形式
返回值类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
……
}
运算符重载
(1)运算符重载的实质是函数重载
(2)可以重载为普通函数,也可以重载为成员函数
1 class Complex 2 { 3 public: 4 double real,imag; 5 Complex( double r = 0.0, double i= 0.0 ):real(r),imag(i) { } 6 Complex operator-(const Complex & c); 7 }; 8 9 Complex operator+( const Complex & a, const Complex & b) 10 { 11 return Complex( a.real + b.real, a.imag + b.imag); //返回一个临时对象 12 } 13 14 Complex Complex::operator-(const Complex & c) 15 { 16 return Complex(real - c.real, imag - c.imag); //返回一个临时对象 17 } 18 19 int main() 20 { 21 Complex a(4,4),b(1,1),c; 22 23 //等价于c=operator+(a,b); 24 c = a + b; 25 cout << c.real << "," << c.imag << endl; 26 27 //a-b等价于a.operator-(b) 28 cout << (a - b).real << "," << (a - b).imag << endl; 29 return 0; 30 }
(3)把含运算符的表达式转换成对运算符函数的调用
(4)把运算符的操作数转换成运算符函数的参数
(5)运算符被多次重载时,根据实参的类型决定调用哪个运算符函数
(6)重载为成员函数时, 参数个数为运算符目数减一;重载为普通函数时, 参数个数为运算符目数
赋值运算符 ‘ =’重载
赋值运算符“ =”只能重载为成员函数
1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class String 6 { 7 private: 8 char * str; 9 public: 10 String ():str(new char[1]) { str[0] = 0;} 11 const char * c_str() { return str; }; 12 String & operator = (const char * s); 13 String::~String( ) { delete [] str; } 14 }; 15 16 String & String::operator = (const char * s) 17 { 18 //重载“=”以使得 obj = “hello”能够成立 19 delete [] str; 20 str = new char[strlen(s)+1]; 21 strcpy( str, s); 22 return * this; 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 String s; 28 s = "Good Luck," ; //等价于 s.operator=("Good Luck,"); 29 cout << s.c_str() << endl; 30 31 /* 这条语句要是不注释掉就会出错,因为这是一个初始化语句而并不是赋值语句 */ 32 // String s2 = "hello!"; 33 34 s = "Shenzhou 8!"; //等价于 s.operator=("Shenzhou 8!"); 35 cout << s.c_str() << endl; 36 return 0; 37 }
浅拷贝和深拷贝
考察下面的代码
1 String S1, S2; 2 S1 = “this”; 3 S2 = “that”; 4 S1 = S2;
如果还用上面的运算符重载,那就会出现问题
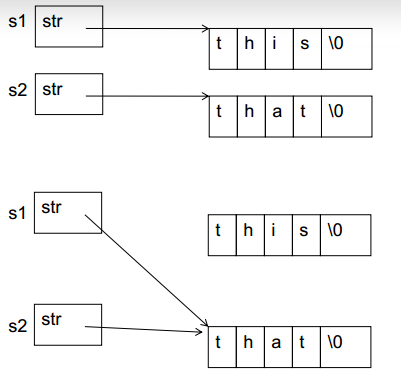
(1)如不定义自己的赋值运算符,那么S1=S2实际上导致 S1.str和 S2.str指向同一地方。
(2)如果S1对象消亡,析构函数将释放S1.str指向的空间,再访问S2的时候就好玩儿了。
(3)另外,如果执行 S1 = "other";会导致S2.str指向的地方被delete
因此,要做如下修改:
1 String & operator = (const String & s) 2 { 3 if( this == & s) 4 return * this; 5 6 delete [] str; 7 str = new char[strlen(s.str)+1]; 8 strcpy( str,s.str); 9 return * this; 10 }
ps:详细完成一个完整的String类,后续再补充
运算符重载为友元函数
一般情况下,将运算符重载为类的成员函数,是较好的选择。但有时,重载为成员函数不能满足使用要求,重载为普通函数,又不能访问类的私有成员,所以需要将运算符重载为友元。
1 class Complex 2 { 3 double real,imag; 4 public: 5 Complex( double r, double i):real(r),imag(i){ }; 6 Complex operator+( double r ); 7 }; 8 9 Complex Complex::operator+( double r ) 10 { 11 //能解释 c+5 12 return Complex(real + r,imag); 13 }
上面的类中重载的加号有局限性
Complex c ;
c = c + 5; //有定义,相当于 c = c.operator +(5);
但是:
c = 5 + c; //编译出错
为了使得上述的表达式能成立,需要将 + 重载为普通函数。但是普通函数又不能访问私有成员,所以,需要将运算符 + 重载为友元。
