目录
Outline
-
MSE
-
Cross Entropy Loss
-
Hinge Loss
MSE
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 0, 2])
y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=4) # max_label=3种
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.float32)
out = tf.random.normal([5, 4])
out
<tf.Tensor: id=117, shape=(5, 4), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[ 0.8138832 , -1.1521571 , 0.05197939, 2.3684442 ],
[ 0.28827545, -0.35568208, -0.3952962 , -1.2576817 ],
[-0.4354525 , -1.9914867 , 0.37045303, -0.38287213],
[-0.7680094 , -0.98293644, 0.62572837, -0.5673917 ],
[ 1.5299634 , 0.38036177, -0.28049606, -0.708137 ]],
dtype=float32)>
loss1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y - out))
loss1
<tf.Tensor: id=122, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.5140966>
loss2 = tf.square(tf.norm(y - out)) / (5 * 4)
loss2
<tf.Tensor: id=99, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.3962512>
loss3 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(y, out))
loss3
<tf.Tensor: id=105, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.3962513>
Entropy
-
Uncertainty
-
measure of surprise
-
lower entropy --> more info.
a = tf.fill([4], 0.25)
a * tf.math.log(a) / tf.math.log(2.)
<tf.Tensor: id=134, shape=(4,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([-0.5, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5], dtype=float32)>
-tf.reduce_sum(a * tf.math.log(a) / tf.math.log(2.))
<tf.Tensor: id=143, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>
a = tf.constant([0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.7])
-tf.reduce_sum(a * tf.math.log(a) / tf.math.log(2.))
