add by zhj:
SqlSession是MyBatis中的非常重要的一个接口,简单的说,它是对java.sql.Connection的进一步封装(使用组合设计模式),提供给用户更强易用的CRUD方法,如下,也提供一获取Connection的方法。
1 public interface SqlSession extends Closeable { 2 3 /** 4 * Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter. 5 * 6 * @param <T> 7 * the returned object type 8 * @param statement 9 * Unique identifier matching the statement to use. 10 * @param parameter 11 * A parameter object to pass to the statement. 12 * @return Mapped object 13 */ 14 <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter); 15 16 /** 17 * Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter. 18 * 19 * @param <E> 20 * the returned list element type 21 * @param statement 22 * Unique identifier matching the statement to use. 23 * @param parameter 24 * A parameter object to pass to the statement. 25 * @return List of mapped object 26 */ 27 <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter); 28 29 /** 30 * Execute an insert statement with the given parameter object. Any generated autoincrement values or selectKey 31 * entries will modify the given parameter object properties. Only the number of rows affected will be returned. 32 * 33 * @param statement 34 * Unique identifier matching the statement to execute. 35 * @param parameter 36 * A parameter object to pass to the statement. 37 * @return int The number of rows affected by the insert. 38 */ 39 int insert(String statement, Object parameter); 40 41 /** 42 * Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned. 43 * 44 * @param statement 45 * Unique identifier matching the statement to execute. 46 * @param parameter 47 * A parameter object to pass to the statement. 48 * @return int The number of rows affected by the update. 49 */ 50 int update(String statement, Object parameter); 51 52 /** 53 * Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned. 54 * 55 * @param statement 56 * Unique identifier matching the statement to execute. 57 * @param parameter 58 * A parameter object to pass to the statement. 59 * @return int The number of rows affected by the delete. 60 */ 61 int delete(String statement, Object parameter); 62 63 /** 64 * Flushes batch statements and commits database connection. Note that database connection will not be committed if 65 * no updates/deletes/inserts were called. To force the commit call {@link SqlSession#commit(boolean)} 66 */ 67 void commit(); 68 69 /** 70 * Flushes batch statements and commits database connection. 71 * 72 * @param force 73 * forces connection commit 74 */ 75 void commit(boolean force); 76 77 /** 78 * Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back. Note that database connection will not be 79 * rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called. To force the rollback call 80 * {@link SqlSession#rollback(boolean)} 81 */ 82 void rollback(); 83 84 /** 85 * Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back. Note that database connection will not be 86 * rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called. 87 * 88 * @param force 89 * forces connection rollback 90 */ 91 void rollback(boolean force); 92 93 /** 94 * Flushes batch statements. 95 * 96 * @return BatchResult list of updated records 97 * @since 3.0.6 98 */ 99 List<BatchResult> flushStatements(); 100 101 /** 102 * Closes the session. 103 */ 104 @Override 105 void close(); 106 107 /** 108 * Clears local session cache. 