原理
"倒排索引"是文档检索系统中最常用的数据结构,被广泛地应用于全文搜索引擎。它主要是用来存储某个单词(或词组)在一个文档或一组文档中的存储位置的映射,即提供了一种根据内容来查找文档的方式。由于不是根据文档来确定文档所包含的内容,而是进行相反的操作,因而称为倒排索引(Inverted Index)。
实现"倒排索引"主要关注的信息为:单词、文档URL及词频。
下面以本实验goods3、goods_visit3、order_items3三张表的数据为例,根据MapReduce的处理过程给出倒排索引的设计思路:
(1)Map过程
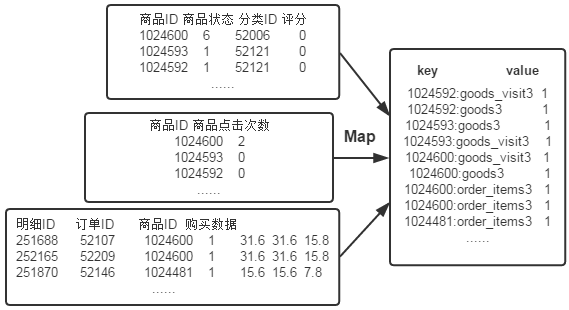
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容。显然,Map过程首先必须分析输入的<key,value>对,得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档URL和词频,接着我们对读入的数据利用Map操作进行预处理,如下图所示:
这里存在两个问题:第一,<key,value>对只能有两个值,在不使用Hadoop自定义数据类型的情况下,需要根据情况将其中两个值合并成一个值,作为key或value值。第二,通过一个Reduce过程无法同时完成词频统计和生成文档列表,所以必须增加一个Combine过程完成词频统计。
这里将商品ID和URL组成key值(如"1024600:goods3"),将词频(商品ID出现次数)作为value,这样做的好处是可以利用MapReduce框架自带的Map端排序,将同一文档的相同单词的词频组成列表,传递给Combine过程,实现类似于WordCount的功能。
(2)Combine过程
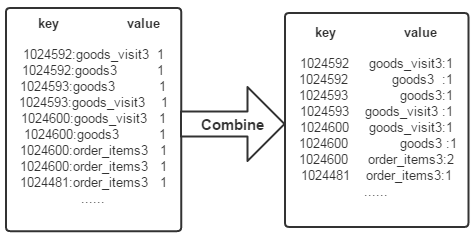
经过map方法处理后,Combine过程将key值相同的value值累加,得到一个单词在文档中的词频,如下图所示。如果直接将下图所示的输出作为Reduce过程的输入,在Shuffle过程时将面临一个问题:所有具有相同单词的记录(由单词、URL和词频组成)应该交由同一个Reducer处理,但当前的key值无法保证这一点,所以必须修改key值和value值。这次将单词(商品ID)作为key值,URL和词频组成value值(如"goods3:1")。这样做的好处是可以利用MapReduce框架默认的HashPartitioner类完成Shuffle过程,将相同单词的所有记录发送给同一个Reducer进行处理。
(3)Reduce过程
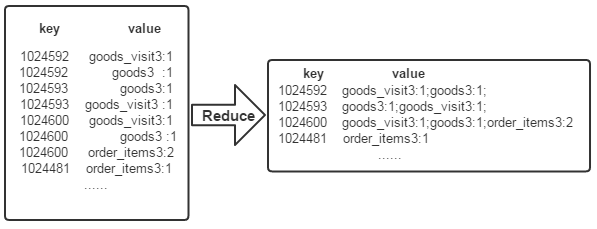
经过上述两个过程后,Reduce过程只需将相同key值的所有value值组合成倒排索引文件所需的格式即可,剩下的事情就可以直接交给MapReduce框架进行处理了。如下图所示
环境
Linux Ubuntu 14.04
jdk-7u75-linux-x64
hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.4.5
hadoop-2.6.0-eclipse-cdh5.4.5.jar
eclipse-java-juno-SR2-linux-gtk-x86_64
内容
现有某电商网站的3张信息数据表,分别为商品库表goods3,商品访问情况表goods_visit3,订单明细表order_items3,goods表记录了商品的状态数据,goods_visit3记录了商品的点击情况,order_items3记录了用户购买的商品的信息数据,它们的表结构及内容如下:
goods3(goods_id,goods_status,cat_id,goods_score)
-
商品ID 商品状态 分类ID 评分
-
1024600 6 52006 0
-
1024593 1 52121 0
-
1024592 1 52121 0
-
1024590 1 52119 0
-
1024589 1 52119 0
-
1024588 1 52030 0
-
1024587 1 52021 0
-
1024586 1 52029 0
-
1024585 1 52014 0
-
1024584 1 52029 0
goods_visit3(goods_id,click_num)
-
商品ID 商品点击次数
-
1024600 2
-
1024593 0
-
1024592 0
-
1024590 0
-
1024589 0
-
1024588 0
-
1024587 0
-
1024586 0
-
1024585 0
-
1024584 0
order_items3(item_id,order_id,goods_id,goods_number,shop_price,goods_price,goods_amount)
-
明细ID 订单ID 商品ID 购买数据 商品销售价格 商品最终单价 商品金额
-
251688 52107 1024600 1 31.6 31.6 15.8
-
252165 52209 1024600 1 31.6 31.6 15.8
-
251870 52146 1024481 1 15.6 15.6 7.8
-
251935 52158 1024481 1 15.6 15.6 7.8
-
252415 52264 1024480 1 69.0 69.0 69.0
