LinkedHashMap 简介
LinkedHashMap数据结构
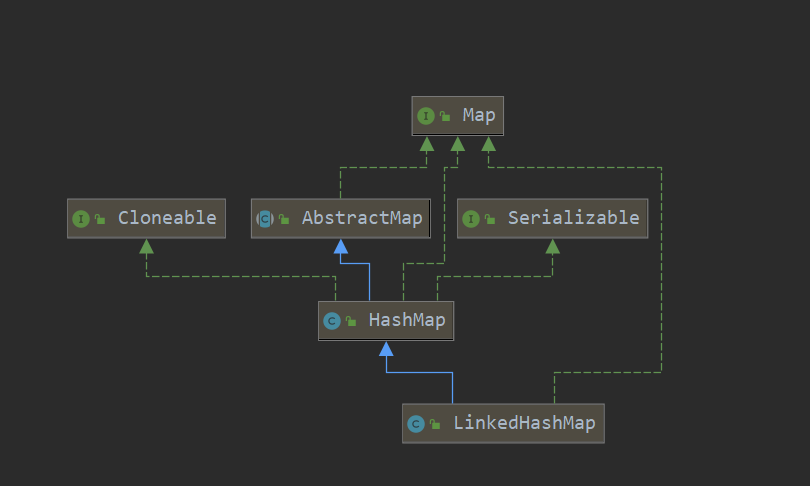
LinkedHashMap UML
LinkedHashMap API
LinkedHashMap 源码
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* <p>Hash table and linked list implementation of the <tt>Map</tt> interface,
* with predictable iteration order. This implementation differs from
* <tt>HashMap</tt> in that it maintains a doubly-linked list running through
* all of its entries. This linked list defines the iteration ordering,
* which is normally the order in which keys were inserted into the map
* (<i>insertion-order</i>). Note that insertion order is not affected
* if a key is <i>re-inserted</i> into the map. (A key <tt>k</tt> is
* reinserted into a map <tt>m</tt> if <tt>m.put(k, v)</tt> is invoked when
* <tt>m.containsKey(k)</tt> would return <tt>true</tt> immediately prior to
* the invocation.)
*
* <p>This implementation spares its clients from the unspecified, generally
* chaotic ordering provided by {@link HashMap} (and {@link Hashtable}),
* without incurring the increased cost associated with {@link TreeMap}. It
* can be used to produce a copy of a map that has the same order as the
* original, regardless of the original map's implementation:
* <pre>
* void foo(Map m) {
* Map copy = new LinkedHashMap(m);
* ...
* }
* </pre>
* This technique is particularly useful if a module takes a map on input,
* copies it, and later returns results whose order is determined by that of
* the copy. (Clients generally appreciate having things returned in the same
* order they were presented.)
*
* <p>A special {@link #LinkedHashMap(int,float,boolean) constructor} is
* provided to create a linked hash map whose order of iteration is the order
* in which its entries were last accessed, from least-recently accessed to
* most-recently (<i>access-order</i>). This kind of map is well-suited to
* building LRU caches. Invoking the {@code put}, {@code putIfAbsent},
* {@code get}, {@code getOrDefault}, {@code compute}, {@code computeIfAbsent},
* {@code computeIfPresent}, or {@code merge} methods results
* in an access to the corresponding entry (assuming it exists after the
* invocation completes). The {@code replace} methods only result in an access
* of the entry if the value is replaced. The {@code putAll} method generates one
* entry access for each mapping in the specified map, in the order that
* key-value mappings are provided by the specified map's entry set iterator.
* <i>No other methods generate entry accesses.</i> In particular, operations
* on collection-views do <i>not</i> affect the order of iteration of the
* backing map.
*
* <p>The {@link #removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry)} method may be overridden to
* impose a policy for removing stale mappings automatically when new mappings
* are added to the map.
*
* <p>This class provides all of the optional <tt>Map</tt> operations, and
* permits null elements. Like <tt>HashMap</tt>, it provides constant-time
* performance for the basic operations (<tt>add</tt>, <tt>contains</tt> and
* <tt>remove</tt>), assuming the hash function disperses elements
* properly among the buckets. Performance is likely to be just slightly
* below that of <tt>HashMap</tt>, due to the added expense of maintaining the
* linked list, with one exception: Iteration over the collection-views
* of a <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> requires time proportional to the <i>size</i>
* of the map, regardless of its capacity. Iteration over a <tt>HashMap</tt>
* is likely to be more expensive, requiring time proportional to its
* <i>capacity</i>.
