1. TreeSet简介
*TreeSet继承了AbstractSet实现了NavigableSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable接口,其中NavigableSet
*
*
*
2. TreeSet 逻辑内存模型
3. TreeSet UML
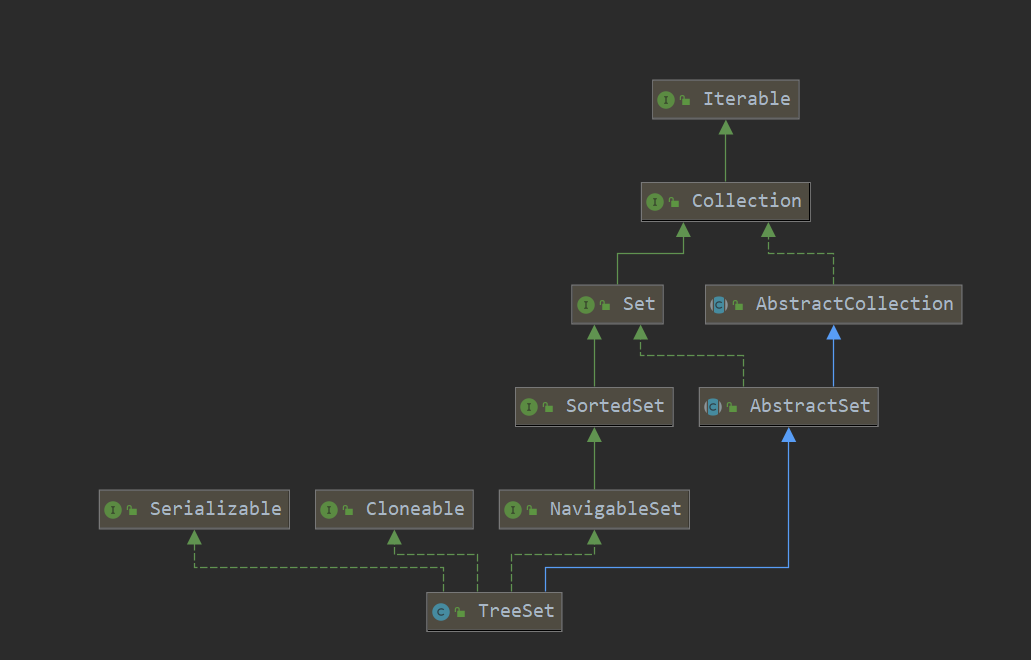
4. TreeSet 源码分析
package java.util;
/**
* A {@link NavigableSet} implementation based on a {@link TreeMap}.
* The elements are ordered using their {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering}, or by a {@link Comparator} provided at set creation
* time, depending on which constructor is used.
*
* <p>This implementation provides guaranteed log(n) time cost for the basic
* operations ({@code add}, {@code remove} and {@code contains}).
*
* <p>Note that the ordering maintained by a set (whether or not an explicit
* comparator is provided) must be <i>consistent with equals</i> if it is to
* correctly implement the {@code Set} interface. (See {@code Comparable}
* or {@code Comparator} for a precise definition of <i>consistent with
* equals</i>.) This is so because the {@code Set} interface is defined in
* terms of the {@code equals} operation, but a {@code TreeSet} instance
* performs all element comparisons using its {@code compareTo} (or
* {@code compare}) method, so two elements that are deemed equal by this method
* are, from the standpoint of the set, equal. The behavior of a set
* <i>is</i> well-defined even if its ordering is inconsistent with equals; it
* just fails to obey the general contract of the {@code Set} interface.
*
* <p><strong>Note that this implementation is not synchronized.</strong>
* If multiple threads access a tree set concurrently, and at least one
* of the threads modifies the set, it <i>must</i> be synchronized
* externally. This is typically accomplished by synchronizing on some
* object that naturally encapsulates the set.
* If no such object exists, the set should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedSortedSet Collections.synchronizedSortedSet}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the set: <pre>
* SortedSet s = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet(...));</pre>
*
* <p>The iterators returned by this class's {@code iterator} method are
* <i>fail-fast</i>: if the set is modified at any time after the iterator is
* created, in any way except through the iterator's own {@code remove}
* method, the iterator will throw a {@link ConcurrentModificationException}.
* Thus, in the face of concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly
* and cleanly, rather than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at
* an undetermined time in the future.
*
* <p>Note that the fail-fast behavior of an iterator cannot be guaranteed
* as it is, generally speaking, impossible to make any hard guarantees in the
* presence of unsynchronized concurrent modification. Fail-fast iterators
* throw {@code ConcurrentModificationException} on a best-effort basis.
* Therefore, it would be wrong to write a program that depended on this
* exception for its correctness: <i>the fail-fast behavior of iterators
* should be used only to detect bugs.</i>
*
* <p>This class is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements maintained by this set
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see Collection
* @see Set
* @see HashSet
* @see Comparable
* @see Comparator
* @see TreeMap
* @since 1.2
*/
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* The backing map.
*/
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
/**
* Constructs a set backed by the specified navigable map.
*/
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the
* natural ordering of its elements. All elements inserted into
* the set must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.
