1.什么是进程
process:运行中的程序的一个副本,是被载入内存的一个指令集合,是资源分配的单位
进程ID(Process ID,PID)号码被用来标记各个进程
UID,GID,和SELinux语境决定对文件系统的存取和访问权限
通常从执行进程的用户来继承
存在生命周期
init:第一个进程,从Centos7以后为systemd
进程:都是由父进程创建,fork(),父子关系,cow:copy on write
进程,线程和协程
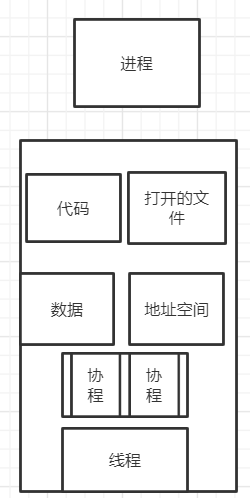
进程更多的状态:
运行态:running
就绪态:ready
睡眠态:分为两种,可中断:interruptable,不可中断:uninterruptable
停止态:stopped,暂停于内存,但不会被调度,除非手动启动
僵死态:zombie,僵尸态,结束进程,父进程结束前,子进程不关闭,杀死父进程可以关闭僵死态的子进程
进程管理和性能相关工具
2.进程树pstree
pstree可以用来显示进程的父子关系,以树形结构显示
-p 显示PID
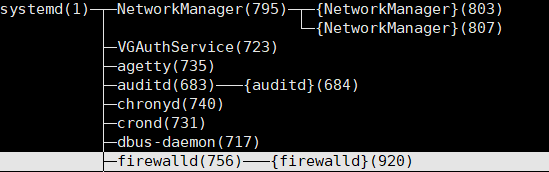
-u 显示用户切换
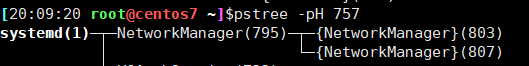
-H pid 高亮显示指定进程及其父辈进程
3.进程信息ps
ps即process state,可以显示当前状态的快照,默认显示当前终端中的进程,Linux系统各进程的相关信息均保存在/proc/PID目录下的文件中
ps格式
ps [option] . . .
UNIX选项 如:-A -e
BSD选项 如:a
a 选项包括所有终端中的进程
x 选项包括不链接终端的进程
u 选项显示进程所有者的信息
f 选项显示进程树
k|--sort 属性 对属性排序,属性前加 - 表示倒序
o 属性. . . 选项显示定制的信息 pid,cmd,%cpu,%mem
-e 显示所有进程,相当于-A
ps axo 接想查询的
[20:38:47 root@centos7 ~]$ps axo pid,cmd,%cpu,%mem PID CMD %CPU %MEM 1 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd -- 0.0 0.8 2 [kthreadd] 0.0 0.0 4 [kworker/0:0H] 0.0 0.0 6 [ksoftirqd/0] 0.0 0.0 7 [migration/0] 0.0 0.0
ps aux显示
[20:41:46 root@centos7 ~]$ps aux USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND root 1 0.0 0.8 125472 3940 ? Ss 19:24 0:01 /usr/lib/systemd root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:24 0:00 [kthreadd] root 4 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 19:24 0:00 [kworker/0:0H] root 6 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:24 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0] root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:24 0:00 [migration/0] root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:24 0:00 [rcu_bh] root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 19:24 0:00 [rcu_sched]
按pid倒叙排序
[20:44:39 root@centos7 ~]$ps aux k -pid
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1673 0.0 0.4 155588 1952 pts/0 R+ 20:46 0:00 ps aux k -pid
root 1671 0.1 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:43 0:00 [kworker/0:1]
root 1656 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:38 0:00 [kworker/0:2]
root 1588 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:11 0:01 [kworker/0:0]
找到未知进程的执行程序文件路径
[20:51:46 root@centos7 ~]$ls -l /proc/740/exe lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jan 4 19:24 /proc/740/exe -> /usr/sbin/chronyd
4.查看进程信息prtstat
可以显示进程信息,来自于psmisc包
格式:
prstat [options] PID . . .
