IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输.可以实现文件复制,上传文件和下载文件.
Jdk提供的流继承了四大类:InputStream(字节输入流),OutputStream(字节输出流),Reader(字符输入流),Writer(字符输出流)。
对文件进行操作:FileInputStream(字节输入流),FileOutputStream(字节输出流),FileReader(字符输入流),FileWriter(字符输出流)
对管道进行操作:PipedInputStream(字节输入流),PipedOutStream(字节输出流),PipedReader(字符输入流),PipedWriter(字符输出流)
PipedInputStream的一个实例要和PipedOutputStream的一个实例共同使用,共同完成管道的读取写入操作。主要用于线程操作。
字节/字符数组:ByteArrayInputStream,ByteArrayOutputStream,CharArrayReader,CharArrayWriter是在内存中开辟了一个字节或字符数组。
Buffered缓冲流::BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream,BufferedReader,BufferedWriter,是带缓冲区的处理流,缓冲区的作用的主要目的是:避免每次和硬盘打交道,提高数据访问的效率。
转化流:InputStreamReader/OutputStreamWriter,把字节转化成字符。
数据流:DataInputStream,DataOutputStream。
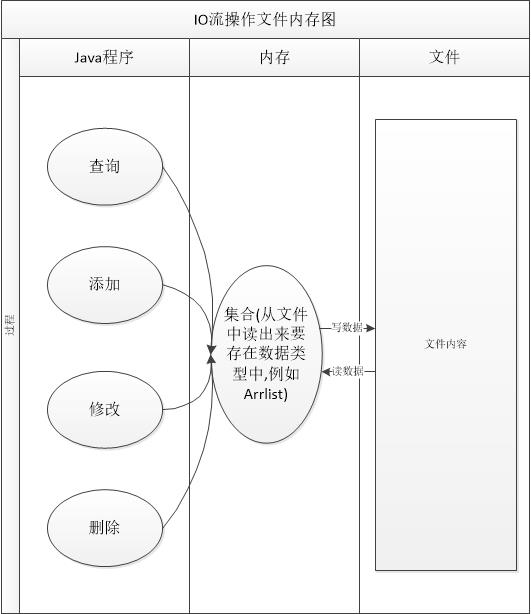
文件中的内容是无法直接操作的,所以要把文件中的数据读取到内存中,然后修改内存中的数据,修改完成后再由内存写入到文件中.
这里我们以操作文件为例子,主讲FileReader和FileWriter以及他们的缓冲流.
IO流
IO流可以吧数据存储到文件,也可以从文件中读取数据
输出流(写数据用)
FileWriter
void write(String str) //写一个字符串数据 void write(String str,int index,int len) //写一个字符串中的一部分数据 void write(int ch) //写一个字符数据,写int类型好处是既可以写char类型的数据,也可以写插入对应的int类型数据 void write(char[] chs) //写一个字符数据 void write(char[] chs,int index,int len) //写一个字符数组一部分
步骤
往文件中写数据(对于cpu来说是往外输出)-->用输出流-->-->FileWriter
输出流写数据的步骤:
A.创建输出流对象
B.调用输出流对象写数据的方法
C.释放资源
构造方法,创建输出流对象
FileWriter(String fileName) //fileName为文件路径不写盘符为相对路径(相对项目)
FileWriter(String fileName,boolean append) //输出到文件时添加到文件尾
成员方法
void write(String str) //调用流对象写数据方法
//数据没有直接写到文件中,其实是写到了内存缓冲区
void flush() //将内存缓冲区中的数据写入文件
void close() //关闭流,不然会一直占用文件无法操作文件.
输入流(读数据用)
FileReader
构造方法 FileReader(String fileName) 成员方法 int read() //一次读取一个字符,返回的是字符的int值.如果没有数据了,返回-1 int read(char[] cbuf) //返回的int是实际读取的字符个数,cbuf是
步骤
A.创建输入流
B.调用输入流对象的读数据方法
C.关闭流
close()和flush()方法区别
A.flush()刷新缓冲区.刷新后流对象还可以继续使用
B.close()先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源.流对象不可以再使用.