-
250983 51937 1024480 1 69.0 69.0 69.0
-
252609 52299 1024480 1 69.0 69.0 69.0
-
251689 52107 1024440 1 31.6 31.6 15.8
-
239369 49183 1024256 1 759.0 759.0 759.0
-
249222 51513 1024140 1 198.0 198.0 198.0
想要查询goods_id相同的商品都在哪几张表并统计出现了多少次。
实验结果如下:
-
商品id 所在表名称:出现次数
-
1024140 order_items3:1;
-
1024256 order_items3:1;
-
1024440 order_items3:1;
-
1024480 order_items3:3;
-
1024481 order_items3:2;
-
1024584 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024585 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024586 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024587 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024588 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024589 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024590 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024592 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024593 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024600 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;order_items3:2;
实验步骤
1.切换到/apps/hadoop/sbin目录下,开启Hadoop。
-
cd /apps/hadoop/sbin
-
./start-all.sh
2.在Linux本地新建/data/mapreduce9目录。
-
mkdir -p /data/mapreduce9
3.在Linux中切换到/data/mapreduce9目录下,用wget命令从http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/goods3、http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/goods_visit3和http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/order_items3网址上下载文本文件goods3,goods_visit3,order_items3。
-
cd /data/mapreduce9
-
wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/goods3
-
wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/goods_visit3
-
wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/order_items3
然后在当前目录下用wget命令从http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/hadoop2lib.tar.gz网址上下载项目用到的依赖包。
-
wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce9/hadoop2lib.tar.gz
将hadoop2lib.tar.gz解压到当前目录下。
-
tar zxvf hadoop2lib.tar.gz
4.首先在HDFS上新建/mymapreduce9/in目录,然后将Linux本地/data/mapreduce9目录下的goods3,goods_visit3和order_items3文件导入到HDFS的/mymapreduce9/in目录中。
-
hadoop fs -mkdir -p /mymapreduce9/in
-
hadoop fs -put /data/mapreduce9/goods3 /mymapreduce9/in
-
hadoop fs -put /data/mapreduce9/goods_visit3 /mymapreduce9/in
-
hadoop fs -put /data/mapreduce9/order_items3 /mymapreduce9/in
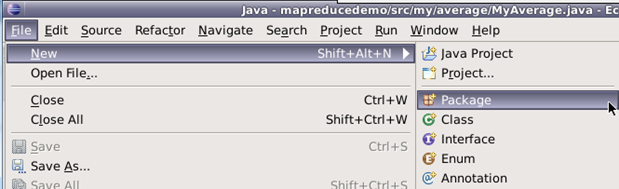
5.新建Java Project项目,项目名为mapreduce9。
