redis中字典有以下要点:
(1)它就是一个键值对,对于hash冲突的处理采用了头插法的链式存储来解决。
(2)对rehash,扩展就是取第一个大于等于used * 2的2 ^ n的数作为新的hash表大小;缩紧就是取第一个大于等于used的2 ^ n的数作为新的hash表大小。后面会介绍到dict结构体中是有dictht ht[2]这个成员变量的,为什么是2个呢?就是为了做rehash时交替使用的。那么何时扩展,何时缩紧呢?有个负载因子的概念(负载因子 = used / size,注意这里面的used也是包括了链式存储解决冲突时候的元素个数),没有执行BGSAVE或者BGREWRITEAOF时大于1就会扩展,小于0.1就会缩紧。搞的时候会用渐进式rehash的方法来搞,再此过程中对于字典的删、改、查会在2个ht上面进行,而增只会在新的ht上进行。
主要关注dict.c和dici.h。
首先先看一下结构体dictht:
1 /* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we 2 * implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */ 3 typedef struct dictht { 4 //每个具体table[i]中的节点数据类型是dictEntry 结构表示, 每个 dictEntry 结构都保存着一个键值对: 5 dictEntry **table; 6 7 // 哈希表大小 8 unsigned long size; 9 10 // 哈希表大小掩码,用于计算索引值,总是等于 size - 1 11 unsigned long sizemask; 12 13 // 该哈希表已有节点的数量 14 unsigned long used; 15 16 } dictht;
再看结构体dictEntry:
1 typedef struct dictEntry { 2 // 键 3 void *key; 4 5 // 值 6 union { 7 void *val; 8 uint64_t u64; 9 int64_t s64; 10 } v; 11 12 13 //next 属性是指向另一个哈希表节点的指针, 这个指针可以将多个哈希值相同的键值对连接在一次, 以此来解决键冲突(collision)的问题。 14 struct dictEntry *next; 15 16 } dictEntry;
对于k1和k0值相等的情况下,见下图:
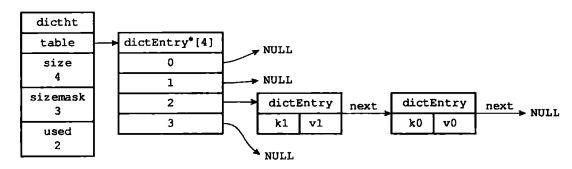
再来看结构体dict:
1 typedef struct dict {//dictCreate创建和初始化 2 // 类型特定函数,实现多态 3 dictType *type; 4 5 // 私有数据 6 void *privdata; 7 8 // 哈希表 9 dictht ht[2]; 10 11 // rehash 索引 12 int rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ 13 14 // 目前正在运行的安全迭代器的数量 15 int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ 16 17 } dict;
再看结构体dictType:
1 typedef struct dictType { 2 unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key); 3 4 void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key); 5 6 void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj); 7 8 int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2); 9 10 void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key); 11 12 void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj); 13 14 } dictType;
里面就是各种函数指针。

dictCreate:创建字典,比较简单,不过多解释
1 /* Create a new hash table */ 2 dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, 3 void *privDataPtr) 4 { 5 dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d)); 6 7 _dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr); 8 9 return d; 10 }
_dictInit:初始化操作
1 /* Initialize the hash table */ 2 int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type, 3 void *privDataPtr) 4 { 5 // 初始化两个哈希表的各项属性值 6 // 但暂时还不分配内存给哈希表数组 7 _dictReset(&d->ht[0]); 8 _dictReset(&d->ht[1]); 9 10 // 设置类型特定函数 11 d->type = type; 12 13 // 设置私有数据 14 d->privdata = privDataPtr; 15 16 // 设置哈希表 rehash 状态 17 d->rehashidx = -1; 18 19 // 设置字典的安全迭代器数量 20 d->iterators = 0; 21 22 return DICT_OK; 23 }
_dictReset:赋初值
1 static void _dictReset(dictht *ht) 2 { 3 ht->table = NULL; 4 ht->size = 0; 5 ht->sizemask = 0; 6 ht->used = 0; 7 }
dictAdd:添加k-v到字典中,调用关系比较乱,我们来看一下
dictAdd
-->dictAddRaw
-->_dictRehashStep
-->dictRehash
-->_dictKeyIndex
-->_dictExpandIfNeeded
-->dictExpand
-->_dictNextPower
-->dictSetKey
-->dictSetVal


有了调用关系就好办了,下面来分别分析以上函数都做了什么。
_dictRehashStep:分步rehash包裹函数
1 static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) { 2 if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1); 3 }
dictRehash:分步rehash