* Furthermore, all such elements must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add an element
* to the set that violates this constraint (for example, the user
* attempts to add a string element to a set whose elements are
* integers), the {@code add} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*/
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the specified
* comparator. All elements inserted into the set must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i> by the specified comparator: {@code comparator.compare(e1,
* e2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements
* {@code e1} and {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add
* an element to the set that violates this constraint, the
* {@code add} call will throw a {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this set.
* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering} of the elements will be used.
*/
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the elements in the specified
* collection, sorted according to the <i>natural ordering</i> of its
* elements. All elements inserted into the set must implement the
* {@link Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such elements must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set.
*
* @param c collection whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws ClassCastException if the elements in {@code c} are
* not {@link Comparable}, or are not mutually comparable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the same elements and
* using the same ordering as the specified sorted set.
*
* @param s sorted set whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set is null
*/
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return m.descendingKeySet().iterator();
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() {
return new TreeSet<>(m.descendingMap());
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality).
*
* @return the number of elements in this set (its cardinality)
*/
public int size() {
return m.size();
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this set contains no elements.
*
* @return {@code true} if this set contains no elements
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return m.isEmpty();
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this set contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this set
* contains an element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this set
* @return {@code true} if this set contains the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in the set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if
* the set contains no element {@code e2} such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns {@code false}.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
/**
* Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.
* More formally, removes an element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>,
* if this set contains such an element. Returns {@code true} if
* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set
* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the
* element once the call returns.)
*
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return {@code true} if this set contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this set.
* The set will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
/**
* Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this set
* @return {@code true} if this set changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the elements provided cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in the set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null or
* if any element is null and this set uses natural ordering, or
* its comparator does not permit null elements
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// Use linear-time version if applicable
if (m.size()==0 && c.size() > 0 &&
c instanceof SortedSet &&
m instanceof TreeMap) {
SortedSet<? extends E> set = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
TreeMap<E,Object> map = (TreeMap<E, Object>) m;
Comparator<?> cc = set.comparator();
Comparator<? super E> mc = map.comparator();
if (cc==mc || (cc != null && cc.equals(mc))) {
map.addAllForTreeSet(set, PRESENT);
return true;
}
}
return super.addAll(c);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} or {@code toElement}
* is null and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 1.6
*/
public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,
toElement, toInclusive));
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code toElement} is null and
* this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator does
* not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 1.6
*/
public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} is null and
* this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator does
* not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
* @since 1.6
*/
public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive));
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} or
* {@code toElement} is null and this set uses natural ordering,
* or its comparator does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {
return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code toElement} is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator does
* not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {
return headSet(toElement, false);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code fromElement} is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator does
* not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {
return tailSet(fromElement, true);
}
public Comparator<? super E> comparator() {
return m.comparator();
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E first() {
return m.firstKey();
}
/**
* @throws NoSuchElementException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E last() {
return m.lastKey();
}
// NavigableSet API methods
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
* @since 1.6
*/
public E lower(E e) {
return m.lowerKey(e);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
* @since 1.6
*/
public E floor(E e) {
return m.floorKey(e);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
* @since 1.6
*/
public E ceiling(E e) {
return m.ceilingKey(e);
}
/**
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
* @since 1.6
*/
public E higher(E e) {
return m.higherKey(e);
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollFirstEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollLastEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this {@code TreeSet} instance. (The elements
* themselves are not cloned.)
*
* @return a shallow copy of this set
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Object clone() {
TreeSet<E> clone;
try {
clone = (TreeSet<E>) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
clone.m = new TreeMap<>(m);
return clone;
}
/**
* Save the state of the {@code TreeSet} instance to a stream (that is,
* serialize it).
*
* @serialData Emits the comparator used to order this set, or
* {@code null} if it obeys its elements' natural ordering
* (Object), followed by the size of the set (the number of
* elements it contains) (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in order (as determined by the
* set's Comparator, or by the elements' natural ordering if
* the set has no Comparator).
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden stuff
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out Comparator
s.writeObject(m.comparator());
// Write out size
s.writeInt(m.size());
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (E e : m.keySet())
s.writeObject(e);
}
/**
* Reconstitute the {@code TreeSet} instance from a stream (that is,
* deserialize it).
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in Comparator
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparator<? super E> c = (Comparator<? super E>) s.readObject();
// Create backing TreeMap
TreeMap<E,Object> tm = new TreeMap<>(c);
m = tm;
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
tm.readTreeSet(size, s, PRESENT);
}
/**
* Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>
* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* set.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED},
* {@link Spliterator#DISTINCT}, {@link Spliterator#SORTED}, and
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Overriding implementations should document
* the reporting of additional characteristic values.
*
* <p>The spliterator's comparator (see
* {@link java.util.Spliterator#getComparator()}) is {@code null} if
* the tree set's comparator (see {@link #comparator()}) is {@code null}.
* Otherwise, the spliterator's comparator is the same as or imposes the
* same total ordering as the tree set's comparator.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this set
* @since 1.8
*/
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return TreeMap.keySpliteratorFor(m);
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143000061671589L;
}