rpm -ql ansible 查看安装文件
/usr/bin/ansible 主程序
/usr/bin/ansible-doc 查看配置文档,模块功能查看工具
/usr/bin/ansible-galaxy 下载/上传优秀代码或者Roles模块的官网平台
/usr/bin/ansible-playbook 定制自动化任务,编排剧本工具/usr/bin/ansible-pull远程执行命令工具
/usr/bin/ansible-valult 文件加密工具(脚本打开看到内容,通过这个加密)
/usr/bin/ansible-console 基于console界面与用户交互的执行工具
cat /etc/ansible/hosts Inventory主机清单
ansible --key-file=/root/id_rsa all -m ping #all Inventory主机清单里面所有的主机
Inventory主机清单
172.168.1.112:22 #修改端口
ansible配置文件详解
[defaults] #通用默认配置
inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #被控制端IP或者DNS列表
library = /usr/share/my_modules/ ##默认搜寻模块的位置
remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #远程执行临时文件
local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp
plugin_filters_cfg = /etc/ansible/plugin_filters.yml
forks = 5 ##并行线程数
poll_interval = 15 ##回频率或轮询间隔时间
sudo_user = root ##sudo远程执行用户名
ask_sudo_pass = True ##使用sudo,是否需要输入密码
ask_pass = True ##是否需要输入密码
transport = smart ##通信机制
remote_port = 22 ##远程SSH端口
module_lang = C ##模块和系统之间通信的语言
module_set_locale = False
gathering = implicit ##控制默认facts收集(远程系统变量)
gather_subset = all
gather_timeout = 10
roles_path = /etc/ansible/roles ##使用playbook搜索Ansible roles
host_key_checking = False ##是否检查远程主机密钥
sudo_exe = sudo ##sudo远程执行命令
sudo_flags = -H -S -n ##传递sudo之外的参数
timeout = 10 ##SSH超时时间
remote_user = root ##远程登录用户名
log_path = /var/log/ansible.log ##日志文件存放路径
module_name = command ##Ansible命令默认执行的模块
executable = /bin/sh ##执行的shell环境,用户shell模块
hash_behaviour = replace ##特定的优先级覆盖变量
jinja2_extensions = jinja2.ext.do,jinja2.ext.i18 ##允许开启jinja2扩展模块
private_key_file = /path/to/file ##私钥文件存储位置
display_skipped_hosts = True ##显示跳过任何任务的状态
system_warnings = True ##禁用系统运行Ansible潜在问题警告
deprecation_warnings = True ##PlayBook输出禁用“不建议使用”警告
command_warnings = False ##command模块Ansible默认发出警告
nocolor = 1 ##输出带上颜色区别,0表示开启,1表示关闭
pipelining = False ##开启pipe SSH通道优化
[accelerate] ##accelerate缓存加速
accelerate_port = 5099 ##加速连接端口5099
accelerate_timeout = 30 ##命令执行超过时间,单位为s
accelerate_connect_timeout = 5.0 ##上一个活动连接的时间,单位为min
accelerate_daemon_timeout = 30 ##允许多个私钥被加载到daemon
accelerate_multi_key = yes ##任何客户端想要连接daemon都要开启这个选项
ansible 主机清单匹配规则:
all 表示主机清单所有主机
ansible all -m ping
* 通配符(机清单)
ansible "*" -m ping
ansible 192.168.1.* -m ping
ansible "*svr" -m ping
或关系
ansible web:db -m ping
ansible 192.168.1.1:192.168.1.22 -m ping
逻辑与(交集)
ansible "web:&db" -m ping # 在web组并且在db组中的机器
逻辑非
ansible 'web:!db' -m ping # 在web组中,但是不在db组中的机器 需要用单引号
正则
ansible "~(web|db)..hh.com" -m ping
sudo 连接方式:sudo 连接方式:
[root@zabbinx ~]# ansible all -m command -a "ls -lh" -u kuwo -k -b -K #-b sudo用户,默认配置文件为root -K sudo密码
SSH password:
SUDO password[defaults to SSH password]:
ansible all -m ping -u kuwo -k -b --become-user mgpj #以kuwo sudo 切换至mgpj用户执行ping
ansible all -m ping -u kuwo --become-user=root -a "ls -l" mgpj #以kuwo sudo 切换至 root用户执行ping
常用模块
ping模块
[root@zabbinx ~]# ansible -uroot --key-file=/root/id_rsa all -m ping
[root@zabbinx ~]# ansible -uroot -k all -m ping
-m command 模块 默认模块 <>|;& $ 这些特殊字符command不支持
参数:
creates 文件存在 就不执行 #ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m command -a "creates=/etc/fstab ls -lh /root" #执行
removes 文件不存在 就不执行 #ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m command -a "removes=/etc/fs ls -lh /root" #不执行
chdir 切换目录 #ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m command -a "chdir=/etc creates=ftab ls -lh /root"
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m command -a "chdir=/opt sh ./a.sh" 执行shell脚本
-m shell 模块 跟command模块的区别 支持<>|;& $ 这些特殊字符
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m shell -a "echo 123|passwd --stdin test" #修改密码
-m script 模块 执行本机的shell脚本 都其他主机运行