向文本文件中写字符时换行的方式mac是 ,linux是 ,windows是
文件复制(传输)时先用FileReader读取数据,再用FileWriter写数据.即先I在O.
//创建输入流对象 FileReader fr = new FileReader("source.txt"); //创建输出流对象 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("target.txt"); /*读写数据 int ch; while((ch=fr.read())!=-1) { //读取到了返回字符int值,读不到返回-1 fw.write(ch); }*/ //读写数据 char[] chs = new char[1024]; //一般写1024的整数倍 int len; while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1) { //读取到字符数组时返回数组长度,读取不到返回-1 fw.write(chs, 0, len); //最后一次读取的len可能小于1024.最后一次读取的放入char数组中覆盖上一次读取的前半部分,没覆盖的后半部分仍然是上次读取的内容,所以要从0读到len,len-1024是倒数第二次读取的内容. } //释放资源 fw.close(); fr.close();
char数组内存中的数据如下
FileReader fr = new FileReader("source.txt"); //调用输入流对象的读数据方法 //int read(char[] cbuf):一次读取一个字符数组的数据,返回的是实际读取的字符个数 char[] chs = new char[5]; //第一次读数据 int len = fr.read(chs); System.out.println("len:"+len); //System.out.println(new String(chs)); System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len)); //第二次读数据 len = fr.read(chs); System.out.println("len:"+len); //System.out.println(new String(chs)); System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len)); //第三次读数据 len = fr.read(chs); System.out.println("len:"+len); //最后一次为4,多以char[4]并没有被覆盖,仍然是r System.out.println(new String(chs,0,len));
当source.txt中为
hello
world
时,内存中char数组三次读取数据是这样的

缓冲流
缓冲流可以提高效率,所以每次用IO流读写时要在外面包装一层缓冲流
特殊功能
BufferedWriter
void newLine() //换行
BufferedReader
String readLine() //读取一行
因此,上面的程序可以这样写
//创建输入缓冲流对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("source.txt")); //创建输出缓冲流对象 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("target.txt")); //读写数据 /* //一次读写一个字符 int ch; while((ch=br.read())!=-1) { bw.write(ch); } */ //一次读写一个字符数组 char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len; while((len=br.read(chs))!=-1) { bw.write(chs,0,len); } //释放资源 bw.close(); br.close();
练习
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ //定义文件路径 String fileName = "students.txt"; //为了让程序能够回到这里来,我们使用循环 while(true) { //这是学生管理系统的主界面 System.out.println("--------欢迎来到学生管理系统--------"); System.out.println("1 查看所有学生"); System.out.println("2 添加学生"); System.out.println("3 删除学生"); System.out.println("4 修改学生"); System.out.println("5 退出"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择:"); //创建键盘录入对象 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String choiceString = sc.nextLine(); //用switch语句实现选择 switch(choiceString) { case "1": //查看所有学生 findAllStudent(fileName); break; case "2": //添加学生 addStudent(fileName); break; case "3": //删除学生 deleteStudent(fileName); break; case "4": //修改学生 updateStudent(fileName); break; case "5": default: System.out.println("谢谢你的使用"); System.exit(0); //JVM退出 break; } } } //从文件中读数据到集合 public static void readData(String fileName,ArrayList<Student> array) throws IOException { //创建输入缓冲流对象 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName)); String line; while((line=br.readLine())!=null) { String[] datas = line.split(","); Student s = new Student(); s.setId(datas[0]); s.setName(datas[1]); s.setAge(datas[2]); s.setAddress(datas[3]); array.add(s); } br.close(); } //把集合中的数据写入文件 public static void writeData(String fileName,ArrayList<Student> array) throws IOException { //创建输出缓冲流对象 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName)); for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) { Student s = array.get(x); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(s.getId()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getAddress()); bw.write(sb.toString()); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); } //修改学生 