
简单爬虫框架:
爬虫调度器 -> URL管理器 -> 网页下载器(urllib2) -> 网页解析器(BeautifulSoup) -> 价值数据
Demo1:
# coding:utf8 import urllib2,cookielib url = "https://www.baidu.com" print '第一种方法' response1 = urllib2.urlopen(url) print response1.getcode() #返回状态码 print len(response1.read()) #返回的网页内容的长度 print "第二种方法" request = urllib2.Request(url) request.add_header("user-agent","Mozilla/5.0") response2 = urllib2.urlopen(request) print response2.getcode() print len(response2.read()) print '第三种方法' cj = cookielib.CookieJar() opener = urllib2.build_opener(urllib2.HTTPCookieProcessor(cj)) urllib2.install_opener(opener) response3 = urllib2.urlopen(url) print response3.getcode() #返回状态码 print cj #返回cookie print response3.read() #返回网页内容
Python有哪几种网页解析器:
正则表达式、html.parser、Beautiful Soup、lxml
BeautifulSoup:
- Python第三方库,用于从HTML或XML中提取数据
- 官网:http://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/
安装并测试beautifulsoup4:
- 安装:pip install beautifulsoup4
- 测试:import bs4
如果PyCharm无法识别beautifulsoup4,则在设置里找到Python Intercepter这一项,改为python2.7版本即可。
Demo2:
# coding:utf-8 import re from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # 示例代码片段(来自beautifulsoup官网) html_doc = """ <html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> <body> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>, <a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and <a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>; and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p> """ soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'html.parser',from_encoding='utf-8') print '获取所有的链接' links = soup.find_all('a') for link in links: print link.name,link['href'],link.get_text() print '获取lacie的链接' link_node = soup.find('a',href='http://example.com/lacie') print link_node.name,link_node['href'],link_node.get_text() print '正则匹配' link_node = soup.find('a', href= re.compile(r"ill")) print link_node.name,link_node['href'],link_node.get_text() print '获取p段落文字' p_node = soup.find('p', class_="title") print p_node.name,p_node.get_text()
实战编写爬取百度百科页面:
目录结构:
注:mac osx下用alt+enter添加相应方法
(爬虫调度器)spider_main.py:
# coding=utf-8 from baike_spider import url_manager,html_downloader,html_parser,html_outputer class SpiderMain(object): def __init__(self): self.urls = url_manager.UrlManager() #url管理器 self.downloader = html_downloader.HtmlDownloader() #下载器 self.parser = html_parser.HtmlParser() #解析器 self.outputer = html_outputer.HtmlOutputer() #输出器 def craw(self, root_url): count = 1 #判断当前爬取的是第几个url self.urls.add_new_url(root_url) while self.urls.has_new_url(): #循环,爬取所有相关页面,判断异常情况 try: new_url = self.urls.get_new_url() #取得url print 'craw %d : %s' % (count, new_url) #打印当前是第几个url html_cont = self.downloader.download(new_url) #下载页面数据 new_urls, new_data = self.parser.parse(new_url,html_cont) #进行页面解析得到新的url以及数据 self.urls.add_new_urls(new_urls) #添加新的url self.outputer.collect_data(new_data) #收集数据 if count == 10: # 此处10可以改为100甚至更多,代表循环次数 break count = count + 1 except: print 'craw failed' self.outputer.output_html() #利用outputer输出收集好的数据 if __name__=="__main__": root_url = "http://baike.baidu.com/view/21087.htm" obj_spider = SpiderMain() # 创建 obj_spider.craw(root_url) # craw方法启动爬虫
(url管理器)url_manager.py:
# coding=utf-8 class UrlManager(object): def __init__(self): self.new_urls = set() # 待爬取url self.old_urls = set() # 已爬取url def add_new_url(self, url): # 向管理器中添加一个新的url if url is None: return if url not in self.new_urls and url not in self.old_urls: self.new_urls.add(url) def add_new_urls(self, urls): # 向管理器中添加新的更多的url if urls is None or len(urls) == 0: return for url in urls: self.add_new_url(url) def has_new_url(self): # 判断管理器是否有新的待爬取的url return len(self.new_urls) != 0 def get_new_url(self): # 从管理器中获取一个新的待爬取的url new_url = self.new_urls.pop() self.old_urls.add(new_url) return new_url
(下载器)html_downloader.py:
import urllib2 class HtmlDownloader(object): def download(self, url): if url is None: return None response = urllib2.urlopen(url) if response.getcode() != 200: return None return response.read()
(解析器)html_parser.py:
import re import urlparse from bs4 import BeautifulSoup class HtmlParser(object): def parse(self,page_url,html_cont): if page_url is None or html_cont is None: return soup = BeautifulSoup(html_cont,'html.parser', from_encoding='utf-8') new_urls = self._get_new_urls(page_url, soup) new_data = self._get_new_data(page_url, soup) return new_urls, new_data def _get_new_urls(self, page_url, soup): new_urls = set() # /view/123.htm links = soup.find_all('a', href=re.compile(r"/view/d+.htm")) for link in links: new_url = link['href'] new_full_url = urlparse.urljoin(page_url, new_url) new_urls.add(new_full_url) return new_urls def _get_new_data(self, page_url, soup): res_data = {} # url res_data['url'] = page_url # <dd class="lemmaWgt-lemmaTitle-title"> <h1>Python</h1> title_node = soup.find('dd',class_="lemmaWgt-lemmaTitle-title").find("h1") res_data['title'] = title_node.get_text() # <div class="lemma-summary" label-module="lemmaSummary"> summary_node = soup.find('div',class_="lemma-summary") res_data['summary'] = summary_node.get_text() return res_data
(数据输出)html_outputer.py:
# coding=utf-8 class HtmlOutputer(object): #初始化 def __init__(self): self.datas = [] def collect_data(self, data): #收集数据 if data is None: return self.datas.append(data) def output_html(self): #输出数据 fout = open('output.html', 'w') fout.write("<html>") fout.write("<head>") fout.write("<meta charset= 'UTF-8'>") fout.write("</head>") fout.write("<body>") fout.write("<table>") # ASCII for data in self.datas: fout.write("<tr>") fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['url']) fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['title'].encode('utf-8')) fout.write("<td>%s</td>" % data['summary'].encode('utf-8')) fout.write("</tr>") fout.write("</html>") fout.write("</body>") fout.write("</table>") fout.close()
运行程序spider_main.py可进行爬取页面,最终文件输出为output.html,里面包含词条和词条解释,爬取完毕。
output.html:
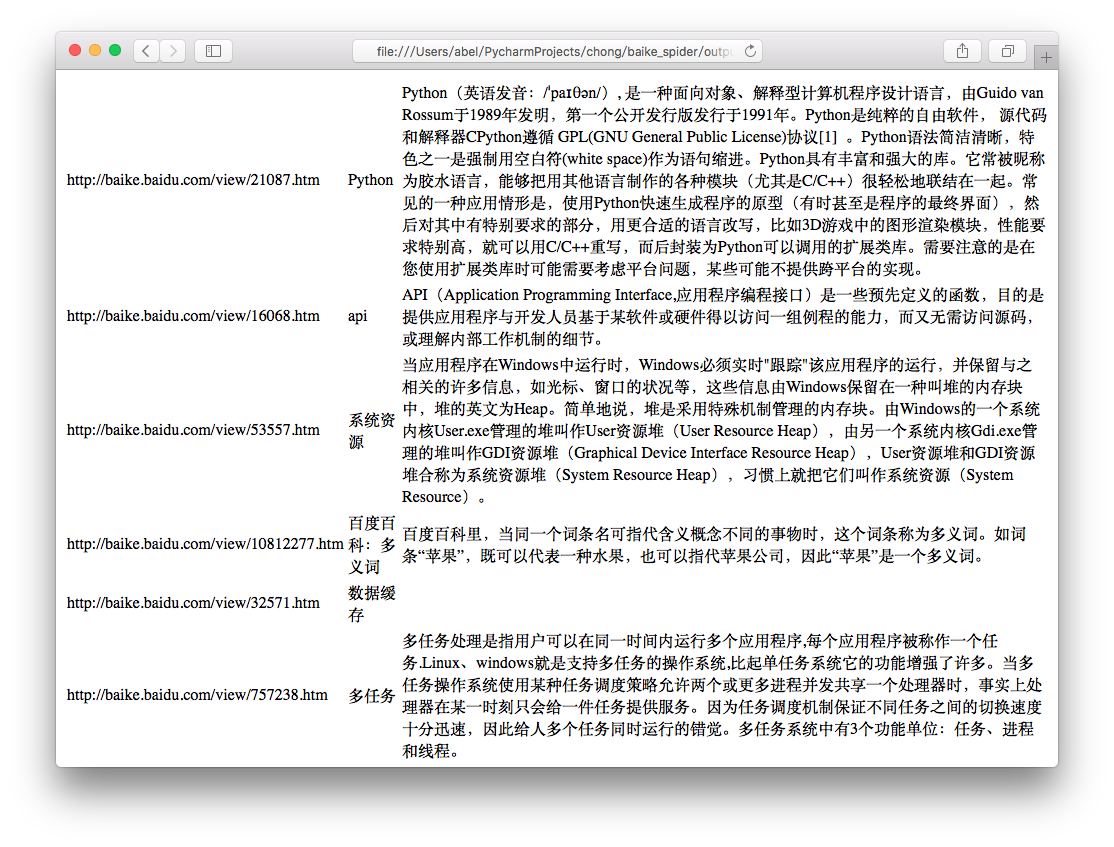
这只是最简单的爬虫,如果想深入学习,还有登录、验证码、Ajax、服务器防爬虫、多线程、分布式等等。