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m script -a "a.sh" #ansible本机的a.sh脚本 在所有主机运行执行仪表
-m copy 模块 拷贝本机的文件到其他主机
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m copy -a "src=/root/1.jpg dest=/opt/3.jpg backup=yes mode=066" #ansible本机的/root/1.jpg 文件拷贝到所有主机/opt/3.jpg 并且备份 给权限066
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m copy -a "src=/root/1.jpg dest=/opt/3.jpg backup=yes mode=066 owner=test"
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m copy -a "content='hello
world' dest=/opt/test.log" #内容生成到所有主机的/opt/test.log文件中
-m fetch 模块 拷贝客服端的文件到服务器,只支持一个文件拷贝 目录可以先tar
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m fetch -a "src=/opt/test.log dest=/root" #拷贝客服端/opt/test.log文件到 ansible主机中的root目录
-m file 模块 创建文件设置文件属性
参数 state=touch创建文件 state=directory创建目录 state=absent删除文件 state=link创建软连接 state=hard创建硬连接
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m file -a 'path=/opt/111111111 state=touch' #path name dest 这3个在这里面都可以用 都是一个意思
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m file -a 'path=/opt/1111111112 state=directory'
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m file -a 'path=/opt/1111111112 state=absent'
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m file -a 'src=/etc/fstab path=/opt/1111111112 state=link'
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m file -a 'path=/opt/ state=absent' 删除文件
-m hostname 模块 修改主机名
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m hostname -a 'name=node'
-m corn 模块 创建计划任务
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m cron -a 'minute=* weekday=1,2,3,4,5 job="/usr/bin/wall FBI" name=wall' #name 名字 就在计划任务上面显示这个#Ansible: wall
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m cron -a 'disable=true job="/usr/bin/wall FBI" name=wall' #禁用计划任务
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m cron -a 'disable=false job="/usr/bin/wall FBI" name=wall' #启用
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m cron -a 'name=wall state=absent' #删除计划任务
-m yum 模块
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m yum -a 'name=ftp'
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m yum -a 'name=ftp state=installed' #安装ftp 默认present 可以指定 `present' or `installed', `latest'安装
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m yum -a 'name=ftp,httpd state=installed' #安装多个
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m yum -a 'name=ftp state=absent' #删除 或者用removed
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m yum -a 'name=dstat update_cache=yes' #一边安装包一边清理缓存
-m service 模块 管理服务
started,stopped,restarted,reloaded, got: restartd"
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m service -a "name=sshd state=stopped" #启动服务器
#ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m service -a "name=sshd state=stopped enabled=yes" #enabled=yes开机启动 查看systemctl is-enabled sshd.service是否开机启动
-m user 模块
#ansible all --key-file=id_rsa -m user -a "name=nginx shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes home=/opt/nginx groups=root,bin uid=90"
#ansible all --key-file=id_rsa -m user -a "name=nginx state=absent remove=yes" #remove=yes删除家目录
主机清单中指定单独主机执行ansible 使用参数 --limit
ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m hostname -a 'name=node' --limit 172.168.1.112
ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m hostname -a 'name=node' --limit all #指定组名也可以的
ansible playbook 使用的yaml 或者 yml 文件:
test.yml文件
- hosts: all
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
tasks:
- name: create file
#remote_user: test
#become: yes #是否允许身份切换
#become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