*
* <p>A linked hash map has two parameters that affect its performance:
* <i>initial capacity</i> and <i>load factor</i>. They are defined precisely
* as for <tt>HashMap</tt>. Note, however, that the penalty for choosing an
* excessively high value for initial capacity is less severe for this class
* than for <tt>HashMap</tt>, as iteration times for this class are unaffected
* by capacity.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access a linked hash map concurrently, and at least
* one of the threads modifies the map structurally, it <em>must</em> be
* synchronized externally. This is typically accomplished by
* synchronizing on some object that naturally encapsulates the map.
*
* If no such object exists, the map should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedMap Collections.synchronizedMap}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the map:<pre>
* Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap(...));</pre>
*
* A structural modification is any operation that adds or deletes one or more
* mappings or, in the case of access-ordered linked hash maps, affects
* iteration order. In insertion-ordered linked hash maps, merely changing
* the value associated with a key that is already contained in the map is not
* a structural modification. <strong>In access-ordered linked hash maps,
* merely querying the map with <tt>get</tt> is a structural modification.
* </strong>)
*
* <p>The iterators returned by the <tt>iterator</tt> method of the collections
* returned by all of this class's collection view methods are
* <em>fail-fast</em>: if the map is structurally modified at any time after
* the iterator is created, in any way except through the iterator's own
* <tt>remove</tt> method, the iterator will throw a {@link
* ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of concurrent
* modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather than risking
* arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw <tt>ConcurrentModificationException</tt> on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>The spliterators returned by the spliterator method of the collections
* returned by all of this class's collection view methods are
* <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>,
* <em>fail-fast</em>, and additionally report {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}.
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @implNote
* The spliterators returned by the spliterator method of the collections
* returned by all of this class's collection view methods are created from
* the iterators of the corresponding collections.
*
* @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map
* @param <V> the type of mapped values
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see Object#hashCode()
* @see Collection
* @see Map
* @see HashMap
* @see TreeMap
* @see Hashtable
* @since 1.4
*/
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
/*
* Implementation note. A previous version of this class was
* internally structured a little differently. Because superclass
* HashMap now uses trees for some of its nodes, class
* LinkedHashMap.Entry is now treated as intermediary node class
* that can also be converted to tree form. The name of this
* class, LinkedHashMap.Entry, is confusing in several ways in its
* current context, but cannot be changed. Otherwise, even though
* it is not exported outside this package, some existing source
* code is known to have relied on a symbol resolution corner case
* rule in calls to removeEldestEntry that suppressed compilation
* errors due to ambiguous usages. So, we keep the name to
* preserve unmodified compilability.
*
* The changes in node classes also require using two fields
* (head, tail) rather than a pointer to a header node to maintain
* the doubly-linked before/after list. This class also
* previously used a different style of callback methods upon
* access, insertion, and removal.
*/
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3801124242820219131L;
/**
* The head (eldest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> head;
/**
* The tail (youngest) of the doubly linked list.
*/
transient LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> tail;
/**
* The iteration ordering method for this linked hash map: <tt>true</tt>
* for access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order.
*
* @serial
*/
final boolean accessOrder;
// internal utilities
// link at the end of list
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
// apply src's links to dst
private void transferLinks(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> src,
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> dst) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> b = dst.before = src.before;
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> a = dst.after = src.after;
if (b == null)
head = dst;
else
b.after = dst;
if (a == null)
tail = dst;
else
a.before = dst;
}
// overrides of HashMap hook methods
void reinitialize() {
super.reinitialize();
head = tail = null;
}
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
Node<K,V> replacementNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> q = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)p;
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> t =
new LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next);
transferLinks(q, t);
return t;
}
TreeNode<K,V> newTreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(hash, key, value, next);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
TreeNode<K,V> replacementTreeNode(Node<K,V> p, Node<K,V> next) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> q = (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)p;
TreeNode<K,V> t = new TreeNode<K,V>(q.hash, q.key, q.value, next);
transferLinks(q, t);
return t;
}
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.before = p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a == null)
tail = b;
else
a.before = b;
}
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
void internalWriteEntries(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws IOException {
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
s.writeObject(e.key);
s.writeObject(e.value);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and load factor.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the specified initial capacity and a default load factor (0.75).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance
* with the default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
/**
* Constructs an insertion-ordered <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with
* the same mappings as the specified map. The <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt>
* instance is created with a default load factor (0.75) and an initial
* capacity sufficient to hold the mappings in the specified map.