-r raw格式显示
[20:57:45 root@centos7 ~]$prtstat 740 Process: chronyd State: S (sleeping) CPU#: 1 TTY: 0:0 Threads: 1 Process, Group and Session IDs Process ID: 740 Parent ID: 1 Group ID: 738 Session ID: 738 T Group ID: -1 Page Faults This Process (minor major): 445 3 Child Processes (minor major): 0 0 CPU Times This Process (user system guest blkio): 0.01 0.08 0.00 0.00 Child processes (user system guest): 0.00 0.00 0.00 Memory Vsize: 120 MB RSS: 1757 kB RSS Limit: 18446744073709 MB Code Start: 0x5638dbdef000 Code Stop: 0x5638dbe2c9fc Stack Start: 0x7fff25a95c50 Stack Pointer (ESP): 0x7fff25a95800 Inst Pointer (EIP): 0x7fdf073c09a3 Scheduling Policy: normal Nice: 0 RT Priority: 0 (non RT)
5.pgrep
-u uid:生效者
-l:显示进程名
-a:显示完整格式的进程名
[21:09:12 root@centos7 ~]$pgrep -u postfix 1273 1730 [21:09:42 root@centos7 ~]$pgrep -lu postfix 1273 qmgr 1730 pickup
注意l和u的顺序
[21:12:33 root@centos7 ~]$pgrep -au yang
1766 -bash
1789 dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/null
6.pidof
命令格式
pidof [options] [program[...]]
-x 按脚本名称查找pid
[09:59:29 root@centos7 ~]$pidof bash 1601
7负载查询uptime
/proc/uptime包括两个值,单位s
系统启动时长
空闲进程的总时长(按总的cpu核数计算)
uptime和w显示以下内容
当前时间
系统已启动的时间
当前上线人数
系统平均负载(1,5,15分钟的平均负载,一般不会超过1,超过5时建议警报)
[10:14:43 root@centos7 ~]$uptime 10:14:52 up 38 min, 2 users, load average: 0.11, 0.06, 0.05 [10:14:52 root@centos7 ~]$w 10:14:57 up 38 min, 2 users, load average: 0.10, 0.06, 0.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/0 10.0.0.1 09:56 1.00s 0.07s 0.00s w root pts/2 10.0.0.1 10:05 7:45 0.08s 0.08s -bash
8.显示cpu相关系统mpstat
来自于sysstat包
[10:17:53 root@centos7 ~]$mpstat Linux 3.10.0-1160.11.1.el7.x86_64 (centos7) 01/05/2021 _x86_64_ (2 CPU) 10:20:32 AM CPU %usr %nice %sys %iowait %irq %soft %steal %guest %gnice %idle 10:20:32 AM all 0.24 0.00 0.50 0.41 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 98.84
9.查看进程实时状态top
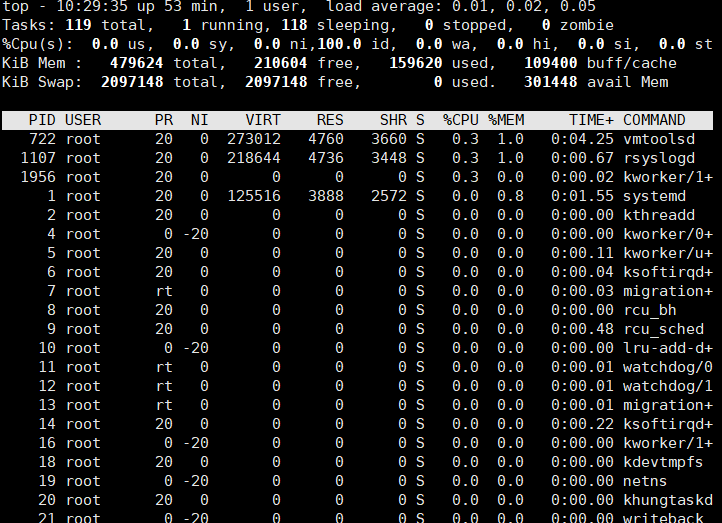
top提供动态的实时进程状态
有许多内置命令
帮助:h或? ,按q或esc退出帮助
排序
P:已占据的CPu百分比,%cpu
M:占据内存百分比,%MEM
T:累计占据cpu时长,time+
首部信息显示:
uptime信息:l命令
tasks及cpu信息:t命令
cpu分别显示:1(数字)
memory信息:m命令
修改刷新时间间隔:s
终止指定进程 :k
保存文件:w
10内存空间
清理缓存
[11:10:51 root@centos7 ~]$cat /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches 0 [11:11:38 root@centos7 ~]$free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 980M 180M 673M 5.6M 127M 773M Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G [11:11:43 root@centos7 ~]$echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches [11:12:22 root@centos7 ~]$free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 980M 170M 764M 5.6M 45M 783M Swap: 2.0G 0B 2.0G