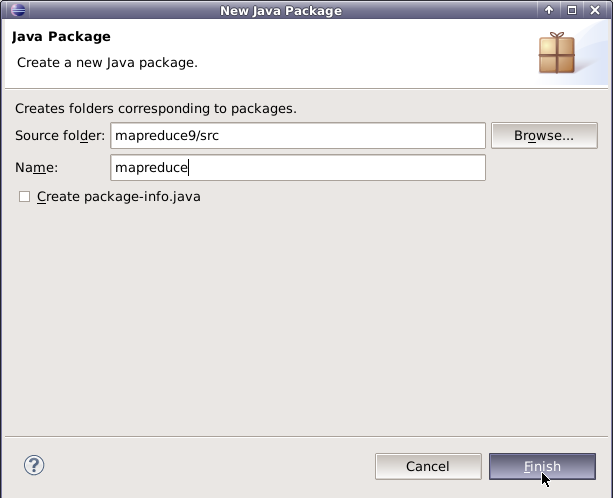
在mapreduce9项目下新建包,包名为mapreduce。
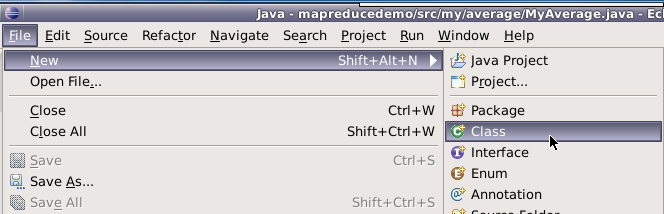
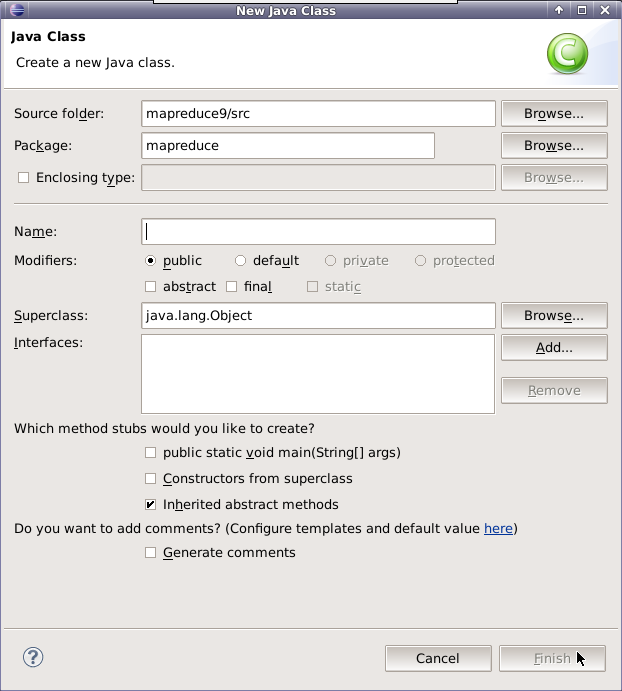
在mapreduce包下新建类,类名为MyIndex。
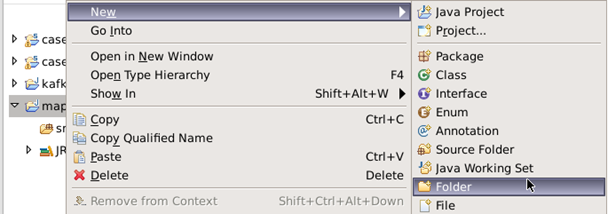
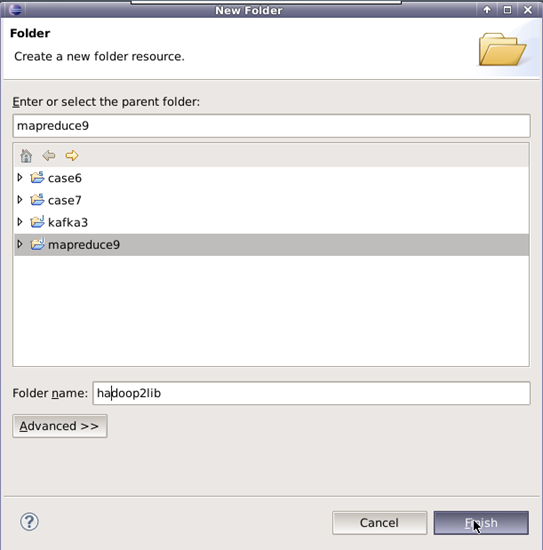
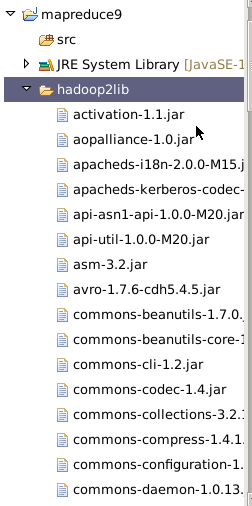
6.添加项目所需的jar包,右键单击项目名,新建一个文件夹,名为hadoop2lib,用于存放项目所需的jar包。
将/data/mapreduce9目录下,hadoop2lib目录中的jar包,拷贝到eclipse中mapreduce9项目的hadoop2lib目录下。
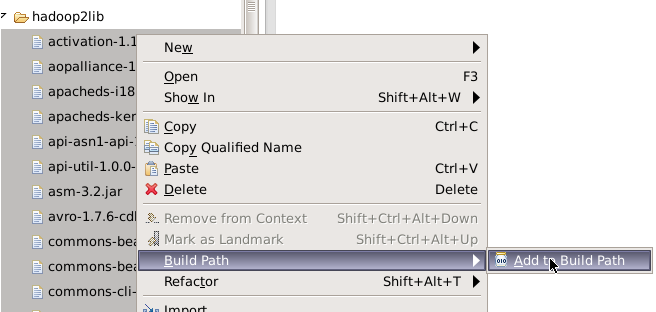
选中所有项目hadoop2lib目录下所有jar包,单击右键选择Build Path=>Add to Build Path。
7.编写Java代码,并描述其设计思路
Map代码
首先使用默认的TextInputFormat类对输入文件进行处理,得到文本中每行的偏移量及其内容。显然,Map过程首先必须分析输入的<key,value>对,得到倒排索引中需要的三个信息:单词、文档URL和词频,这里存在两个问题:第一,<key,value>对只能有两个值,在不使用Hadoop自定义数据类型的情况下,需要根据情况将其中两个值合并成一个值,作为key或value值。第二,通过一个Reduce过程无法同时完成词频统计和生成文档列表,所以必须增加一个Combine过程完成词频统计。
-
public static class doMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text>{
-
public static Text myKey = new Text(); // 存储单词和URL组合
-
public static Text myValue = new Text(); // 存储词频
-
//private FileSplit filePath; // 存储Split对象
-
-
@Override // 实现map函数
-
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
String filePath=((FileSplit)context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString();
-
if(filePath.contains("goods")){
-
String val[]=value.toString().split(" ");
-
int splitIndex =filePath.indexOf("goods");
-
myKey.set(val[0] + ":" + filePath.substring(splitIndex));
-
}else if(filePath.contains("order")){
-
String val[]=value.toString().split(" ");
-
int splitIndex =filePath.indexOf("order");
-
myKey.set(val[2] + ":" + filePath.substring(splitIndex));
-
}
-
myValue.set("1");
-
context.write(myKey, myValue);
-
}
-
}
Combiner代码
经过map方法处理后,Combine过程将key值相同的value值累加,得到一个单词在文档中的词频。如果直接将输出作为Reduce过程的输入,在Shuffle过程时将面临一个问题:所有具有相同单词的记录(由单词、URL和词频组成)应该交由同一个Reducer处理,但当前的key值无法保证这一点,所以必须修改key值和value值。这次将单词作为key值,URL和词频组成value值。这样做的好处是可以利用MapReduce框架默认的HashPartitioner类完成Shuffle过程,将相同单词的所有记录发送给同一个Reducer进行处理。
-
public static class doCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
-
public static Text myK = new Text();
-
public static Text myV = new Text();
-
-
@Override //实现reduce函数
-
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
// 统计词频
-
int sum = 0 ;
-
for (Text value : values) {
-
sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString());
-
}
-
int mysplit = key.toString().indexOf(":");