*
* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null
*/
public LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
super();
accessOrder = false;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty <tt>LinkedHashMap</tt> instance with the
* specified initial capacity, load factor and ordering mode.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity
* @param loadFactor the load factor
* @param accessOrder the ordering mode - <tt>true</tt> for
* access-order, <tt>false</tt> for insertion-order
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is negative
* or the load factor is nonpositive
*/
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
*/
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after) {
V v = e.value;
if (v == value || (value != null && value.equals(v)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>A return value of {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i>
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return defaultValue;
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void clear() {
super.clear();
head = tail = null;
}
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map should remove its eldest entry.
* This method is invoked by <tt>put</tt> and <tt>putAll</tt> after
* inserting a new entry into the map. It provides the implementor
* with the opportunity to remove the eldest entry each time a new one
* is added. This is useful if the map represents a cache: it allows
* the map to reduce memory consumption by deleting stale entries.
*
* <p>Sample use: this override will allow the map to grow up to 100
* entries and then delete the eldest entry each time a new entry is
* added, maintaining a steady state of 100 entries.
* <pre>
* private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 100;
*
* protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
* return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
* }
* </pre>
*
* <p>This method typically does not modify the map in any way,
* instead allowing the map to modify itself as directed by its
* return value. It <i>is</i> permitted for this method to modify
* the map directly, but if it does so, it <i>must</i> return
* <tt>false</tt> (indicating that the map should not attempt any
* further modification). The effects of returning <tt>true</tt>
* after modifying the map from within this method are unspecified.
*
* <p>This implementation merely returns <tt>false</tt> (so that this
* map acts like a normal map - the eldest element is never removed).
*
* @param eldest The least recently inserted entry in the map, or if
* this is an access-ordered map, the least recently accessed
* entry. This is the entry that will be removed it this
* method returns <tt>true</tt>. If the map was empty prior
* to the <tt>put</tt> or <tt>putAll</tt> invocation resulting
* in this invocation, this will be the entry that was just
* inserted; in other words, if the map contains a single
* entry, the eldest entry is also the newest.
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the eldest entry should be removed
* from the map; <tt>false</tt> if it should be retained.
*/
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of
* the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal,
* which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the
* <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>,
* <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt>
* operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt>
* operations.
* Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential
* performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of
* {@code HashMap}.
*
* @return a set view of the keys contained in this map
*/
public Set<K> keySet() {
Set<K> ks = keySet;
if (ks == null) {
ks = new LinkedKeySet();
keySet = ks;
}
return ks;
}
final class LinkedKeySet extends AbstractSet<K> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<K> iterator() {
return new LinkedKeyIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsKey(o); }
public final boolean remove(Object key) {
return removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true) != null;
}
public final Spliterator<K> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED |
Spliterator.ORDERED |
Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super K> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
action.accept(e.key);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
* The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is
* modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress
* (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation),
* the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>,
* <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not
* support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
* Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential
* performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of
* {@code HashMap}.
*
* @return a view of the values contained in this map
*/
public Collection<V> values() {
Collection<V> vs = values;
if (vs == null) {
vs = new LinkedValues();
values = vs;
}
return vs;
}
final class LinkedValues extends AbstractCollection<V> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<V> iterator() {
return new LinkedValueIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) { return containsValue(o); }
public final Spliterator<V> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED |
Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super V> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
action.accept(e.value);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation, or through the
* <tt>setValue</tt> operation on a map entry returned by the
* iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Set.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt> and
* <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not support the
* <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
* Its {@link Spliterator} typically provides faster sequential
* performance but much poorer parallel performance than that of
* {@code HashMap}.
*
* @return a set view of the mappings contained in this map
*/
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new LinkedEntrySet()) : es;
}
final class LinkedEntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { LinkedHashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new LinkedEntryIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
public final boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Object value = e.getValue();
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
return false;
}
public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.SIZED |
Spliterator.ORDERED |
Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
action.accept(e);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
// Map overrides
public void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
action.accept(e.key, e.value);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
if (function == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int mc = modCount;
for (LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = head; e != null; e = e.after)
e.value = function.apply(e.key, e.value);
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
// Iterators
abstract class LinkedHashIterator {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> next;
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> current;
int expectedModCount;
LinkedHashIterator() {
next = head;
expectedModCount = modCount;
current = null;
}
public final boolean hasNext() {
return next != null;
}
final LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> nextNode() {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> e = next;
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
if (e == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
current = e;
next = e.after;
return e;
}
public final void remove() {
Node<K,V> p = current;
if (p == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
current = null;
K key = p.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, false);
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
}
final class LinkedKeyIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<K> {
public final K next() { return nextNode().getKey(); }
}
final class LinkedValueIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<V> {
public final V next() { return nextNode().value; }
}
final class LinkedEntryIterator extends LinkedHashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
}
LinkedHashMap 关键技术
LinkedHashMap 示例
面试session