一般情况下,应用在系统上稳定运行了,free值也会保持在一个稳定值的。不用清理缓存,否则,清空buffer,强制腾出free的大小,可能只是把问题给暂时屏蔽了。除非在软件开发阶段,需要临时清理buffer。
11.监视磁盘I/O iotop
来自于iotop包
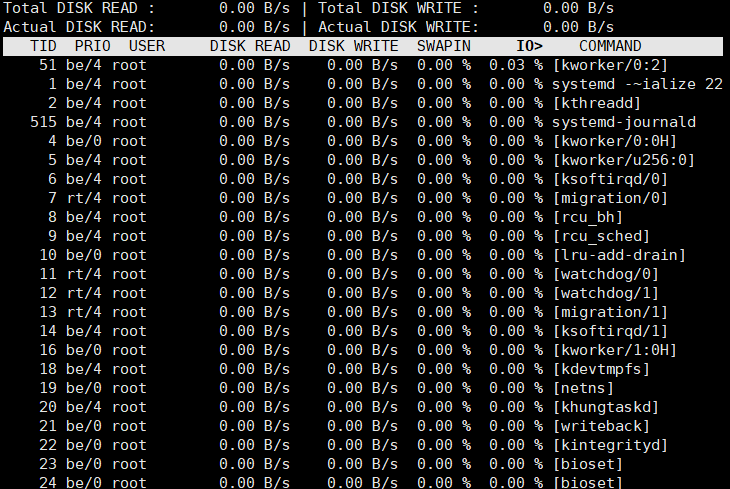
iotop命令是一个 用来监视磁盘I/O使用状况的top类工具iotop 具有与top相似的UI,其中包括PID,用户,I/O,进程等相关信息,可查看每个进程是如何使用IO
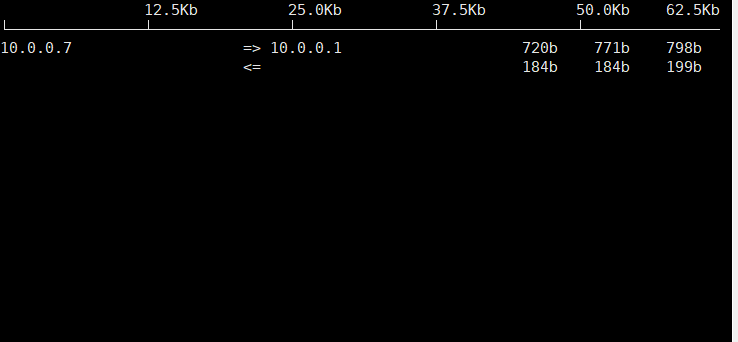
12.显示网络带宽使用情况iftop
通过EPEL源的iftop包
[14:32:07 root@centos7 ~]$iftop -ni eth0
13.查看进程打开文件lsof
lsof查看当前系统文件的工具。在linux环境下,一切皆文件,用户通过文件不仅可以访问常规数据,还可以访问网络连接和硬件如传输控制协议(tcp)和用户数据报协议(udp)套接字等,系统在后台在后台都为该应用程序分配了一个文件描述符
-a:列出打开文件存在的进程
-c《进程名》:列出指定进程所打开的文件
-g:列出GID号进程详情
-p:《进程号》:列出指定进程号所打开的文件
-u:列出UID号进程详情
-i《条件》:列出符合条件的进程(4。6。协议。端口。ip)
[14:47:47 root@centos7 ~]$lsof|head COMMAND PID TID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME systemd 1 root cwd DIR 253,0 239 64 / systemd 1 root rtd DIR 253,0 239 64 / systemd 1 root txt REG 253,0 1632736 478680 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd systemd 1 root mem REG 253,0 20064 34234110 /usr/lib64/libuuid.so.1.3.0 systemd 1 root mem REG 253,0 265576 33618 列出当前所有打开的文件 [15:11:18 root@centos7 ~]$lsof -p 12375 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME pickup 12375 postfix cwd DIR 253,0 201 67457751 /var/spool/postfix pickup 12375 postfix rtd DIR 253,0 239 64 / pickup 12375 postfix txt REG 253,0 285160 67457684 /usr/libexec/postfix/pickup pickup 12375 postfix mem REG 253,0 61560 33597143 /usr/lib64/libnss_files-2.17.so 指定进程号,可以查看该进程打开的文件 [15:12:57 root@centos7 ~]$lsof /var/log/messages COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME rsyslogd 1107 root 6w REG 253,0 3530818 100694078 /var/log/messages 查看当前那个进程正在使用此文件 [15:14:31 root@centos7 ~]$lsof -c bc COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME bc 12534 root cwd DIR 253,0 251 100663361 /root bc 12534 root rtd DIR 253,0 239 64 / bc 12534 root txt REG 253,0 83424 774372 /usr/bin/bc bc 12534 root mem REG 253,0 106176928 55352 /usr/lib/locale/locale-archive bc 12534 root mem REG 253,0 19248 33597126 /usr/lib64/libdl-2.17.so bc 12534 root mem REG 253,0 2156272 33594212 /usr/lib64/libc-2.17.so bc 12534 root mem REG 253,0 174576 33618750 /usr/lib64/libtinfo.so.5.9 查看指定程序打开的文件 [15:17:27 root@centos7 ~]$lsof -i :9090 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME systemd 1 root 24u IPv6 55969 0t0 TCP *:websm (LISTEN) 查看端口连接状况 [15:20:17 root@centos7 ~]$lsof -i@127.0.0.1 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME chronyd 734 chrony 5u IPv4 18020 0t0 UDP localhost:323 master 1201 root 13u IPv4 20430 0t0 TCP localhost:smtp (LISTEN) 查看连接ip,端口等一些服务的连接情况
14.cockpit