1 class Complex 2 { 3 double real,imag; 4 public: 5 Complex( double r, double i):real(r),imag(i){ }; 6 Complex operator+( double r ); 7 friend Complex operator + (double r,const Complex & c); 8 }; 9 10 Complex Complex::operator+( double r ) 11 { 12 //能解释 c+5 13 return Complex(real + r,imag); 14 } 15 16 Complex operator+ (double r,const Complex & c) 17 { 18 //能解释 5+c 19 return Complex( c.real + r, c.imag); 20 }
设计一个变长数组类
想要达到下面目的
1 int main() 2 { 3 CArray a; //开始里的数组是空的 4 /* 5 要用动态分配的内存来存放数组元素,需要一个指针成员变量 6 */ 7 for( int i = 0;i < 5;++i) 8 a.push_back(i); 9 10 CArray a2,a3; 11 /* 12 要重载“=” 13 */ 14 a2 = a; 15 for( int i = 0; i < a.length(); ++i ) 16 /* 17 要重载“[ ]” 18 */ 19 cout << a2[i] << " " ; 20 21 a2 = a3; //a2是空的 22 for( int i = 0; i < a2.length(); ++i ) //a2.length()返回0 23 cout << a2[i] << " "; 24 cout << endl; 25 26 a[3] = 100; 27 /* 28 要自己写复制构造函数 29 */ 30 CArray a4(a); 31 for( int i = 0; i < a4.length(); ++i ) 32 cout << a4[i] << " "; 33 34 return 0; 35 }
类的设计如下:
1 class CArray { 2 int size; //数组元素的个数 3 int *ptr; //指向动态分配的数组 4 public: 5 CArray(int s = 0); //s代表数组元素的个数 6 CArray(CArray & a); 7 ~CArray(); 8 void push_back(int v); //用于在数组尾部添加一个元素v 9 CArray & operator=( const CArray & a); 10 //用于数组对象间的赋值 11 int length() { return size; } //返回数组元素个数 12 int & CArray::operator[](int i) //返回值为 int 不行!不支持 a[i] = 4 13 { 14 //用以支持根据下标访问数组元素, 15 // 如n = a[i] 和a[i] = 4; 这样的语句 16 return ptr[i]; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 CArray::CArray(int s):size(s) 21 { 22 if( s == 0) 23 ptr = NULL; 24 else 25 ptr = new int[s]; 26 } 27 28 CArray::CArray(CArray & a) 29 { 30 if( !a.ptr) { 31 ptr = NULL; 32 size = 0; 33 return; 34 } 35 ptr = new int[a.size]; 36 memcpy( ptr, a.ptr, sizeof(int ) * a.size); 37 size = a.size; 38 } 39 40 CArray::~CArray() 41 { 42 if( ptr) delete [] ptr; 43 } 44 45 CArray & CArray::operator=( const CArray & a) 46 { 47 //赋值号的作用是使“=”左边对象里存放的数组,大小和内容都和右边的对象一样 48 if( ptr == a.ptr) //防止a=a这样的赋值导致出错 49 return * this; 50 51 if( a.ptr == NULL) { //如果a里面的数组是空的 52 if( ptr ) 53 delete [] ptr; 54 ptr = NULL; 55 size = 0; 56 return * this; 57 } 58 59 if( size < a.size) { //如果原有空间够大,就不用分配新的空间 60 if(ptr) 61 delete [] ptr; 62 ptr = new int[a.size]; 63 } 64 65 memcpy( ptr, a.ptr, sizeof(int) * a.size); 66 size = a.size; 67 return * this; 68 } 69 70 void CArray::push_back(int v) 71 { 72 //在数组尾部添加一个元素 73 if( ptr) { 74 int * tmpPtr = new int[size + 1]; //重新分配空间 75 memcpy(tmpPtr, ptr, sizeof(int) * size); //拷贝原数组内容 76 delete [] ptr; 77 ptr = tmpPtr; 78 } 79 else //数组本来是空的 80 ptr = new int[1]; 81 82 ptr[size++] = v; //加入新的数组元素 83 }
流运算符的重载
假定c是Complex复数类的对象,现在希望写“ cout << c;”,就能以“ a+bi”的形式输出c的值,写“ cin>>c;”,就能从键盘接受“ a+bi”形式的输入,并且使得c.real = a,c.imag = b。