#become_user: test #切换指定的用户
file: name=/opt/test state=touch
ansible-playbook -utest -k test.yml #普通用户执行
ansible-playbook --list-hosts test.yml#获取当前yml里面的清单主机列表
ansible-playbook -utest -k test.yml --limit 172.168.1.112 test.yml 里面清单主机中的特定这台主机执行
ansible-playbook --list-tasks test.yml #查看任务
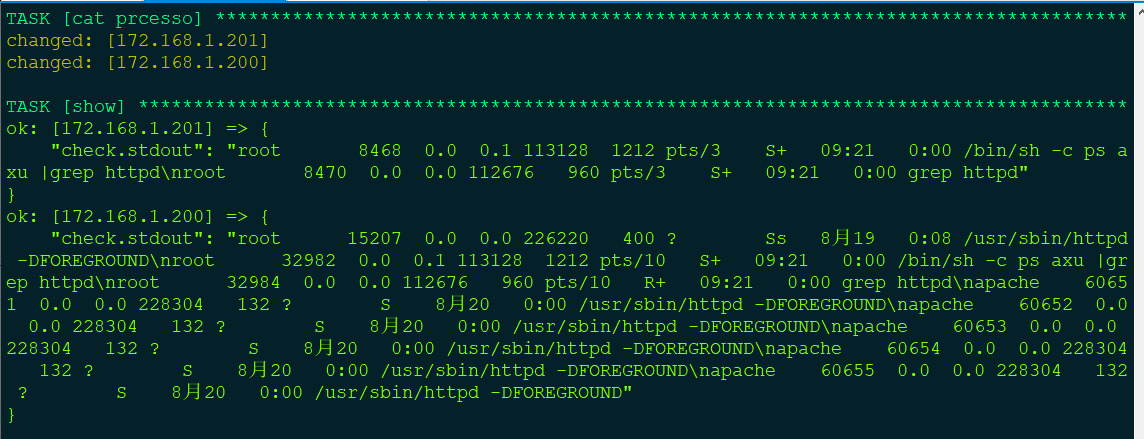
- hosts: web tasks: - name: cat prcesso shell: ps axu |grep httpd register: check #定义变量存储返回的结果 - name: show debug: var=check.stdout verbosity=0 #check.stdout 显示出的信息会看的更清晰点 ~
playbook 之 notify 和 handlers 配合使用,执行yml文件的时候,里面内容会自动执行; notify 当某文件程序目录发生变化的时候 通知handlers处理,
- hosts: all
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
tasks:
- name: create file
#remote_user: test
#become: yes #是否允许身份切换
#become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
#become_user: test #切换指定的用户
file: name=/opt/test state=touch
notify: stop httpd #create file执行完后 通知handlers里面的name: stop httpd 做停止服务
- name: create user
user: name=newusers2 system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
notify: #下面可以通知handlers多个name做处理,必须是发生改变 或 新建的时候 替换的时候 才会执行 也就是说颜色是黄色的才执行
- restart httpd #通知handlers 描述的名字
- stop httpd
- name: install httpd
yum: name=httpd
- name: create content
copy: content="hello" dest=/opt/test
ignore_errors: True #忽略错误,执行出错了 忽略 继续执行后面的任务,不会退出来
- name: start service
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
handlers: #触发器
- name: restart httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
- name: stop httpd
service: name=httpd state=stopped
ansible-playbook -utest -k test.yml #普通用户执行
ansible-playbook --list-hosts test.yml#获取当前yml里面的清单主机列表
ansible-playbook -utest -k test.yml --limit 172.168.1.112 test.yml 里面清单主机中的特定这台主机执行
ansible-playbook --list-tasks test.yml #查看任务
playbook 之 tags:加标签,作用是将来可以调用这个标签里面的内容,多个动作可以用一个标签,也就是标签名相同
- hosts: all become: yes become_method: sudo tasks: - name: create file #remote_user: test #become: yes #become_method: sudo #become_user: test file: name=/opt/test state=touch #notify: stop httpd tags: createfile #定义标签 - name: create user user: name=newusers2 system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin notify: - restart httpd - stop httpd - name: install httpd yum: name=httpd
ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test.yml -t starthttpd #-t starthttpd 指定标签名
ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test.yml -t starthttpd,createfile #同时执行2个标签
playbook之变量
ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m setup #查看系统变量,这些变量都是可以直接拿到playbook里面直接使用的
ansible all --key-file=/root/id_rsa -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_swapfree_mb' #过滤变量信息
参数 -e
- hosts: all
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: create user
user: name={{ arg }} system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa -e 'arg=uuuukkk' test2.yml
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa -e 'arg1=2 arg2=1 arg2=3' test2.yml #指定多个变量
/etc/ansible/hosts 在主机清单中定义变量,可以定义主机变量 和 公共变量
普通变量:单一的单个主机有效, 优先级比公共变量高
/etc/ansible/hosts 文件中组db里面的172.168.1.112 定义了一个单一变量 hostname
[db]
172.168.1.112 hostname=node1 #定义个hostname变量
yml内容:
- hosts: all
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: hostname
hostname: name={{ hostname }}
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test2.yml #执行后 就修改主机名为node1
公共变量(组变量):针对一个组的主机定义变量
/etc/ansible/hosts 文件中组db里面,下面定义个db的组变量
[db]
172.168.1.112 hostname=node1 #定义个单一变量
[db:vars] #对DB组定义了公共变量
host=www
domian=com
yml文件:
- hosts: db
become: yes
become_method: sudo
tasks:
- name: hostname
hostname: name={{ host }}.{{ hostname }}.{{domian}} #调用host公共变量 hostname单一变量 domian公共变量