109 */ 110 void clearCache(); 111 112 /** 113 * Retrieves current configuration. 114 * 115 * @return Configuration 116 */ 117 Configuration getConfiguration(); 118 119 /** 120 * Retrieves a mapper. 121 * 122 * @param <T> 123 * the mapper type 124 * @param type 125 * Mapper interface class 126 * @return a mapper bound to this SqlSession 127 */ 128 <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type); 129 130 /** 131 * Retrieves inner database connection. 132 * 133 * @return Connection 134 */ 135 Connection getConnection(); 136 }
MyBatis提供了SqlSession接口的默认实现DefaultSqlSession,我们平时使用的就是它
DefaultSqlSession类中最核心的对象是Executor对象。
它有有三种类型:SIMPLE(简易执行器,不配置就是默认执行器)、REUSE(重用预处理语句)、BATCH(批量更新、批量专用处理器)。每种类型对应Executor接口的一个实现类:SimpleExecutor,ReuseExecutor,BatchExecutor
这里以ReuseExecutor为例进行说明,Executor中最核心的是StatementHandler对象和Transaction对象
1. StatementHandler对象
ReuseExecutor执行查询是调用ReuseExecutor.doQuery,源码如下
1 @Override 2 public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 3 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 4 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 5 Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 6 return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); 7 } 8 9 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { 10 Statement stmt; 11 BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql(); 12 String sql = boundSql.getSql(); 13 if (hasStatementFor(sql)) { 14 stmt = getStatement(sql); 15 applyTransactionTimeout(stmt); 16 } else { 17 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); 18 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); 19 putStatement(sql, stmt); 20 } 21 handler.parameterize(stmt); 22 return stmt; 23 }
它会先获取Connection对象,然后依次调用StatementHandler的prepare,parameterize,query方法,其实就是依次对sql预编译,设置sql中的参数值,执行查询。
2. Transaction对象
ManagedTransaction,完整路径是org.apache.ibatis.transaction.managed.ManagedTransactionConnection connection = getConnection(statementLog),源码如下。可以看到,它最终是调用Transaction对象中的相应方法
1 protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException { 2 Connection connection = transaction.getConnection(); 3 if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) { 4 return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack); 5 } else { 6 return connection; 7 } 8 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/jian0110/p/9452592.html
作者:JJian
SqlSession是Mybatis最重要的构建之一,可以简单的认为Mybatis一系列的配置目的是生成类似 JDBC生成的Connection对象的SqlSession对象,这样才能与数据库开启“沟通”,通过SqlSession可以实现增删改查(当然现在更加推荐是使用Mapper接口形式),那么它是如何执行实现的,这就是本篇博文所介绍的东西,其中会涉及到简单的源码讲解。
了解SqlSession的运作原理是学习Mybatis插件的必经之路,因为Mybatis的插件会在SqlSession运行过程中“插入”运行,如果没有很好理解的话,Mybatis插件可能会覆盖相应的源码造成严重的问题。鉴于此,本篇博文尽量详细介绍SqlSession运作原理!
建议:在我之前的博文《Mybatis缓存(1)--------系统缓存及简单配置介绍》中介绍到SqlSession的产生过程,可以先理解后再读此博文可能会更加好理解!
1、SqlSession简单介绍
(1)SqlSession简单原理介绍
SqlSession提供select/insert/update/delete方法,在旧版本中使用使用SqlSession接口的这些方法,但是新版的Mybatis中就会建议使用Mapper接口的方法。
映射器其实就是一个动态代理对象,进入到MapperMethod的execute方法就能简单找到SqlSession的删除、更新、查询、选择方法,从底层实现来说:通过动态代理技术,让接口跑起来,之后采用命令模式,最后还是采用了SqlSession的接口方法(getMapper()方法等到Mapper)执行SQL查询(也就是说Mapper接口方法的实现底层还是采用SqlSession接口方法实现的)。
注:以上虽然只是简单的描述,但实际上源码相对复杂,下面将结合源码进行简单的介绍!
(2)SqlSession重要的四个对象
1)Execute:调度执行StatementHandler、ParmmeterHandler、ResultHandler执行相应的SQL语句;
2)StatementHandler:使用数据库中Statement(PrepareStatement)执行操作,即底层是封装好了的prepareStatement;