1 class Complex 2 { 3 double real,imag; 4 public: 5 Complex( double r=0, double i=0):real(r),imag(i){ }; 6 friend ostream & operator<<( ostream & os, const Complex & c); 7 friend istream & operator>>( istream & is,Complex & c); 8 }; 9 10 ostream & operator<<( ostream & os,const Complex & c) 11 { 12 os << c.real << "+" << c.imag << "i"; //以"a+bi"的形式输出 13 return os; 14 } 15 16 istream & operator>>( istream & is,Complex & c) 17 { 18 string s; 19 is >> s; //将"a+bi"作为字符串读入, “a+bi” 中间不能有空格 20 int pos = s.find("+", 0); 21 string sTmp = s.substr(0, pos); //分离出代表实部的字符串 22 c.real = atof(sTmp.c_str()); //atof库函数能将const char*指针指向的内容转换成 float 23 sTmp = s.substr(pos+1, s.length()-pos-2); //分离出代表虚部的字符串 24 c.imag = atof(sTmp.c_str()); 25 return is; 26 }
类型转换运算符
类型强制转换运算符被重载时不能写返回值类型,实际上其返回值类型就是该类型强制转换运算符代表的类型
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Complex 4 { 5 double real,imag; 6 public: 7 Complex(double r=0,double i=0):real(r),imag(i) { }; 8 //重载强制类型转换运算符 double 9 operator double () { return real; } 10 11 }; 12 13 int main() 14 { 15 Complex c(1.2,3.4); 16 cout << (double)c << endl; //输出 1.2 17 double n = 2 + c; //等价于 double n=2+c.operator double() 18 cout << n; //输出 3.2 19 }
自增,自减运算符的重载
1、前置运算符作为一元运算符重载
(1)重载为成员函数:
T & operator++();
T & operator--();
(2)重载为全局函数:
T1 & operator++(T2);
T1 & operator—(T2);
2、后置运算符作为二元运算符重载,多写一个没用的参数
(1)重载为成员函数:
T operator++(int);
T operator--(int);
(2)重载为全局函数:
T1 operator++(T2,int );
T1 operator—( T2,int);
1 class CDemo 2 { 3 private: 4 int n; 5 public: 6 CDemo(int i=0):n(i) { } 7 CDemo & operator++(); //用于前置形式 8 CDemo operator++( int ); //用于后置形式 9 operator int ( ) { return n; } 10 friend CDemo & operator--(CDemo & ); 11 friend CDemo operator--(CDemo & ,int); 12 }; 13 14 CDemo & CDemo::operator++() 15 { 16 //前置 ++ 17 n++; 18 return * this; 19 } // ++s即为: s.operator++(); 20 21 CDemo CDemo::operator++( int k ) 22 { 23 //后置 ++ 24 CDemo tmp(* this); //记录修改前的对象 25 n++; 26 return tmp; //返回修改前的对象 27 } // s++即为: s.operator++(0); 28 29 CDemo & operator--(CDemo & d) 30 { 31 //前置-- 32 d.n--; 33 return d; 34 } //--s即为: operator--(s); 35 36 CDemo operator--(CDemo & d,int) 37 { 38 //后置-- 39 CDemo tmp(d); 40 d.n--; 41 return tmp; 42 } //s--即为: operator--(s, 0); 43 44 int main() 45 { 46 CDemo d(5); 47 cout << (d++ ) << ","; //等价于 d.operator++(0); 48 cout << d << ","; 49 cout << (++d) << ","; //等价于 d.operator++(); 50 cout << d << endl; 51 cout << (d-- ) << ","; //等价于 operator--(d,0); 52 cout << d << ","; 53 cout << (--d) << ","; //等价于 operator--(d); 54 cout << d << endl; 55 return 0; 56 }
运算符重载的注意事项
(1)C++不允许定义新的运算符 ;
(2)重载后运算符的含义应该符合日常习惯;
complex_a + complex_b
word_a > word_b
date_b = date_a + n
(3)运算符重载不改变运算符的优先级;
(4)以下运算符不能被重载:“.” 、“.*” 、“::” 、“?:” 、 sizeof;
(5)重载运算符()、 []、 ->或者赋值运算符=时,运算符重载函数必须声明为类的成员函数。