-
// 重新设置value值由URL和词频组成
-
myK.set(key.toString().substring(0, mysplit));
-
myV.set(key.toString().substring(mysplit + 1) + ":" + sum);
-
context.write(myK, myV);
-
}
-
}
Reduce代码
经过上述两个过程后,Reduce过程只需将相同key值的value值组合成倒排索引文件所需的格式即可,剩下的事情就可以直接交给MapReduce框架进行处理了。
-
public static class doReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
-
-
public static Text myK = new Text();
-
public static Text myV = new Text();
-
-
@Override // 实现reduce函数
-
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
// 生成文档列表
-
String myList = new String();
-
-
for (Text value : values) {
-
myList += value.toString() + ";";
-
}
-
myK.set(key);
-
myV.set(myList);
-
context.write(myK, myV);
-
}
-
}
完整代码
-
package mapreduce;
-
import java.io.IOException;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
-
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
-
public class MyIndex {
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
-
Job job = Job.getInstance();
-
job.setJobName("InversedIndexTest");
-
job.setJarByClass(MyIndex.class);
-
-
job.setMapperClass(doMapper.class);
-
job.setCombinerClass(doCombiner.class);
-
job.setReducerClass(doReducer.class);
-
-
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
-
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
-
-
Path in1 = new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce9/in/goods3");
-
Path in2 = new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce9/in/goods_visit3");
-
Path in3 = new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce9/in/order_items3");
-
Path out = new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce9/out");
-
-
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, in1);
-
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, in2);
-
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, in3);
-
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, out);
-
-
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
-
}
-
-
public static class doMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text>{
-
public static Text myKey = new Text();
-
public static Text myValue = new Text();
-
//private FileSplit filePath;
-
-
@Override
-
protected void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
String filePath=((FileSplit)context.getInputSplit()).getPath().toString();
-
if(filePath.contains("goods")){