3)ParammeterHandler:处理SQL参数;
4)ResultHandler:结果集ResultSet封装处理返回。
2、SqlSession四大对象
(1)Execute执行器:
执行器起到至关重要的作用,它是真正执行Java与数据库交互的东西,参与了整个SQL查询执行过程中。
1)主要有三种执行器:简易执行器SIMPLE(不配置就是默认执行器)、REUSE是一种重用预处理语句、BATCH批量更新、批量专用处理器
1 package org.apache.ibatis.session; 2 3 /** 4 * @author Clinton Begin 5 */ 6 public enum ExecutorType { 7 SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH 8 }
2)执行器作用:Executor会先调用StatementHandler的prepare()方法预编译SQL语句,同时设置一些基本的运行参数,然后调用StatementHandler的parameterize()方法(实际上是启用了ParameterHandler设置参数)设置参数,resultHandler再组装查询结果返回调用者完成一次查询完成预编译,简单总结起来就是即先预编译SQL语句,之后设置参数(跟JDBC的prepareStatement过程类似)最后如果有查询结果就会组装返回。
首先,以SimpleExecutor为例,查看源码我们得到如下几点重要知识点:
第一:Executor通过Configuration对象中newExecutor()方法中选择相应的执行器生成
1 public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { 2 executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; 3 executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; 4 Executor executor; 5 if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { 6 executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); 7 } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { 8 executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); 9 } else { 10 executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); 11 } 12 if (cacheEnabled) { 13 executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); 14 } 15 executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); 16 return executor; 17 }
(注:最后interceptorChain.pluginAll()中执行层层动态代理,最后在可以在调用真正的Executor前可以修改插件代码,这也就是为什么学会Mybatis的插件必须要知道SqlSession的运行过程)
第二:在执行器中StatementHandler是根据Configuration构建的
1 public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { 2 super(configuration, transaction); 3 } 4 5 @Override 6 public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { 7 Statement stmt = null; 8 try { 9 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 10 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); 11 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 12 return handler.update(stmt); 13 } finally { 14 closeStatement(stmt); 15 } 16 }
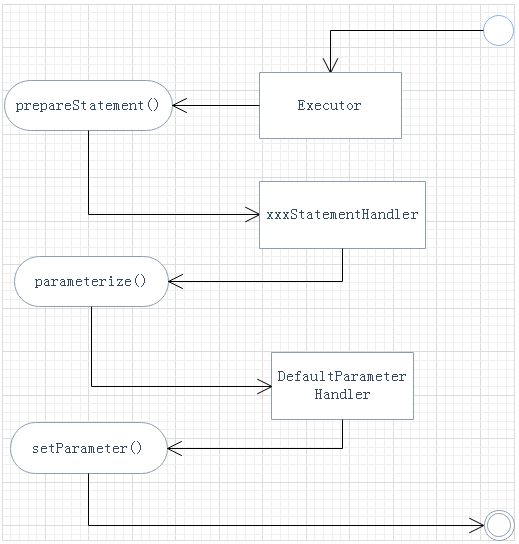
第三:Executor会执行StatementHandler的prepare()方法进行预编译---->填入connection对象等参数---->再调用parameterize()方法设置参数---->完成预编译
1 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt; 3 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); 4 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); 5 handler.parameterize(stmt); 6 return stmt; 7 }
总结以上绘制简单思维图如下:
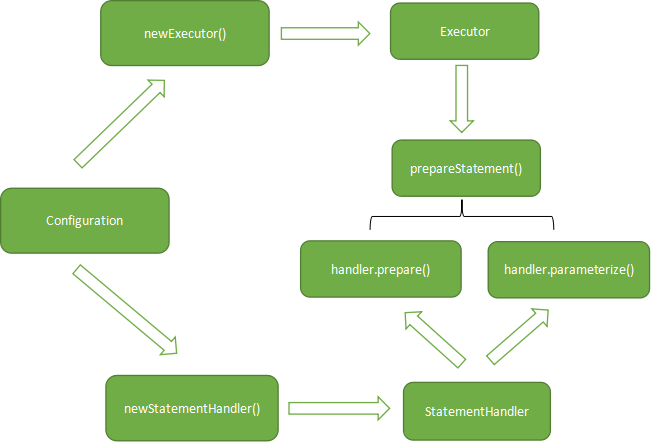
(2)StatementHanlder数据库会话器
1)作用:简单来说就是专门处理数据库会话。详细来说就是进行预编译并且调用ParameterHandler的setParameters()方法设置参数。
2)数据库会话器主要有三种:SimpleStatementHandler、PrepareStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler,分别对应Executor的三种执行器(SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH)
我们从上述Executor的prepareStatement()方法中调用了StatementHandler的parameterize()开始一步步地查看源码,如下得到几点重要的知识点:
第一:StatementHandler的生成是由Configuration方法中newStatementHandler()方法生成的,但是正在创建的是实现了StatementHandler接口的RoutingStatementHandler对象
1 public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, 2 RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { 3 StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 4 statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); 5 return statementHandler; 6 }
