主题
以前我一直有一个问题不懂.并且觉得很神奇.就是Mybatis我们开发的时候只需要定义接口,并没有写实现类,为什么我们运行的时候就可以直接使用? 现在我想分享下这部分大致是怎么实现的.
在启动的时候
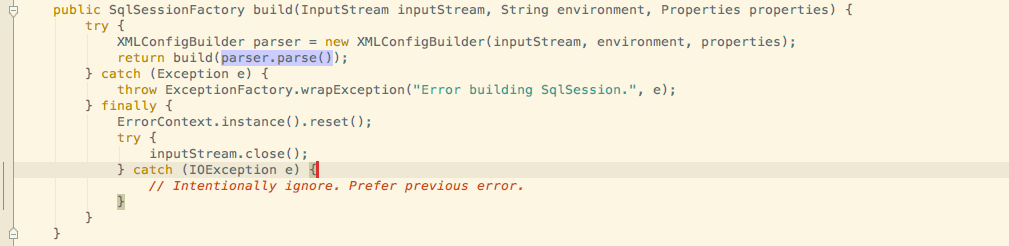
根据之前的分享,在初始化阶段Build SqlSessionFactory的时候需要用到XMLConfigBuilder去parse XML文件生成Configuration对象,在 parse的步骤中其中有一步就是parse mappers节点
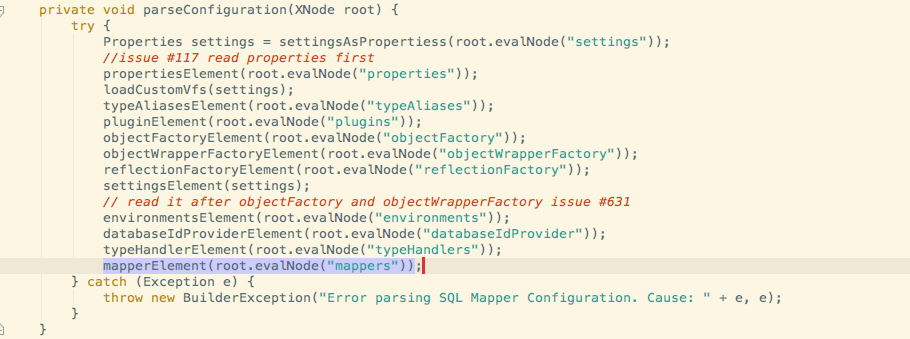
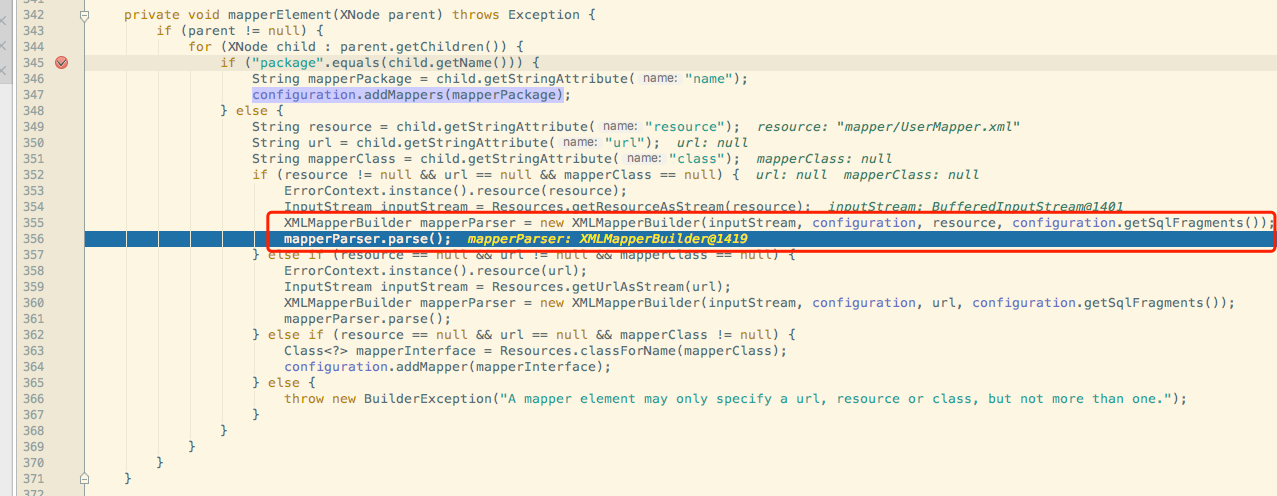
在parse mapper过程中会用到XMLMapperBuilder去parse.一步一步进入断点.