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test2.yml 主机名就修改成了www.node1.com
通过yml文件定义变量
testvars.yml: #存放变量的文件
var1: open
var2: nginx
test.yml
- hosts: db
vars_files: #指定存放变量testvars.yml文件
- testvars.yml
tasks:
- name: create fiel
file: name=/opt/{{ var2 }} state=touch #var2 获取的是 testvars.yml文件的变量
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test.yml
playbook之模版template: 是一个模块 只能在playbook中使用
1 cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ./templates/nginx.conf.j2 #templates 在当前目录下面建立一个templates目录,默认从这个目录查找,如果不是,需要定义绝对路劲
2 修改/templates/nginx.conf.j2文件 找到修改修改的变量 例如 worker_processes {{ cpu }}; 工作进程个数. 定义cpu模版内容
3 调用变量, 可以是单一变量 系统setup变量 公共变量 yml文件变量
--- - hosts: db become: yes become_method: sudo vars_files: - testvars.yml #这里面使用的是文件变量 这个文件变量中有定义个cpu: 5 tasks: - name: install nginx yum: name=nginx - name: copy file template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #使用template模块 拷贝这个文件的时候,会根据模版中的变量名找值 notify: reload nginx - name: start nginx service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes handlers: - name: reload nginx service: name=nginx state=restarted
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa test.yml
变量的优先级: 命令-e变量 > playbook里面定义的变量 > 主机清单里面定义的变量(普通变量>公共变量)
playbook 之 when 判断语句
-m setup 查看到各个主机的 ansible_os_family 家庭版本系列 ansible_distribution 系统 ansible_distribution_major_version系统版本
---
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
vars_files:
- testvars.yml
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
- name: copy file 6
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "6" #当系统版本是6的时候 拷贝下面文件
template: src=nginx6.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: reload nginx
- name: copy file 7
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7" #当系统版本是7的时候 拷贝下面文件
template: src=nginx7.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: reload nginx
- name: start nginx
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: reload nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
playbook之with_items 迭代 也就是循环
---
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
vars_files:
- testvars.yml
tasks:
- name: file
file: name=/opt/{{ item }} state=touch #item 代表with_items里面的值 类似于for 里面的值
when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7" #如果是7 才执行创建文件
with_items: #相当于是for循环
- file1
- file2
- file3
- file4
- file5
- name: install
with_items:
- htop
- sl
- hping3
yum: name={{item}}
- name: test
user: name={{item.name}}
with_item:
- {name:'test',group:'test2'}
#这种方式也支持 with_items: {name: 'test' , gr: 'g1'} user: name={{item.name}} group={{item.gr}}
playbook之template 的 if 判断
for.yml:
---
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
vars:
http:
- web1
- web2
service:
- db:
name1: mysql
name2: sqlserver
tasks:
- name: file
template: src=for.conf.j2 dest=/opt/for.conf
templates目录下面for.conf.j2
{%for k in http %} #for 循环http
{{k}} #获取到web1 web2
{%endfor%}
{%for i in service %}
{%if i.db %} #判断i.db是否有值
{{i.db}}
{%else%}
aaaa #没有就显示aaa
{%endif%}
{{i.name1}}
{{i.name2}}
{%endfor%}
#ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa for.yml 执行会自动找templates目录下面for.conf.j2文件
Roles角色 其实就是把各种yml里面的模块拆分开来使用 比如有4个模块,这时候我们就建4个文件 来单独存放
ansible roles 各个目录作用
role_name/:我们定义的role的名字
file/:用于存放copy或script等模块调用的函数
tasks/:用于定义各种task,此目录一定要有main.yml;其他文件需要main.yml包含调用
handlers:用于定义各种handlers,此目录一定要有main.yml;其他文件需要main.yml包含调用
vars:用于定义variables,此目录一定要有main.yml;其他文件需要main.yml包含调用
templates/:存储由template模块调用的模板文本;
meta/:定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系,此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
default/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于设定默认变量;
.