第二:RoutingStatementHandler的通过适配器模式找到对应(根据上下文)的StatementHandler执行的,并且有SimpleStatementHandler、PrepareStatementHandler、CallableStatementHandler,分别对应Executor的三种执行器(SIMPLE、REUSE、BATCH)
1 public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { 2 3 switch (ms.getStatementType()) { 4 case STATEMENT: 5 delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 6 break; 7 case PREPARED: 8 delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 9 break; 10 case CALLABLE: 11 delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 12 break; 13 default: 14 throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType()); 15 }
之后主要以PrepareStatementHandler为例,我们观察到:它是实现BaseStatementHandler接口的,最后BaseStatementHandler又是实现StatementHandler接口的
1 public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler 2 ...... 3 public abstract class BaseStatementHandler implements StatementHandler
它主要有三种方法:prepare、parameterize和query,我们查看源码:
第三:在BaseStatementHandler中重写prepare()方法,instantiateStatement()方法完成预编译,之后设置一些基础配置(获取最大行数,超时)
1 @Override 2 public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException { 3 ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); 4 Statement statement = null; 5 try { 6 statement = instantiateStatement(connection); 7 setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout); 8 setFetchSize(statement); 9 return statement; 10 } catch (SQLException e) { 11 closeStatement(statement); 12 throw e; 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 closeStatement(statement); 15 throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); 16 } 17 }
第四:instantiateStatement()预编译实际上也是使用了JDBC的prepareStatement()完成预编译
@Override protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException { String sql = boundSql.getSql(); if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) { String[] keyColumnNames = mappedStatement.getKeyColumns(); if (keyColumnNames == null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, PreparedStatement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, keyColumnNames); } } else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() != null) { return connection.prepareStatement(sql, mappedStatement.getResultSetType().getValue(), ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY); } else { return connection.prepareStatement(sql); } }
第五:在prepareStatement中重写parameterize()方法。prepare()预编译完成之后,Executor会调用parameterize()方法(在上面的Executor部分中已经做了介绍),实际上是调用ParameterHandler的setParameters()方法
1 @Override 2 public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException { 3 parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement); 4 }
(3)ParameterHandler参数处理器
作用:对预编译中参数进行设置,如果有配置typeHandler,自然会对注册的typeHandler对参数进行处理
查看并学习源码,得到以下几点重要知识点:
第一:Mybatis提供了ParamterHandler的默认实现类DefalutParameterHandler
1 public interface ParameterHandler { 2 3 Object getParameterObject(); 4 5 void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) 6 throws SQLException; 7 8 }
(其中:getParameterObject是返回参数对象,setParameters()是设置预编译参数)
第二:从parameterObject中取到参数,然后使用typeHandler(注册在Configuration中)进行参数处理:
