很多应用中都需要用到地图联动、多屏对比、二三维分屏、大屏显示,有图形可视化的地方就有事件响应触发:鼠标按下、移动、鼠标滚轮,由此触发了地图上坐标或范围的变化,将这些变化发送给另一个地图并响应这些变化,即完成地图联动。
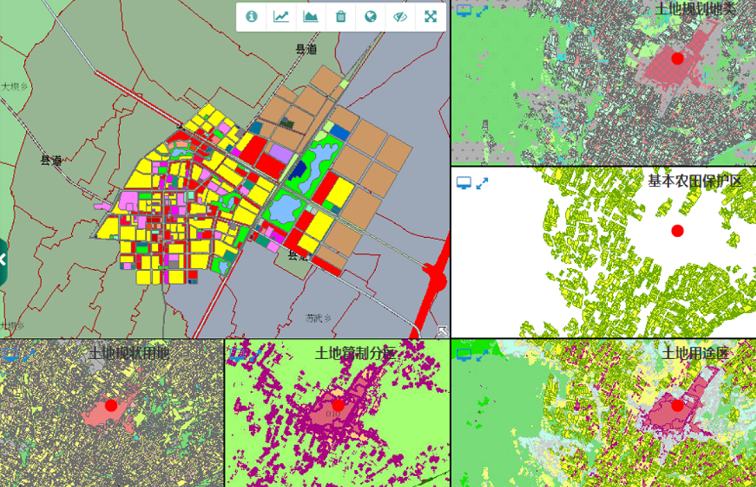
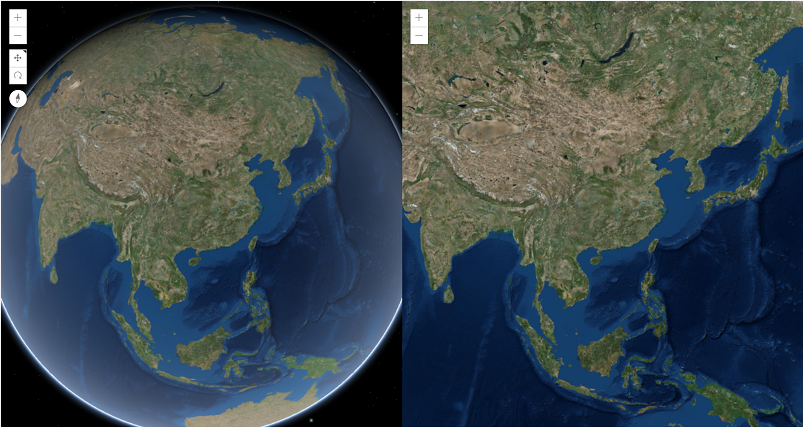
下面以二维地图分屏和二三维地图分屏分别说明实现思路(以ArcGIS开发为例,其他思路可参考)。
1、二维地图分屏对比(地图空间参考一般会一致)
1)页面布局,将网页布局设计成1~N个DIV;
2)事件监听,对鼠标在地图上的事件进行监听,一个地图事件触发后,其他地图响应。
※※※ MouseDown、MouseOver、MouseWheel,3个主要事件响应,对应地图上pan-end、mouse-move、zoom-end,地图联动变化核心:【map.setExtent(evt.extent)】,参考代码如下:
//放大联动 this._activeMapEventHandlers.push(this.activeMap.on("zoom-end", function (evt) { self._maps.forEach(function (map) { if (map != self.activeMap) { map.setExtent(evt.extent); } }); })); //平移联动 this._activeMapEventHandlers.push(this.activeMap.on("pan-end", function (evt) { self._maps.forEach(function (map) { if (map != self.activeMap) { map.setExtent(evt.extent); } }); })); //鼠标联动 this._activeMapEventHandlers.push(this.activeMap.on("mouse-move", function (evt) { self._maps.forEach(function (map) { var idx = self._maps.indexOf(map); var graphicLayer = map.getLayer("layer") var graphic = self._mouseGraphics[idx]; if (map != self.activeMap) { graphicLayer.show(); graphic.setGeometry(evt.mapPoint); } else { graphicLayer.hide(); } }); }));
2、二三维分屏联动对比
与二维相比,三维在地图空间参考上具有差异性,三维地图一般是WGS84、WGS84魔卡托,还有诸如国内火星坐标系(CGCS2000)等,会导致投影坐标存在投影转换,二维平面坐标就是XY(另加Scale),三维立体坐标拥有XYZ(另加Scale),以及XYZ上的旋倾角,遵循右手笛卡尔坐标系,见下图:
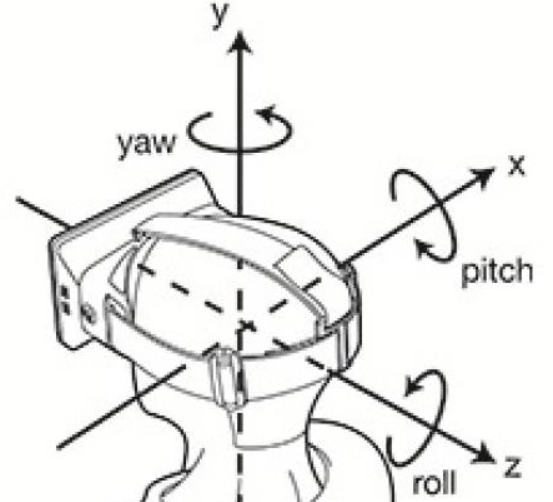
pitch是围绕X轴旋转,也叫做俯仰角;yaw是围绕Y轴旋转,也叫偏航角;roll是围绕Z轴旋转,也叫翻滚角。
由此可见,二三维联动的核心:二维的中心(X,Y)+Scale(缩放系数),三维的“七参数”:(X,Y,Z,Pitch,Yaw,Roll,Scale(缩放系数)),转换投影变动就能实现。
ArcGIS JS二三维联动同步具体设计实现与二维类似,给出核心同步代码参考:
var synchronizeView = function(view, others) { others = Array.isArray(others) ? others : [others]; var viewpointWatchHandle; var viewStationaryHandle; var otherInteractHandlers; var scheduleId; var clear = function() { if (otherInteractHandlers) { otherInteractHandlers.forEach(function(handle) { handle.remove(); }); } viewpointWatchHandle && viewpointWatchHandle.remove(); viewStationaryHandle && viewStationaryHandle.remove(); scheduleId && clearTimeout(scheduleId); otherInteractHandlers = viewpointWatchHandle = viewStationaryHandle = scheduleId = null; }; //鼠标事件监听、动画交互 var interactWatcher = view.watch('interacting,animation', function(newValue) { if (!newValue) { return; } if (viewpointWatchHandle || scheduleId) { return; } //同步联动视图(每个地图的View),viewpoint:Camera,rotation,scale scheduleId = setTimeout(function() { scheduleId = null; viewpointWatchHandle = view.watch('viewpoint', function(newValue) { others.forEach(function(otherView) { otherView.viewpoint = newValue; }); }); }, 0); //视图交互响应 otherInteractHandlers = others.map(function(otherView) { return watchUtils.watch(otherView, 'interacting,animation', function( value) { if (value) { clear(); } }); }); viewStationaryHandle = watchUtils.whenTrue(view, 'stationary', clear); }); return { remove: function() { this.remove = function() {}; clear(); interactWatcher.remove(); } } };
以上介绍了地图开发中常用到的分屏对比实现思路,仅供参考。
版权声明:欢迎转载,转载请说明出处。