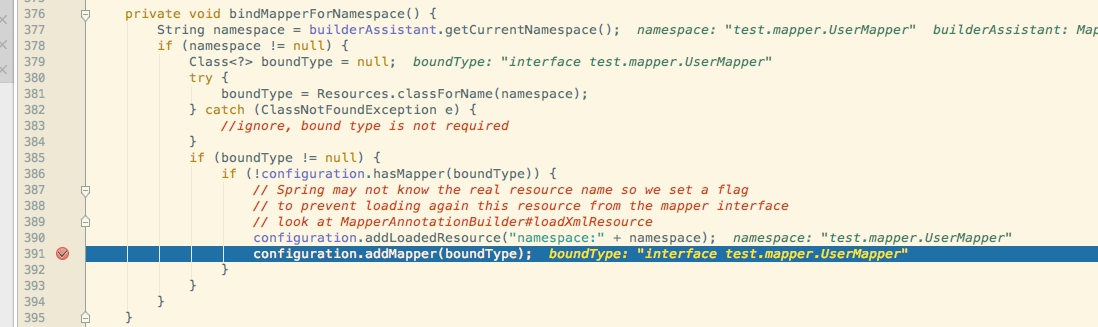
会发现后面会调用configuration的addMapper方法.它会调用MapperRegistry的addMapper方法
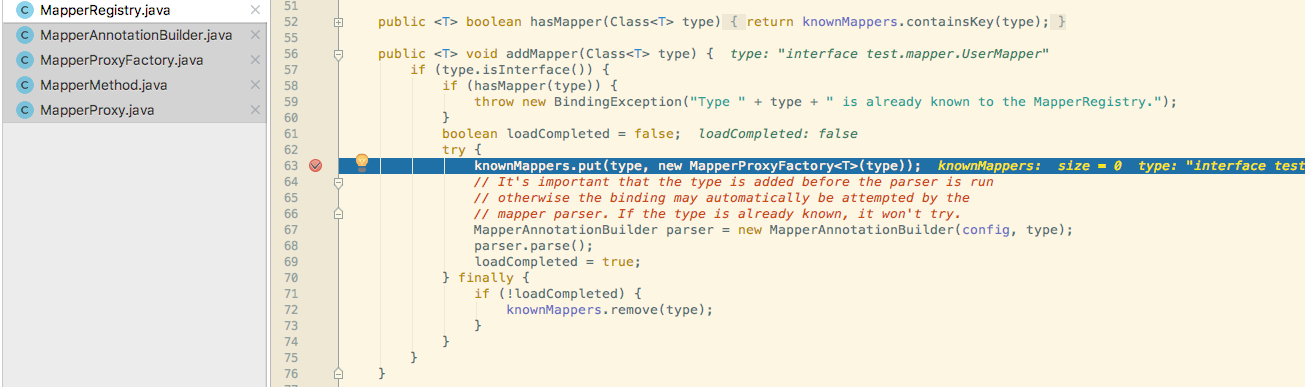
MapperRegistry相当用knownMappers这个hashmap于为每个Mapper注册一次,其中key是你自定义的Mapper接口的class,Value是MapperProxyFactory类的对象.
