1. 文件管理
应用程序无法操控硬件,硬件只有操作系统可以操作(除了C语言),文件存在于磁盘之上,因此Python是无法直接调用文件的,需要将指令发送个操作系统,让操作系统操作硬件进而操作文件。
文件管理的三个步骤:打开文件、操作文件、关闭文件。
Python文件管理:
文件操作包括r(读)、w(写,覆盖)、a(追加)、rb(以二进制方式读)、wb(以二进制方式写)、ab(以二进制方式追加)等方式,先以r的方式讲解文件管理。
1.1 r
1> 打开文件。
#打开文件,发送给操作系统,文件名必须是字符串类型.指定以读(r)的模式打开,用utf-8的字符编码打开。
f = open('E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
result:
OSError: [Errno 22] Invalid argument: 'u202aE:\Learning\python est.txt'
注意:有部分 表示转义,如U、 、 等,需要将真实的文件地址在此转义回来,通常有三种可行的方法:
1. 用 再次转义,每个 都必须转义:
f = open('E:\Learning\python\test.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
2. 将 换成 / :
f = open('E:/Learning/python/test.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
3.前面加r进行转义:
f = open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8'
result:
进程完成,退出码 0
2> 打开文件获得了读的权限,现在进行读。
#读。操作系统接收到读的指令后读取相应的文件到内存中。
f.read() #发送给操作系统指令让其读
3> 读完之后再关闭文件,完成一个文件操作的步骤。
#关闭。操作系统接收到指令后关闭文件。
f.close() #发送给操作系统指令,让其关闭文件,进行资源回收。
文件打开后若不关闭会进行堆积,导致计算机内存溢出,运行速度变慢,因此必须将不再使用的文件关闭。
使用with命令可以在完成文件操作后自动关闭文件。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f : #声明变量f
data = f.read()
print(data)
result: #读取到test.txt文件内容
zxcvbnm
asdfghjkl
qwertyuiop
plmoknijb
uhbygvtdcrdxeszwaq
qazwsxedcrfvtgbyhn
yhnujmikopl
qdawfxegcthv
yjbuknilmop
#read后可以跟数字表示读取数字指定数量的字符
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r') as f :
data = f.read(5)
print(data)
result:
zxcvb
#readline():按行读,括号有数字的话表示读取数字指定的行。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r') as f :
data = f.readline()
print(data)
result:zxcvbnm
#readlines():读取多行,即读取所有文件内容为列表。可以通过for循环将列表内容取出。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r') as f :
data = f.readlines()
for i in data:
print(i)
result:
zxcvbnm
asdfghjkl
qwertyuiop
plmoknijb
uhbygvtdcrdxeszwaq
qazwsxedcrfvtgbyhn
yhnujmikopl
qdawfxegcthv
yjbuknilmop
#for语句可以直接遍历定义的变量
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r') as f :
for i in f:
print(i)
result:
zxcvbnm
asdfghjkl
qwertyuiop
plmoknijb
uhbygvtdcrdxeszwaq
qazwsxedcrfvtgbyhn
yhnujmikopl
qdawfxegcthv
yjbuknilmop
#readable():是否可读,返回布尔类型,类似的,有writeable()是否可写。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','w') as f :
res = f.readable()
print(res)
result:
False
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r') as f :
res = f.readable()
print(res)
result:
True
1.2 w
使用with命令,获取写的操作步骤,向文件写入内容之后关闭文件管理。
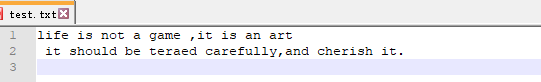
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') as f :
f.write('life is not a game ,it is an art' )
result:

#writeline()可以将内容以字符串的形式写入到文件当中。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','w') as f :
f.writelines(['l','o','v','e'])
result:

1.3 a
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','a',encoding='utf-8') as f :
f.write('
it should be teraed carefully,and cherish it.' ) #
表示换行
result:
1.4 rd
以二进制形式来进行读写是不需要再定义字符类型(encouding)。
源文件:

with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
data = f.read()
print(data)
result: #以二进制读,汉字会被转化成二进制文件
b'life is not a game ,it is an art.
it should be teraed carefully,and cherish it.
xe7x94x9fxe6xb4xbbxe4xb8x8dxe6x98xafxe6xb8xb8xe6x88x8fxefxbcx8cxe8x80
#要显示原本的格式,需要进行解码
print(data.decode())
result:
life is not a game ,it is an art.
it should be teraed carefully,and cherish it.
生活不是游戏,而是艺术。
艺术是值得珍爱的。
1.5 wb、ab
二进制写入的时候需要加b进行二进制的声明,或者使用人encode进行转码。需要注意的是ASCII码并不支持中文字体库,因此加b进行二进制写入对汉字无效。
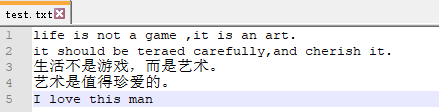
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','ab') as f :
data = f.write(b'I love this man')
result:
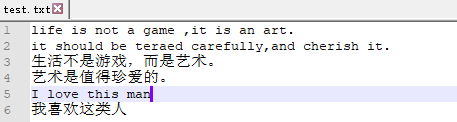
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','ab') as f :
data = f.write('
我喜欢这类人'.encode(utf-8))
result:
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','ab') as f :
data = f.write(b'
我喜欢这类人')
result:
SyntaxError: bytes can only contain ASCII literal characters.
2. 光标的移动
原文件:E:Learningpython est.txt
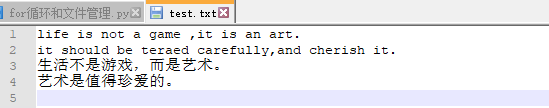
Python读取文件是按照光标的移动来读的,比如先进行一次读取全部文件内容后光标移动到末尾,再次进行读的时候光标再向后移动,内容为空,所以读取文件内容是空的。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f :
res = f.read()
conta = f.read()
print(conta)
result:
进程完成,退出码 0
对于实验原文件,指定读取5个字符后光标移动到i之前,再指定读取两个字符时会将is读取出来。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f :
res = f.read(5)
conta = f.read(2)
print(conta)
result:
is
seek(num1,num2)可以控制光标的移动。seek光标移动有三种模式,这三种模式通过num2指定:
num2的数值:0,顶头; 1,相对位置; 2,末尾。1和2只能在bytes模式下运行,(0,1)、(0,2)除外。
在seek中num1代表光标移动的字节。不声明用rb读取时read读取的是字符。
1>num2= 0,顶格模式
需要注意的是,在utf-8中一个汉字占用3个字节,生僻字占用字节更多,因此对汉字进行光标操作时num1一般为3的整数倍,保证汉字不出现“半个”的情形,使得转码能够进行。
#修改原文件:
语言具有无与伦比的魅力。
life is not a game ,it is an art.
it should be teraed carefully,and cherish it.
生活不是游戏,而是艺术。
艺术是值得珍爱的。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f :
f.seek(3,0) #光标顶格后移动三个字节,移动到“言”之前
conta = f.read(3) #十进制下read读取三个字符
print(conta)
result:
言具有
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f :
f.seek(4,0)
conta = f.read(3)
print(conta)
result: #移动4个字节,在十进制下,汉字无法读取。
UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xa8 in position 0: invalid start byte
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
f.seek(4,0)
conta = f.read(3)
print(conta)
result:
b'xa8x80xe5' #二进制下可以读取文件,但无法对4字节的汉字转码
print(conta.decode())
result:
UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xa8 in position 0: invalid start byte
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
f.seek(3,0)
conta = f.read(3)
print(conta.decode())
result:
言 #在二进制rb下,read也是按字节来读的。
2> num2=1,相对位置模式
1和2模式除了(0,1)和(0,2),其余情况不能在utf-8模式下运行。
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f :
f.read(3)
f.seek(3,1)
conta = f.read(3)
print(conta.decode())
result:
io.UnsupportedOperation: can't do nonzero cur-relative seeks
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
f.read(3) #先移动三个字节,“言”之前
f.seek(3,1) #按相对位置移动三个字节,“言”之后
conta = f.read(3) #再读三个字节,读取“具”
print(conta.decode(utf-8)) #转码
result:
具
3> num2=2,末尾模式
末尾模式下指定num1,num1数值可正可负,负数表示向前移动,正数表示向后移动(无意义),光标移动到指定的位置然后再开始读取。
#将光标移动到最末尾:
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
f.seek(0,2)
conta = f.read(3)
print(conta.decode())
result: #内容为空
进程完成,退出码 0
with open(r'E:Learningpython est.txt','rb') as f :
f.seek(-12,2) #向前移动12个字节
conta = f.read(3) #先读取3个字节
data = f.read() #在读取光标后所有内容
print(conta.decode())
print(data.decode())
result:
得
珍爱的