-
String val[]=value.toString().split(" ");
-
int splitIndex =filePath.indexOf("goods");
-
myKey.set(val[0] + ":" + filePath.substring(splitIndex));
-
}else if(filePath.contains("order")){
-
String val[]=value.toString().split(" ");
-
int splitIndex =filePath.indexOf("order");
-
myKey.set(val[2] + ":" + filePath.substring(splitIndex));
-
}
-
myValue.set("1");
-
context.write(myKey, myValue);
-
}
-
}
-
public static class doCombiner extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
-
public static Text myK = new Text();
-
public static Text myV = new Text();
-
-
@Override
-
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
int sum = 0 ;
-
for (Text value : values) {
-
sum += Integer.parseInt(value.toString());
-
}
-
int mysplit = key.toString().indexOf(":");
-
myK.set(key.toString().substring(0, mysplit));
-
myV.set(key.toString().substring(mysplit + 1) + ":" + sum);
-
context.write(myK, myV);
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static class doReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
-
-
public static Text myK = new Text();
-
public static Text myV = new Text();
-
-
@Override
-
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
-
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
-
-
String myList = new String();
-
-
for (Text value : values) {
-
myList += value.toString() + ";";
-
}
-
myK.set(key);
-
myV.set(myList);
-
context.write(myK, myV);
-
}
-
}
-
}
8.在MyIndex类文件中,右键并点击=>Run As=>Run on Hadoop选项,将MapReduce任务提交到Hadoop中。
9.待执行完毕后,进入命令模式下,在hdfs上从Java代码指定的路径中查看实验结果。
-
hadoop fs -ls /mymapreduce9/out
-
hadoop fs -cat /mymapreduce9/out/part-r-00000
实验结果如下图:
-
商品id 所在表名称:出现次数
-
1024140 order_items3:1;
-
1024256 order_items3:1;
-
1024440 order_items3:1;
-
1024480 order_items3:3;
-
1024481 order_items3:2;
-
1024584 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024585 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024586 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024587 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024588 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024589 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024590 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024592 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;
-
1024593 goods3:1;goods_visit3:1;
-
1024600 goods_visit3:1;goods3:1;order_items3:2;