├── roles
│ ├── httpd
│ │ ├── files #用于存放copy或script等模块调用的函数
│ │ │ └── httpd.conf.j2
│ │ └── tasks
│ │ ├── copy_file.yml #用于定义各种task,此目录一定要有main.yml;其他文件需要main.yml包含调用
│ │ ├── create_user.yml
│ │ ├── install_http.yml
│ │ └── main.yml
│ └── nginx
│ ├── files
│ │ └── httpd.conf.j2
│ ├── tasks
│ │ ├── create_group.yml
│ │ ├── create_user.yml
│ │ ├── install_nginx.yml
│ │ ├── main.yml
│ │ ├── restart_nginx.yml
│ │ ├── start_nginx.yml
│ │ └── template_file.yml
│ └── templates #存储由template模块调用的模板文本;
│ └── nginx.conf.j2
├── roles_http.yml #httpd使用的角色文件 需要跟roles目录同级
├── roles_nginx.yml #nginx使用的角色文件
└── roles_totle.yml #httpd和nginx 使用的角色文件
roles_nginx.yml
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
roles: #调用角色
- nginx #调用nginx角色 这个是一个目录名
create_group.yml
- name: create group
group: name=nginx
install_nginx.yml
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx
main.yml 文件 调用所有yml文件执行的先后顺序
- import_tasks: create_group.yml
- import_tasks: create_user.yml
- import_tasks: install_nginx.yml
- import_tasks: template_file.yml
- import_tasks: start_nginx.yml
- import_tasks: restart_nginx.yml
- import_tasks: roles/httpd/tasks/copy_file.yml #调用其他角色里面的任务
template_file.yml
- name: copy conf
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf #会在当前目录的上一级files文件里面找nginx.conf.j2
其他文件不记录到这了
在roles目录下面执行 ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa roles_nginx.yml
roles 之 标签使用:
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
roles: #调用角色
- {role: nginx,tags: ['web','http']} #调用nginx角色 这个是一个目录名,tags是标签名字,可以多个 用列表方式
- {role: app,tags: ['web_1','http_2']}
在roles目录下面执行 ansible-playbook --key-file=/root/id_rsa -t http roles_nginx.yml
roles 之 when 判断使用
- hosts: db
become: yes #是否允许身份切换
become_method: sudo #切换用户身份的方式,有sudo、su、pbrun等方式,默认为sudo
roles: #调用角色
- {role: nginx,tags: ['web','http'],when: ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"} #判断如果是7的系统 就执行
roles 之 notify 和 handles使用
新建一个handlers目录 handlers:用于定义各种handlers,此目录一定要有main.yml;其他文件需要main.yml包含调用
文件mian.yml 必须要有这个名字的文件在这目录里面
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx stated=restarted
vars目录定义变量的目录:
文件mian.yml 必须要有这个名字的文件在这目录里面
var: 123 #自定义变量
var_1: 223
template_file.yml #会获取到上面的变量内容 -m setup变量也可以使用
- name: copy conf
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx