一、函数模板
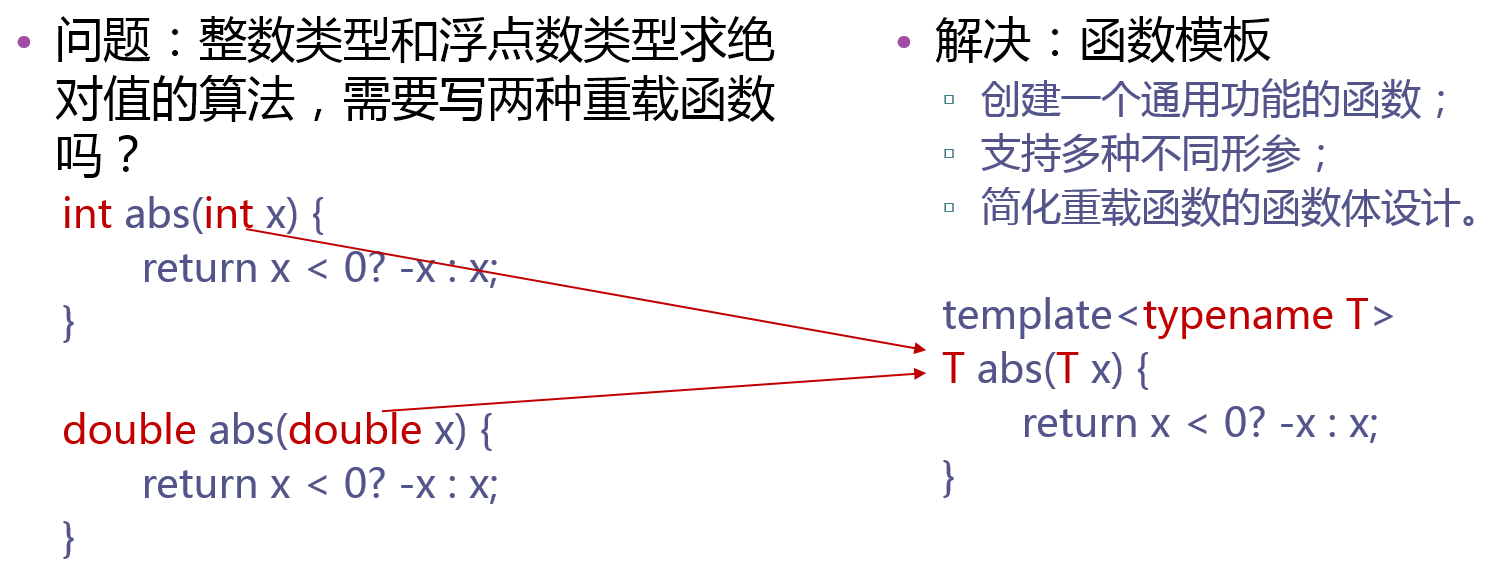
我们可能会遇到功能相同,但参数不同,而不得不写大量重载函数,如求绝对值,根据参数是整数还是浮点数而重载函数。
这不仅会导致冗余,如果修改算法时,没有各个函数体中同步修改,会造成在同一个系统中,处理同类型的问题,用的算法不一致。
解决:使用模板
求绝对值问题
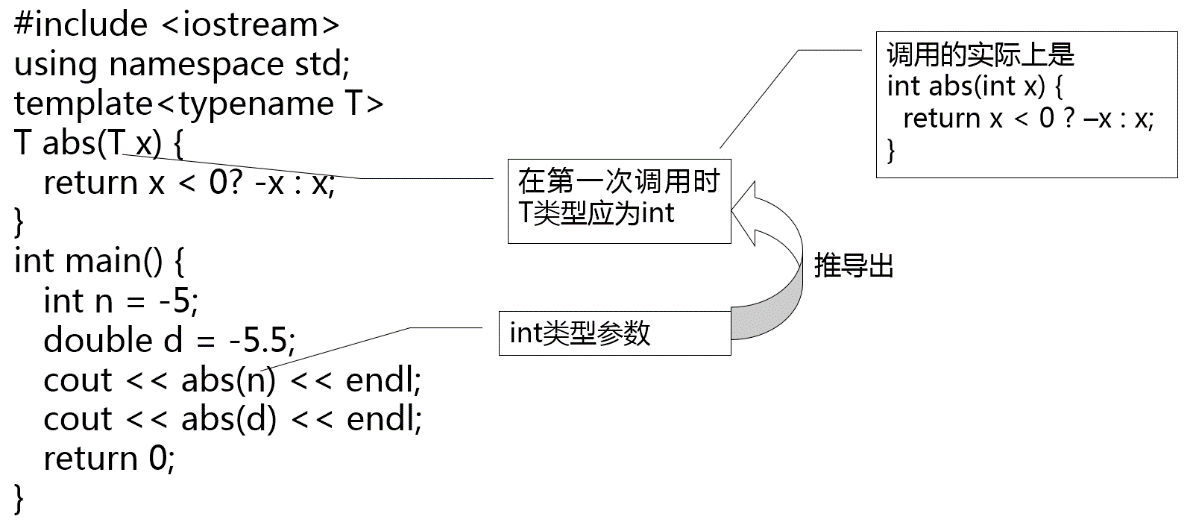
语法:
template <模板参数表>
函数定义
模板参数表的内容
- 类型参数:class(或typename) 标识符
- 常量参数:类型说明符 标识符
- 模板参数:template <参数表> class标识符
//9_1.cpp #include <iostream> using namespace std; template <class T> //定义函数模板 void outputArray(const T *array, int count) { for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) cout << array[i] << " "; //如果数组元素是类的对象,需要该对象所属类重载了流插入运算符“<<” cout << endl; } int main() { const int A_COUNT = 8, B_COUNT = 8, C_COUNT = 20; int a [A_COUNT] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; double b[B_COUNT] = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8 }; char c[C_COUNT] = "Welcome!"; cout << " a array contains:" << endl; outputArray(a, A_COUNT); cout << " b array contains:" << endl; outputArray(b, B_COUNT); cout << " c array contains:" << endl; outputArray(c, C_COUNT); return 0; } 运行结果如下: a array contains: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 b array contains: 1.1 2.2 3.3 4.4 5.5 6.6 7.7 8.8 c array contains: W e l c o m e!
注意
- 一个函数模板并非自动可以处理所有类型的数据
- 只有能够进行函数模板中运算的类型,可以作为类型实参
- 自定义的类,需要重载模板中的运算符,才能作为类型实参
二、类模板
作用
使用类模板使用户可以为类声明一种模式,使得类中的某些数据成员、某些成员函数的参数、某些成员函数的返回值,能取任意类型(包括基本类型的和用户自定义类型)。
声明
- 类模板
-
template <模板参数表> class 类名 {类成员声明};
-
- 如果需要在类模板以外定义其成员函数,则要采用以下的形式
-
template <模板参数表> 类型名 类名<模板参数标识符列表>::函数名(参数表)
-
示例
#include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; struct Student { int id; //学号 float gpa; //平均分 }; template <class T> class Store {//类模板:实现对任意类型数据进行存取 private: T item; // item用于存放任意类型的数据 bool haveValue; // haveValue标记item是否已被存入内容 public: Store(); T &getElem(); //提取数据函数 void putElem(const T &x); //存入数据函数 }; template <class T> Store<T>::Store(): haveValue(false) { } template <class T> T &Store<T>::getElem() { //如试图提取未初始化的数据,则终止程序 if (!haveValue) { cout << "No item present!" << endl; exit(1); //使程序完全退出,返回到操作系统。 } return item; // 返回item中存放的数据 } template <class T> void Store<T>::putElem(const T &x) { // 将haveValue 置为true,表示item中已存入数值 haveValue = true; item = x; // 将x值存入item } int main() { Store<int> s1, s2; s1.putElem(3); s2.putElem(-7); cout << s1.getElem() << " " << s2.getElem() << endl; Student g = { 1000, 23 }; Store<Student> s3; s3.putElem(g); cout << "The student id is " << s3.getElem().id << endl; Store<double> d; cout << "Retrieving object D... "; cout << d.getElem() << endl; //d未初始化,执行函数D.getElement()时导致程序终止 return 0; }