博客地址:https://ainyi.com/77
企业运营后台页面很多,路由如若不区分模块化配置,所有路由挤在同一个文件将不好维护,所以路由的配置也要模块化
分享两个解决方案 —— Vue 路由配置的模块化(Plan A and Plan B)
注册需要
首先路由注册需要啥
// main.js
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
// 这里的 router 是这样的
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [],
... // 其他配置
})
也就是说注册需要 new 一个 Router 实例,实例里的 routes 是数组,里面配置每个页面的路由
模块拆分(Plan A)
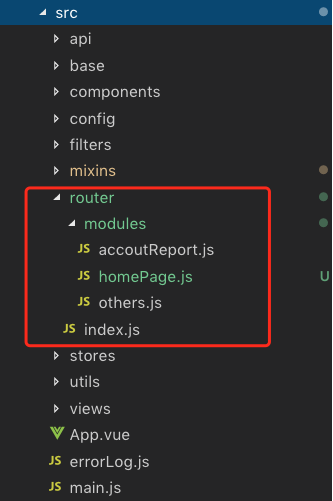
src 下 router 的目录结构
---src
----router
------modules
--------xxxx.js // 模块 xxx
--------other.js // 模块 other
------index.js // 路由配置入口和出口 index
例如
然后配置 modules 里面模块路由
// 配置 other
import err from '@/views/others/Error.vue'
export default function(router) {
router.push({
path: '/error',
name: 'error',
component: err
})
}
// 配置 accoutReport
export default function(router) {
router.push({
path: '/accout-report',
redirect: '/accout-report/list'
})
// 列表
router.push({
path: '/accout-report/list',
name: 'list',
component: () => import('@/views/accoutReport/List.vue')
})
// 新增
router.push({
path: '/accout-report/create',
name: 'create',
component: () => import('@/views/accoutReport/Create.vue')
})
// 编辑
router.push({
path: '/accout-report/edit/:id',
name: 'edit',
component: () => import('@/views/accoutReport/steps/CreateStep2.vue')
})
// 详情
router.push({
path: '/accout-report/detail/:id',
name: 'detail',
component: () => import('@/views/accoutReport/Detail.vue')
})
}
如有其他模块,依次像上面一样配置
关键是路由配置入口出口文件 index.js
// index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import App from '@/views/Layouts.vue'
import otherRouter from '@/router/modules/others'
import accoutReport from '@/router/modules/accoutReport'
// import store from '@/stores'
Vue.use(Router)
let routes = []
let rootRouter = {
path: '/',
component: App,
children: [],
redirect: '/accout-report/list'
}
let redirectRouter = {
path: '*',
redirect: '/error'
}
otherRouter(rootRouter.children)
accoutReport(rootRouter.children)
// 如有多个模块,依次在这里配置
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: routes.concat([rootRouter, redirectRouter])
})
export default router
上述代码,除了 other,所有页面路由配置在 rootRouter 的 children 下面,有一个父级 router 包裹着
代码都看得懂,这里就不多说哈~
最后在 main.js 中注册
模块拆分(Plan B)
该方法较为难懂一些,可以看看
目录结构跟 Plan A 类似,不过在 src 下多了一个 router.js 配置文件作为路由出口文件
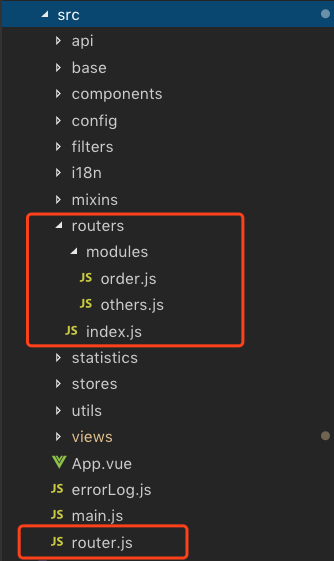
src 下 router 的目录结构
---src
----router
------modules
--------xxxx.js // 模块 xxx
--------other.js // 模块 other
------index.js // 路由配置中转文件
----router.js // 路由配置出口文件
例如
模块 modules 里文件配置
// order.js
import { getFindBusinessServiceList } from '@/utils/config-utils'
const OrderRouter = [
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/cost/order-list'
},
{
path: '/cost',
component: () => import('@/views/Layouts'),
redirect: '/cost/order-list',
children: [
{
path: 'order-list',
component: () => import('@/views/orderManagement/List'),
beforeEnter: async (to, from, next) => {
await getFindBusinessServiceList() // 进入该路由前异步请求,结束后进入该路由
next()
}
},
{
path: 'order-detail',
component: () => import('@/views/orderManagement/Detail')
},
// 下面是重定向,可不配置
{
path: 'orderDetail',
redirect: 'order-detail'
},
{
path: 'order',
redirect: 'order-list'
}
]
}
]
export default OrderRouter
上述路由配置在 Layouts 路由下的 children
接下来关键,路由配置中转文件 index.js
遍历 modules 文件夹下的每个模块文件,赋值和导出
// index.js
import { camelCase } from 'lodash-es'
const requiredModules = require.context('./modules', false, /.js$/)
const routers = {}
requiredModules.keys().forEach(fileName => {
// 不加载index.js
if (fileName === './index.js') return
// 转为驼峰命名
const moduleName = camelCase(fileName.replace(/(./|.js)/g, ''))
routers[moduleName] =
requiredModules(fileName).default || requiredModules(fileName)
})
export default routers
然后在 src 下的出口文件 router.js 包装
// router.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import routers from '@/routers/index'
Vue.use(Router)
let routes = []
Object.values(routers).forEach(router => {
routes.push(...router)
})
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes
})
最后在 main.js 中注册
博客地址:https://ainyi.com/77