cockpit是一个基于web界面的应用,它提供了对系统的图形化管理
安装cockpit
[19:00:51 root@centos7 ~]$yum -y install cockpit [19:00:51 root@centos7 ~]$systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket 打开浏览器,访问一下地址: https://主机ip:9090
15信号发送kill
显示当前系统可用信号
kill -l
1) SIGHUP 无需关闭进程而让其重读配置文件
2) SIGINT 终止正在运行的进程,相当于ctrl+c
3) SIGQUIT 相当于ctrl+
9) SIGKILL 强制杀死正在运行的进程
15) SIGTERM 终止正在运行的进程,默认信号
18) SIGCONT 继续运行
19) SIGSTOP 后台休眠
指定信号的方法
信号的数字标识:1,2,9
范例
[19:11:10 root@centos7 ~]$kill -9 `pidof ping`
15.作业管理
前台作业:通过终端启动,且启动后一直占据终端
后台作业:可通过终端启动,但启动后即转入后台运行(释放终端)

让作业运行与后台
运行中的作业:crtl+z 进入后台休眠
尚未启动的作业:command &后台运行
后台作业虽然被送往后台运行,但其依然与终端相关;退出终端,将关闭后台作业。如果希望送往后台后,剥离与终端的关系
nohup command &>/dev/null &
[19:11:22 root@centos7 ~]$nohup ping www.baidu.com &>/dev/null & 后台运行,关闭终端一 [19:19:47 root@centos7 ~]$ps aux |grep ping root 1528 0.0 0.1 150092 1980 ? S 19:19 0:00 ping www.baidu.com 在终端二里仍看到在运行
查看当前终端所有作业
jobs
fg 加作业编号:把指定的后台作业调回前台
bg 作业编号:让送往后台的作业在后台继续运行
kill 作业编号:终止指定的作业
并行运行
利用后台执行,实现并行功能,即同时运行多个进程,提高效率
方法一
cat all.sh f1.sh& f2.sh& f3.sh&
方法二
(f1.sh&);(f2.sh&);(f3.sh&)
方法三
f1.sh&f2.sh&f3.sh&
范例
多组命令实现并行
[19:26:54 root@centos7 ~]$cat ping.sh #!/bin/bash net=10.0.0. for i in {1..254};do { ping -c1 -w1 $net$i >/dev/null && echo $net$i is up || echo $net$i is down;}& done
函数实现
#!/bin/bash myping(){ ping -c2 -i0.3 -W1 $1 &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "$1 is up" else echo "$1 is down" fi } for i in {1..254} do myping 192.168.0.$i & done
16.任务计划
通过任务计划,可以让系统自动的按时间或周期性任务执行任务
周期性计划任务cron
cron依赖于crond服务,确保crond守护处于运行状态
systemctl status crond
centos7以后版本
service crond status
centos6
cron任务分为
系统cron任务:系统维护作业,/etc/crontab主配置文件,/etc/cron.d/子配置文件
用户cron任务:保存在/var/spool/cron/username,利用crontab命令管理
系统cron计划任务
/etc/crontab 格式说明
[19:44:47 root@centos7 ~]$cat /etc/crontab SHELL=/bin/bash #默认的shell类型 PATH=/sbin:/bin:/user/sbin:/usr/bin #默认的PATH变量值,可以修改 MAILTO=root #默认标准输出和错误发给邮件root,可以指向其他用户 # For details see man 4 crontabs # Example of job definition: # .---------------- minute (0 - 59) # | .------------- hour (0 - 23) # | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31) # | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ... # | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat # | | | | | # * * * * * user-name command to be executed
crontab命令格式:
crontab [-u user] [-e |-l|-r] [-i]
-l 列出所有任务
-e 编辑任务
-r 移除所有任务
-u user 指定用户管理cron任务,仅root可运行
[20:30:26 root@centos7 ~]$crontab -e */10 * * * 1-5 /root/nihao.sh 周一到周五每10分钟执行一次脚本,注意要给脚本执行权限
11月每天的6-12点之间每隔2小时执行/app/bin/test.sh
[20:30:26 root@centos7 ~]$crontab -e * 6-12/2 * * * /app/bin/test.sh