<tf.Tensor: id=157, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.3567797>
a = tf.constant([0.01, 0.01, 0.01, 0.97])
-tf.reduce_sum(a * tf.math.log(a) / tf.math.log(2.))
<tf.Tensor: id=167, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.24194068>
Cross Entropy
-
for p = q
- Minima: H(p,q) = H(p)
-
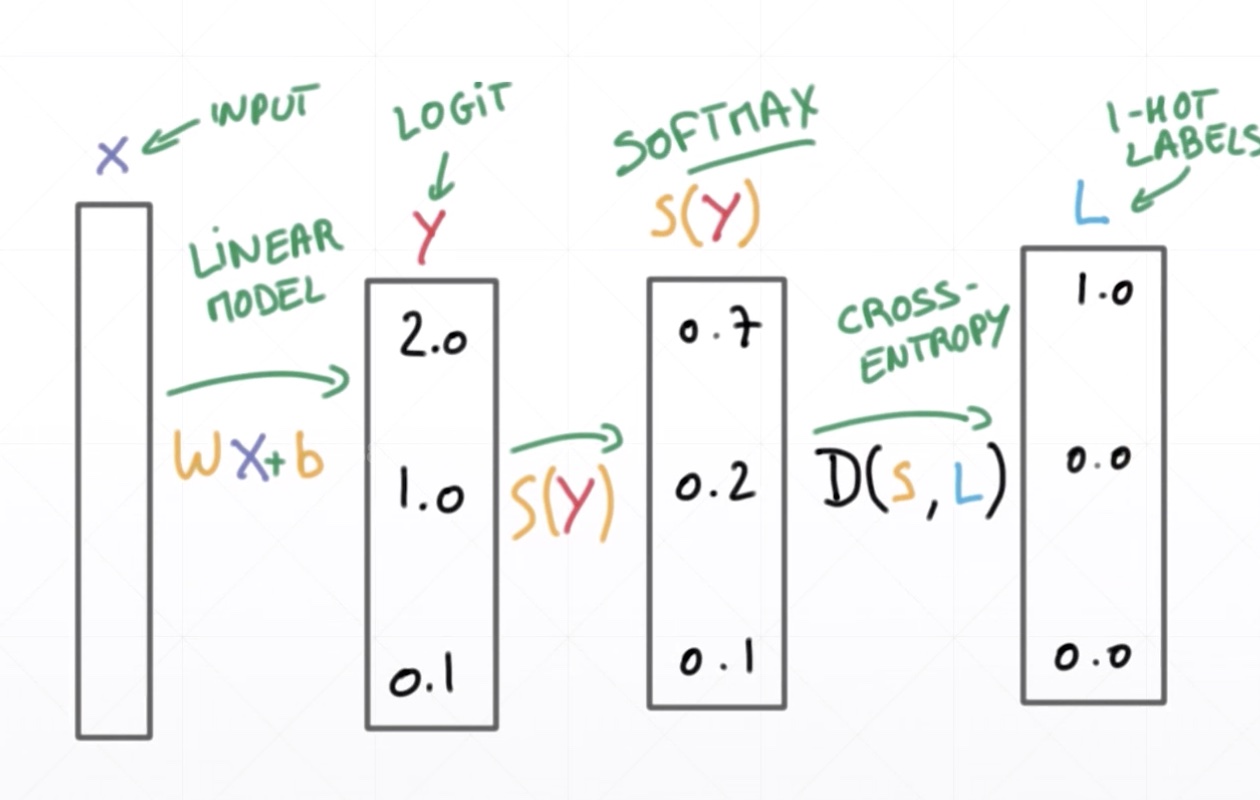
for P: one-hot encodint
- # p,q即真实值和预测值相等的话交叉熵为0
Binary Classification
- Two cases(第二种格式只需要输出一种情况,节省计算,无意义)
Single output
Classification
tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy([0, 1, 0, 0], [0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25])
<tf.Tensor: id=186, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.3862944>
tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy([0, 1, 0, 0], [0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.1])
<tf.Tensor: id=205, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.3978953>
tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy([0, 1, 0, 0], [0.1, 0.7, 0.1, 0.1])
<tf.Tensor: id=243, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.35667497>
tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy([0, 1, 0, 0], [0.01, 0.97, 0.01, 0.01])
<tf.Tensor: id=262, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=0.030459179>
tf.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()([1],[0.1])
<tf.Tensor: id=306, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.3025842>
tf.losses.binary_crossentropy([1],[0.1])
<tf.Tensor: id=333, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.3025842>
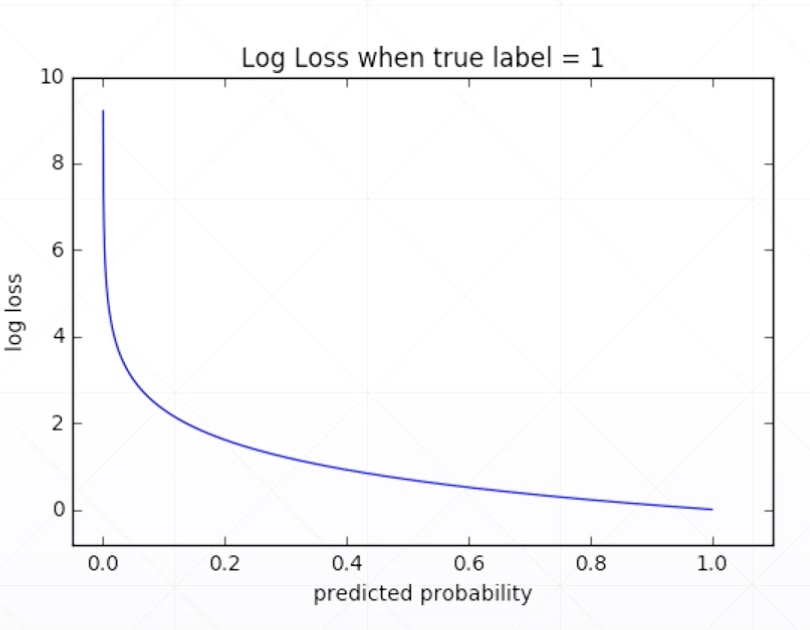
Why not MSE?
-
sigmoid + MSE
- gradient vanish
-
converge slower
-
However
- e.g. meta-learning
logits-->CrossEntropy