public static void updateStudent(String fileName) throws IOException { //创建集合对象 ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>(); //从文件中把数据读取到集合中 readData(fileName, array); //修改学生的思路:键盘录入一个学号,到集合中去查找,看是否有学生使用的是该学号,如果有就修改该学生 //创建键盘录入对象 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要修改的学生的学号:"); String id = sc.nextLine(); //定义一个索引 int index = -1; //遍历集合 for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) { //获取每一个学生对象 Student s = array.get(x); //拿学生对象的学号和键盘录入的学号进行比较 if(s.getId().equals(id)) { index = x; break; } } if(index == -1) { System.out.println("不好意思,你要修改的学号对应的学生信息不存在,请回去重新你的选择"); }else { System.out.println("请输入学生新姓名:"); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入学生新年龄:"); String age = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入学生新居住地:"); String address = sc.nextLine(); //创建学生对象 Student s = new Student(); s.setId(id); s.setName(name); s.setAge(age); s.setAddress(address); //修改集合中的学生对象 array.set(index, s); //把集合中的数据重新写回到文件 writeData(fileName, array); //给出提示 System.out.println("修改学生成功"); } } //删除学生 public static void deleteStudent(String fileName) throws IOException { //创建集合对象 ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>(); //从文件中把数据读取到集合中 readData(fileName, array); //删除学生的思路:键盘录入一个学号,到集合中去查找,看是否有学生使用的是该学号,如果有就删除该学生 //创建键盘录入对象 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你要删除的学生的学号:"); String id = sc.nextLine(); //我们必须给出学号不存在的时候的提示 //定义一个索引 int index = -1; //遍历集合 for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) { //获取到每一个学生对象 Student s = array.get(x); //拿这个学生对象的学号和键盘录入的学号进行比较 if(s.getId().equals(id)) { index = x; break; } } if(index == -1) { System.out.println("不好意思,你要删除的学号对应的学生信息不存在,请回去重新你的选择"); }else { array.remove(index); //把集合中的数据重新写回到文件 writeData(fileName, array); System.out.println("删除学生成功"); } } //添加学生 public static void addStudent(String fileName) throws IOException { //创建集合对象 ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>(); //从文件中把数据读取到集合中 readData(fileName, array); //创建键盘录入对象 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //为了让id能够被访问到,我们就把id定义在了循环的外面 String id; //为了让代码能够回到这里,用循环 while(true) { System.out.println("请输入学生学号:"); //String id = sc.nextLine(); id = sc.nextLine(); //判断学号有没有被人占用 //定义标记 boolean flag = false; //遍历集合,得到每一个学生 for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) { Student s = array.get(x); //获取该学生的学号,和键盘录入的学号进行比较 if(s.getId().equals(id)) { flag = true; //说明学号被占用了 break; } } if(flag) { System.out.println("你输入的学号已经被占用,请重新输入"); }else { break; //结束循环 } } System.out.println("请输入学生姓名:"); String name = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入学生年龄:"); String age = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入学生居住地:"); String address = sc.nextLine(); //创建学生对象 Student s = new Student(); s.setId(id); s.setName(name); s.setAge(age); s.setAddress(address); //把学生对象作为元素添加到集合 array.add(s); //把集合中的数据重新写回到文件 writeData(fileName, array); //给出提示 System.out.println("添加学生成功"); } //查看所有学生 public static void findAllStudent(String fileName) throws IOException { //创建集合对象 ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>(); //从文件中把数据读取到集合中 readData(fileName, array); //首先来判断集合中是否有数据,如果没有数据,就给出提示,并让该方法不继续往下执行 if(array.size() == 0) { System.out.println("不好意思,目前没有学生信息可供查询,请回去重新选择你的操作"); return; } // 其实就是一个tab键的位置 System.out.println("学号 姓名 年龄 居住地"); for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) { Student s = array.get(x); System.out.println(s.getId()+" "+s.getName()+" "+s.getAge()+" "+s.getAddress()); } }
本程序内存图