题目链接
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1955
题目描述
在实现程序自动分析的过程中,常常需要判定一些约束条件是否能被同时满足。
考虑一个约束满足问题的简化版本:假设x1,x2,x3...代表程序中出现的变量,给定n个形如xi=xj或xi≠xj的变量相等/不等的约束条件,请判定是否可以分别为每一个变量赋予恰当的值,使得上述所有约束条件同时被满足。例如,一个问题中的约束条件为:x1=x2,x2=x3,x3=x4,x4≠x1,这些约束条件显然是不可能同时被满足的,因此这个问题应判定为不可被满足。
现在给出一些约束满足问题,请分别对它们进行判定。
输入输出格式
输入格式:从文件prog.in中读入数据。
输入文件的第1行包含1个正整数t,表示需要判定的问题个数。注意这些问题之间是相互独立的。
对于每个问题,包含若干行:
第1行包含1个正整数n,表示该问题中需要被满足的约束条件个数。接下来n行,每行包括3个整数i,j,e,描述1个相等/不等的约束条件,相邻整数之间用单个空格隔开。若e=1,则该约束条件为xi=xj;若e=0,则该约束条件为xi≠xj;
输出格式:输出到文件 prog.out 中。
输出文件包括t行。
输出文件的第 k行输出一个字符串“ YES” 或者“ NO”(不包含引号,字母全部大写),“ YES” 表示输入中的第k个问题判定为可以被满足,“ NO” 表示不可被满足。
输入输出样例
2
2
1 2 1
1 2 0
2
1 2 1
2 1 1
NO
YES
2
3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 1 1
4
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 1
1 4 0
YES
NO
说明
【样例解释1】
在第一个问题中,约束条件为:x1=x2,x1≠x2。这两个约束条件互相矛盾,因此不可被同时满足。
在第二个问题中,约束条件为:x1=x2,x1=x2。这两个约束条件是等价的,可以被同时满足。
【样例说明2】
在第一个问题中,约束条件有三个:x1=x2,x2=x3,x3=x1。只需赋值使得x1=x1=x1,即可同时满足所有的约束条件。
在第二个问题中,约束条件有四个:x1=x2,x2=x3,x3=x4,x4≠x1。由前三个约束条件可以推出x1=x2=x3=x4,然而最后一个约束条件却要求x1≠x4,因此不可被满足。
【数据范围】
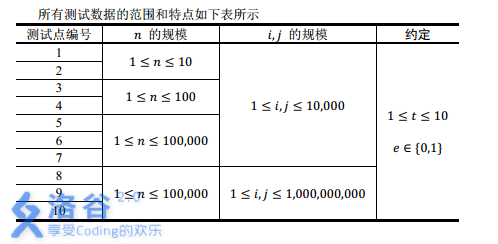
【时限2s,内存512M】
题目分析
这道题是一个很显然的并查集,但是看到数据范围
我们竟然需要开一个1e9的数组!
