int(movie['year']) title = movie['title'] print("Adding movie:", year, title) table.put_item(Item=movie) with open("moviedata.json") as json_file: movie_list = json.load(json_file, parse_float=Decimal) load_movies(movie_list)
python MoviesLoadData.py

3.
import boto3 from pprint import pprint from boto3.dynamodb.conditions import Key, Attr session = boto3.Session( aws_access_key_id='AKIAUBZTK6DYWI3IVIIA', aws_secret_access_key='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' ) dynamodb = session.resource('dynamodb', region_name='us-east-2' )
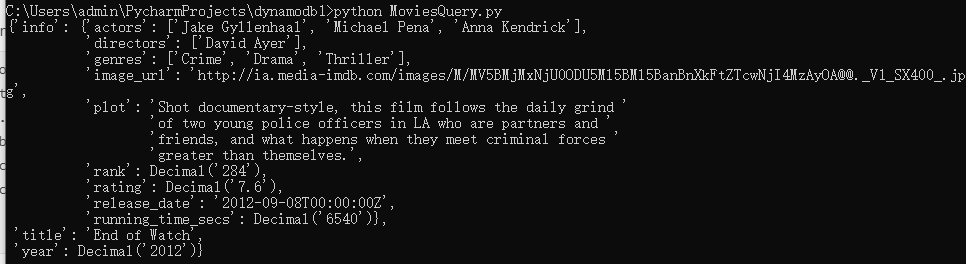
def read_item(year, title): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') response = table.get_item(Key={'year': year, 'title': title}) movie = response['Item'] pprint(movie) read_item(2012, 'End of Watch')
def query_movies(year): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') response = table.query( KeyConditionExpression=Key('year').eq(year) ) movies = response['Items'] print(f"Movies from {year}") for movie in movies: print(movie['year'], ":", movie['title']) query_movies(2012)

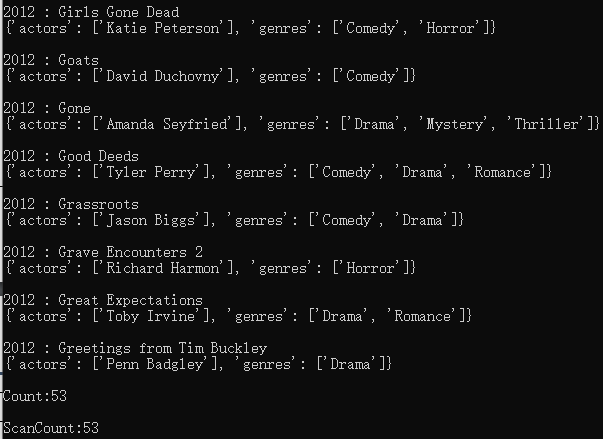
def query_and_project_movies(year): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') # Expression attribute names can only reference items in the projection expression. response = table.query(ProjectionExpression="#yr, title, info.genres,info.actors[0]",ExpressionAttributeNames={"#yr": "year"},KeyConditionExpression= Key('year').eq(year) & Key('title').between('D', 'H')) print(f"Get year, title, genres, and lead actor") movies = response['Items'] for movie in movies: print(f" {movie['year']} : {movie['title']}") pprint(movie['info']) print(f" Count:{response['Count']}") print(f" ScanCount:{response['ScannedCount']}") query_and_project_movies(2012)
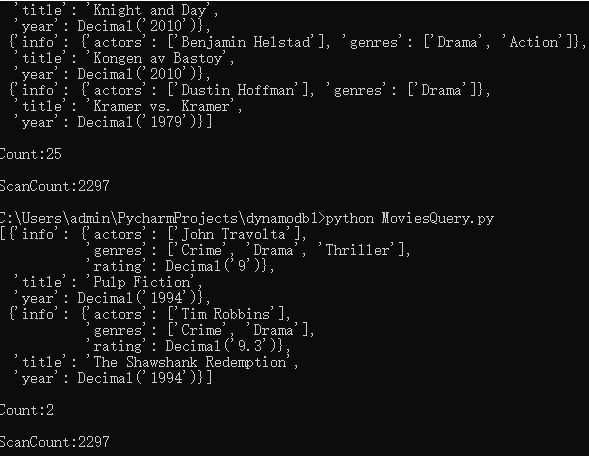
def table_scan1(): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') response = table.scan( ProjectionExpression="#yr, title, info.genres, info.actors[0]", ExpressionAttributeNames={"#yr": "year"}, FilterExpression=Key('title').begins_with('K') ) pprint(response['Items']) print(f" Count:{response['Count']}") print(f" ScanCount:{response['ScannedCount']}") table_scan1()

from decimal import * def table_scan2(): table = dynamodb.Table('Movies') response = table.scan( ProjectionExpression="#yr, title, info.genres, info.actors[0], info.rating", ExpressionAttributeNames={"#yr": "year"}, FilterExpression=Attr('info.rating').gte(Decimal(9)) ) pprint(response['Items']) print(f" Count:{response['Count']}") print(f" ScanCount:{response['ScannedCount']}") table_scan2()
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/GettingStarted.Python.03.html