文字描述
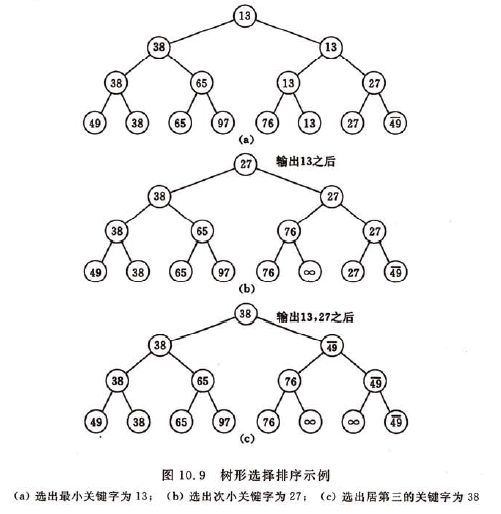
树形选择排序又称锦标赛排序; 比如,在8个运动员中决出前3名至多需要11场比赛, 而不是7+6+5=18场比赛(它的前提是甲胜乙,乙胜丙,则甲必能胜丙)
首先对n个记录的关键字进行两两比较,然后在(n/2)个较小者之间再进行两两比较,直至选出最小关键字的记录为止,这个过程可用一颗有n个叶子结点的完全二叉树表示。关于完全二叉树的定义和与本排序算法用到的性质见附录1
示意图
算法分析
由于含n个叶子结点的完全二叉树的深度为[log2n]+1, 则在树形选择排序中,除了最小关键字外,每选择一个次小关键字仅需进行log2n次比较,因此它的时间复杂度为nlogn.。但是它需要的辅助空间为2*n-1。而且它在选择过程中,和"最大值"进行了多余的比较。 另外,该算法是不稳定的。
代码实现

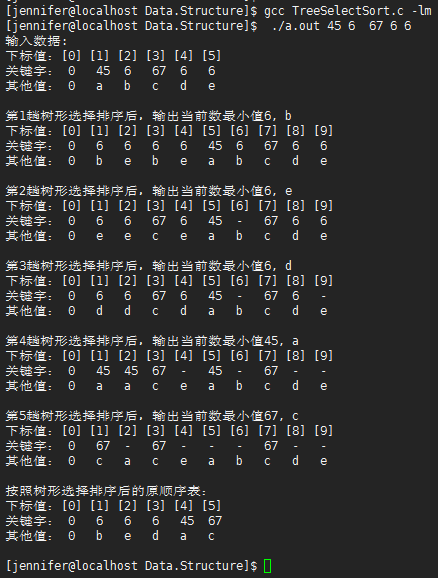
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <math.h> 4 /* 5 * double log2(double x); 以2为底的对数 6 * double ceil(double x); 取上整 7 * double floor(double x); 取下整 8 * double fabs(double x); 取绝对值 9 */ 10 11 #define DEBUG 12 13 #define EQ(a, b) ((a) == (b)) 14 #define LT(a, b) ((a) < (b)) 15 #define LQ(a, b) ((a) <= (b)) 16 17 #define MAXSIZE 100 18 #define INF 1000000 19 typedef int KeyType; 20 typedef char InfoType; 21 typedef struct{ 22 KeyType key; 23 InfoType otherinfo; 24 }RedType; 25 26 typedef struct{ 27 RedType r[MAXSIZE+1]; 28 int length; 29 }SqList; 30 31 void PrintList(SqList L){ 32 int i = 0; 33 printf("下标值:"); 34 for(i=0; i<=L.length; i++){ 35 printf("[%d] ", i); 36 } 37 printf(" 关键字:"); 38 for(i=0; i<=L.length; i++){ 39 if(EQ(L.r[i].key, INF)){ 40 printf(" %-3c", '-'); 41 }else{ 42 printf(" %-3d", L.r[i].key); 43 } 44 } 45 printf(" 其他值:"); 46 for(i=0; i<=L.length; i++){ 47 printf(" %-3c", L.r[i].otherinfo); 48 } 49 printf(" "); 50 return ; 51 } 52 53 /*树形选择排序算法*/ 54 void TreeSelectSort(SqList *L) 55 { 56 //为实现该排序所需的辅助树 57 SqList tree; 58 //辅助树的大小 59 tree.length = L->length-1 + L->length; 60 61 tree.r[0].otherinfo = '0'; 62 int i = 0, low = 1; 63 //由后向前填充此树的叶子结点 64 for(i=0; i<L->length; i++){ 65 tree.r[tree.length-i] = L->r[L->length-i]; 66 } 67 //由后向前填充此树的非叶子结点 68 for(i=(tree.length-L->length); i>=1; i--){ 69 tree.r[i] = (LT(tree.r[2*i].key, tree.r[2*i+1].key)?tree.r[2*i]:tree.r[2*i+1]); 70 } 71 //纪录当前辅助树的最小结点 72 RedType minred; 73 //记录最小结点在叶子结点中的下标值 74 int minindex = 0; 75 while(low <= L->length){ 76 minred = tree.r[1]; 77 #ifdef DEBUG 78 printf("第%d趟树形选择排序后,输出当前数最小值%d, %c ", low, minred.key, minred.otherinfo); 79 PrintList(tree); 80 #endif 81 //不断移走最小结点 82 L->r[low++] = minred; 83 minindex = tree.length; 84 //找到最小值在辅助树叶子结点中的下标值 85 for(minindex=tree.length; (minindex>(tree.length-L->length)); minindex--){ 86 if(EQ(tree.r[minindex].key, minred.key) && EQ(tree.r[minindex].otherinfo, minred.otherinfo)){ 87 break; 88 } 89 } 90 //设置一个最大值标志,INF表示无穷大 91 tree.r[minindex].key = INF; 92 //重新调整此辅助树,使根结点关键字值最小 93 for(i=(minindex/2); i>=1; i/=2){ 94 tree.r[i] = (LT(tree.r[2*i].key, tree.r[2*i+1].key)?tree.r[2*i]:tree.r[2*i+1]); 95 } 96 } 97 #ifdef DEBUG 98 printf("按照树形选择排序后的原顺序表: "); 99 PrintList(*L); 100 #endif 101 } 102 103 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 104 { 105 if(argc < 2){ 106 return -1; 107 } 108 SqList L; 109 int i = 0; 110 for(i=1; i<argc; i++){ 111 if(i>MAXSIZE) 112 break; 113 L.r[i].key = atoi(argv[i]); 114 L.r[i].otherinfo = 'a'+i-1; 115 } 116 L.length = (i-1); 117 L.r[0].key = 0; 118 L.r[0].otherinfo = '0'; 119 printf("输入数据: "); 120 PrintList(L); 121 //对顺序表L作树形选择排序 122 TreeSelectSort(&L); 123 return 0; 124 }
运行
附录1 完全二叉树
定义:设二叉树深度为h,除第h层外,其他各层(1 ~ h-1)的结点数都达到最大个数,第h层所有的结点都集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
性质:
1] 结点i (i>1)的双亲结点为i/2
2] 结点i的左孩子结点为2*i, 右孩子结点为2*i+1
3] 叶子结点数n0, 度为2(有左、右孩子结点)的结点数n2, 则n0 = n2+1
性质3]证明:
设n1为二叉树中度为1的结点数。因为二叉树中所有结点数的度均不大于2。所以二叉树的结点数n = n0 + n1 +n2 -- (1)。
又除根结点外,其余结点都有一个分支进入,设B为分支总数,则n=B+1。由于这些分支是由度为1或2的结点射出的,所以又有B=n1+2*n2,于是得n = B+1 = n1+2*n2+1 – (2)。
由(1)和(2)知, n0 = n2 +1