那么很显然的会MLE
所以我们要用到离散化
然后就可以了qwq
参考代码
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 //#define DEBUG(x) cerr << #x << "=" << x << endl 8 const int maxn = 1e5 + 7; 9 10 int n, t, f[maxn], book[maxn * 3]; 11 12 struct node 13 { 14 int x; 15 int y; 16 int e; 17 }a[maxn]; 18 19 bool cmp(node a, node b) 20 { 21 return a.e > b.e; 22 } 23 24 inline void first(int k) 25 { 26 for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) f[i] = i; 27 } 28 29 int get(int x) 30 { 31 return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = get(f[x]); 32 } 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 37 cin.tie(0); 38 cin >> t; 39 while (t--) 40 { 41 cin >> n; 42 int tot = -1; 43 int flag = 1; 44 memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); 45 memset(f, 0, sizeof(f)); 46 memset(book, 0, sizeof(book)); 47 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 48 { 49 cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y >> a[i].e; 50 book[++tot] = a[i].x; 51 book[++tot] = a[i].y; 52 } 53 sort(book, book + tot); 54 int reu = unique(book, book + tot) - book; 55 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 56 { 57 a[i].x = lower_bound(book, book + reu, a[i].x) - book; 58 a[i].y = lower_bound(book, book + reu, a[i].y) - book; 59 } 60 first(reu); 61 sort(a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp); 62 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 63 { 64 int r1 = get(a[i].x); 65 int r2 = get(a[i].y); 66 if (a[i].e) 67 { 68 f[r1] = r2; 69 } 70 else if (r1 == r2) 71 { 72 cout << "NO" << endl; 73 flag = 0; 74 break; 75 } 76 } 77 if (flag) 78 cout << "YES" << endl; 79 } 80 return 0; 81 }
离散化
定义
对于离散化来说主要有三个步骤
一.去重(用unique去重函数)
二.排序
三.二分索引(用lower_bound函数)
1 const int N = 1e5 + 7; 2 3 int t[N], a[N]; 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 8 cin.tie(0); 9 cin >> n; 10 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 11 { 12 cin >> a[i]; 13 t[i] = a[i]; 14 } 15 sort(t + 1, t + n + 1); 16 m = unique(t + 1, t + n + 1) - t - 1; 17 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 18 a[i] = lower_bound(t + 1, t + m + 1, a[i]) - t; 19 }
在这段代码中,a[ ]经过离散,范围就变成了m。解释一下,unique是c++自带的一个函数,表示对一个数列去重,然后返回不重复的元素个数,当然在后面要减去首地址。那么这种离散化对于有重复元素的数列也可以适用,但是复杂度会高些。有一种离散化的方式复杂度会低一些,但是不能处理有重复元素的数列,所以在此不再赘述
举个例子:原数据:{6, 8, 4, 9, 5, 6, 7, 4},首先排序后得到{4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9},去重{4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},然后原序列就变成了{3, 5, 1, 6, 2, 3, 4, 1}。
lower_bound( )
这里是关于lower_bound( )和upper_bound( )的常见用法
lower_bound( )和upper_bound( )都是利用二分查找的方法在一个排好序的数组中进行查找的,这两个函数都需要加载头文件#include<algorithm>
在从小到大的排序数组中,
lower_bound( begin,end,num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
upper_bound( begin,end,num):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个大于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
在从大到小的排序数组中,重载lower_bound()和upper_bound()
lower_bound( begin,end,num,greater<type>() ):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于或等于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
upper_bound( begin,end,num,greater<type>() ):从数组的begin位置到end-1位置二分查找第一个小于num的数字,找到返回该数字的地址,不存在则返回end。通过返回的地址减去起始地址begin,得到找到数字在数组中的下标。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 //#define DEBUG(x) cerr << #x << "=" << x << endl 8 #define LL long long 9 const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; 10 const int INF = 2 * int(1e9) + 10; 11 12 int cmd(int a, int b) 13 { 14 return a > b; 15 } 16 17 int main() 18 { 19 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 20 cin.tie(0); 21 int num[6] = {1, 2, 4, 7, 15, 34}; 22 sort(num, num + 6); //按从小到大排序 23 int pos1 = lower_bound(num, num + 6, 7) - num; //返回数组中第一个大于或等于被查数的值 24 int pos2 = upper_bound(num, num + 6, 7) - num; //返回数组中第一个大于被查数的值 25 cout << pos1 << " " << num[pos1] << endl; 26 cout << pos2 << " " << num[pos2] << endl; 27 sort(num, num + 6, cmd); //按从大到小排序 28 int pos3 = lower_bound(num, num + 6, 7, greater<int>()) - num; //返回数组中第一个小于或等于被查数的值 29 int pos4 = upper_bound(num, num + 6, 7, greater<int>()) - num; //返回数组中第一个小于被查数的值 30 cout << pos3 << " " << num[pos3] << endl; 31 cout << pos4 << " " << num[pos4] << endl; 32 return 0; 33 }