Factory一个就是一个工厂类,它肯定需要生产对应的对象,从名字上也能发现它生产的就是MapperProxy

1 /** 2 * Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors. 3 * <p> 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * <p> 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * <p> 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 package org.apache.ibatis.binding; 17 18 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; 19 20 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 21 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 22 import java.util.Map; 23 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; 24 25 /** 26 * @author Lasse Voss 27 */ 28 public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { 29 30 private final Class<T> mapperInterface; 31 private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>(); 32 33 public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { 34 this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; 35 } 36 37 public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { 38 return mapperInterface; 39 } 40 41 public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() { 42 return methodCache; 43 } 44 45 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 46 protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { 47 return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperInterface}, mapperProxy); 48 } 49 50 public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { 51 final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); 52 return newInstance(mapperProxy); 53 } 54 55 }

1 /** 2 * Copyright 2009-2015 the original author or authors. 3 * <p> 4 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 5 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 6 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 7 * <p> 8 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 9 * <p> 10 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 11 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 12 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 13 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 14 * limitations under the License. 15 */ 16 package org.apache.ibatis.binding; 17 18 import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil; 19 import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; 20 21 import java.io.Serializable; 22 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 23 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 24 import java.util.Map; 25 26 /** 27 * @author Clinton Begin 28 * @author Eduardo Macarron 29 */ 30 public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { 31 32 private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; 33 private final SqlSession sqlSession; 34 private final Class<T> mapperInterface; 35 private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; 36 37 public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { 38 this.sqlSession = sqlSession; 39 this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; 40 this.methodCache = methodCache; 41 } 42 43 @Override 44 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { 45 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { 46 try { 47 return method.invoke(this, args); 48 } catch (Throwable t) { 49 throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); 50 } 51 } 52 final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); 53 return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); 54 } 55 56 private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { 57 MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); 58 if (mapperMethod == null) { 59 mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()); 60 methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); 61 } 62 return mapperMethod; 63 } 64 65 }
从代码中我们可以得知,这里是用了JDK动态代理,MapperProxy类implements了InvocationHandler,
如果是调用自定义Mapper的Object类中的方法,比如toString,那就直接调用,否则的话调用mapperMethod.execute去执行对应的方法(比如selectById).那么mapperMethod是什么呢?
这个类的对象其实就是对应你写的Mapper里的方法,你的每个方法对应1个MapperMethod,相当于是Java的Method的包装.
另外还包含了你在XML里定义的SQL字符串, 是select还是insert还是update,delete操作等信息.相当于融合了你定义的Mapper里的Method和你为每个Method在XML里的写的信息.
这样你调用mapperMethod.execute的时候就能找到对应的SQL去执行了.
通过SqlSession获取Mapper
初始化完成后就如同之前的介绍,会在confuguration的mapperRegistry里注册好了各种MapperFactory.那么通过SqlSession去获取Mapper的时候也是类似的.会调用configuration去获取Mapper,内部会调用mapperRegistry去获取Mapper

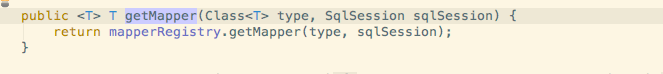
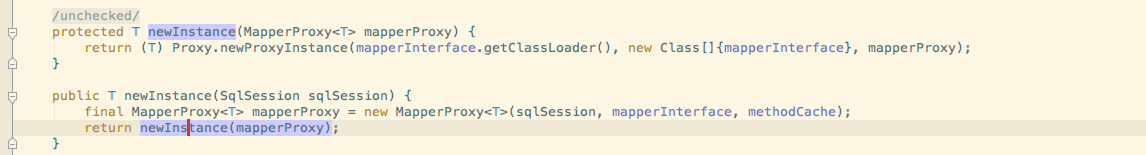
然后通过MapperProxyFactory去创建一个MapperProxy并返还

小结
1.说白了,其实就是利用JDK动态代理,返回给你1个实现了你写的Mapper接口的对象,而其中的Invocation接口的实现类就是MapperProxy.
2.在初始化阶段会为你写的每个Mapper在Configuration的MapperRegistry里注册一个MapperFactory,当你要获取Mapper实例的时候就通过这个Factory来new.
3.当你调用Mapper.XXX方法的时候,比如select,就会调用MapperProxy的invoke方法,获取你定义在Mapper里的xxx方法对应的MapperMethod对象,这个对象就是Method的封装,同时在XML里找到对应的select语句再执行.
4.你写的每个Mapper类的对象对应1个MapperProxyFactory生成1个MapperProxy,你在Mapper中定义的每个方法对应1个MapperMethod,它是Java的Method的封装