1 @Override 2 public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) { 3 ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); 4 List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); 5 if (parameterMappings != null) { 6 for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { 7 ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); 8 if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { 9 Object value; 10 String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); 11 if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params 12 value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); 13 } else if (parameterObject == null) { 14 value = null; 15 } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { 16 value = parameterObject; 17 } else { 18 MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); 19 value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); 20 } 21 TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); 22 JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); 23 if (value == null && jdbcType == null) { 24 jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); 25 } 26 try { 27 typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); 28 } catch (TypeException e) { 29 throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e); 30 } catch (SQLException e) { 31 throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping: " + parameterMapping + ". Cause: " + e, e); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }
(4)ResultSetHandler结果集处理器
作用:很简单,就是组装结果返回结果集
第一:ResultSetHandler接口,handlerResultSets()是包装并返回结果集的,handleOutputParameters()是处理存储过程输出参数的
1 public interface ResultSetHandler { 2 3 <E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException; 4 5 <E> Cursor<E> handleCursorResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException; 6 7 void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException;
第二:Mybatis提供了默认的ResultSetHandler实现类DefaultResultSetHandler,其中重点是handlerResultSets()的实现,但是其实现过程比较复杂,这里不过多介绍(emmmmm....个人目前能力还达理解,仍需努力)
第三:在Executor中doQuery()方法返回了封装的结果集
1 @Override 2 public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException { 3 Statement stmt = null; 4 try { 5 Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); 6 StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); 7 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); 8 return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler); 9 } finally { 10 closeStatement(stmt); 11 } 12 }
第四:实际上是返回结果是调用了resultSetHandler的handleResultSets()方法
1 @Override 2 public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException { 3 PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; 4 ps.execute(); 5 return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps); 6 }
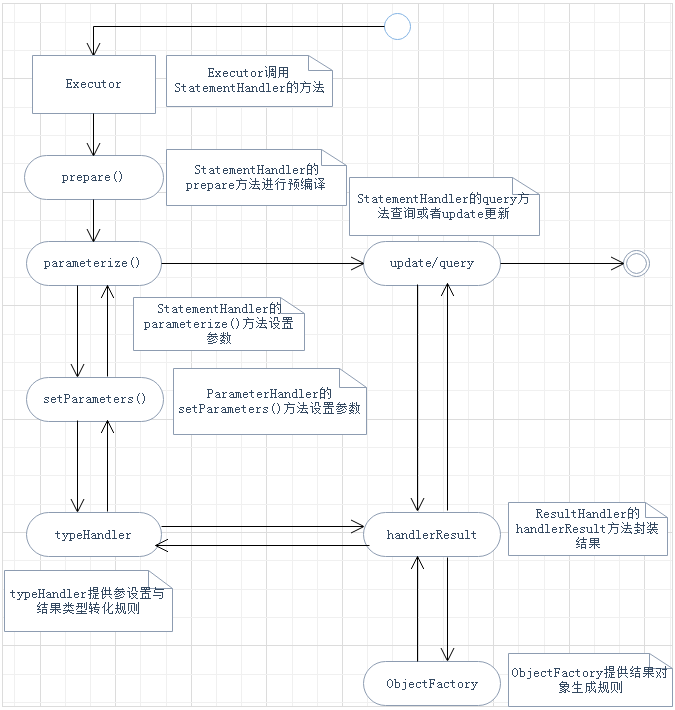
3、SqlSession运行总结
(1)文字总结
SqlSession的运行主要是依靠Executor执行器调用(调度)StatementHandler、parameterHanlder、ResultSetHandler,Executor首先通过创建StamentHandler执行预编译并设置参数运行,而整个过程需要如下几步才能完成:
1 private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { 2 Statement stmt; 3 Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); 4 stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); 5 handler.parameterize(stmt); 6 return stmt; 7 }
1)prepare预编译SQL
由适配模式生成的RoutingStatementHandler根据上下文选择生成三种相应的XXXStatementHandler;
在生成的XXXStatementHandler内部instantiateStatement()方法执行底层JDBC的prepareStatement()方法完成预编译
2)parameterize设置参数
默认是DefaultParameterHandler(实现了parameterHandler接口)中setParameter()方法完成参数配置,其中参数从ParameterObject中取出,交给typeHandler处理
3)doUpdate/doQuery执行SQL
返回的结果通过默认的DefaultResultSetHandler(实现了ResultSetHandler接口)封装
(2)运行图总结
1)SqlSession内部总运行图
2)prepare()方法运行图:
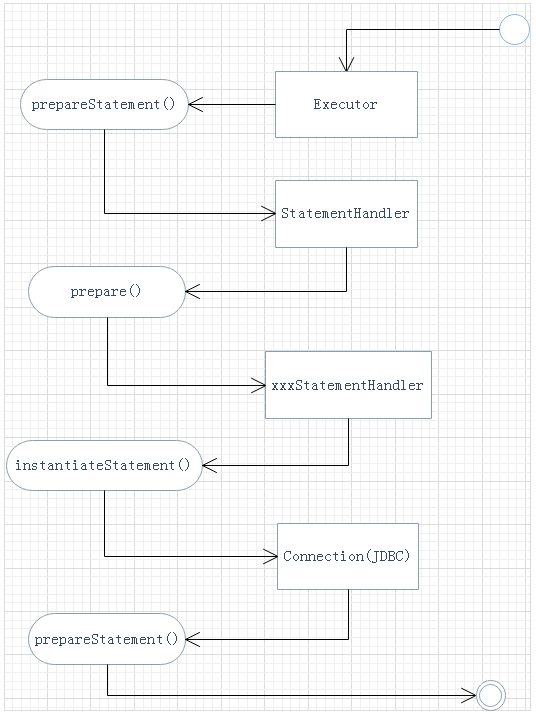
3)parameterize()方法运行图