1 int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) { 2 // 只可以在 rehash 进行中时执行 3 if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return 0; 4 5 // 进行 N 步迁移 6 while(n--) { 7 dictEntry *de, *nextde; 8 9 /* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */ 10 // 如果 0 号哈希表为空,那么表示 rehash 执行完毕 11 if (d->ht[0].used == 0) { 12 zfree(d->ht[0].table); 13 d->ht[0] = d->ht[1]; 14 _dictReset(&d->ht[1]); 15 d->rehashidx = -1; 16 return 0; 17 } 18 19 /* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more 20 * elements because ht[0].used != 0 */ 21 assert(d->ht[0].size > (unsigned)d->rehashidx); 22 23 // 略过数组中为空的索引,找到下一个非空索引 24 while(d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) d->rehashidx++; 25 26 // 指向该索引的链表表头节点 27 de = d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx]; 28 /* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */ 29 while(de) { 30 unsigned int h; 31 32 nextde = de->next; 33 34 /* Get the index in the new hash table */ 35 h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[1].sizemask; 36 37 de->next = d->ht[1].table[h]; 38 d->ht[1].table[h] = de; 39 40 // 更新计数器 41 d->ht[0].used--; 42 d->ht[1].used++; 43 44 // 继续处理下个节点 45 de = nextde; 46 } 47 // 将刚迁移完的哈希表索引的指针设为空 48 d->ht[0].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL; 49 // 更新 rehash 索引 50 d->rehashidx++; 51 } 52 53 return 1; 54 }
dictExpand:扩充函数,是否需要rehash的标志rehashidx也是从这里面搞的,这样它就不为-1了。
1 /* Expand or create the hash table */ 2 int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size) 3 { 4 // 新哈希表 5 dictht n; /* the new hash table */ 6 7 unsigned long realsize = _dictNextPower(size); 8 9 /* the size is invalid if it is smaller than the number of 10 * elements already inside the hash table */ 11 if (dictIsRehashing(d) || d->ht[0].used > size) 12 return DICT_ERR; 13 14 /* Allocate the new hash table and initialize all pointers to NULL */ 15 n.size = realsize; 16 n.sizemask = realsize-1; 17 n.table = zcalloc(realsize*sizeof(dictEntry*)); 18 n.used = 0; 19 20 //下面是要区分2种情况的,需要注意了 21 22 /* Is this the first initialization? If so it's not really a rehashing 23 * we just set the first hash table so that it can accept keys. */ 24 // 如果 0 号哈希表为空,那么这是一次初始化: 25 if (d->ht[0].table == NULL) { 26 d->ht[0] = n; 27 return DICT_OK; 28 } 29 30 /* Prepare a second hash table for incremental rehashing */ 31 // 如果 0 号哈希表非空,那么这是一次 rehash : 32 // 程序将新哈希表设置为 1 号哈希表, 33 // 并将字典的 rehash 标识打开,让程序可以开始对字典进行 rehash 34 d->ht[1] = n; 35 d->rehashidx = 0; 36 return DICT_OK; 37 38 }
dictAddRaw:添加新的键到字典
1 /* Low level add. This function adds the entry but instead of setting 2 * a value returns the dictEntry structure to the user, that will make 3 * sure to fill the value field as he wishes. 4 * 5 * This function is also directly exposed to user API to be called 6 * mainly in order to store non-pointers inside the hash value, example: 7 * 8 * entry = dictAddRaw(dict,mykey); 9 * if (entry != NULL) dictSetSignedIntegerVal(entry,1000); 10 * 11 * Return values: 12 * 13 * If key already exists NULL is returned. 14 * If key was added, the hash entry is returned to be manipulated by the caller. 15 */ 16 dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key) 17 { 18 int index; 19 dictEntry *entry; 20 dictht *ht; 21 22 if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); 23 24 /* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if 25 * the element already exists. */ 26 if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key)) == -1) 27 return NULL; 28 29 /* Allocate the memory and store the new entry */ 30 ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0]; 31 entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry)); 32 entry->next = ht->table[index]; 33 ht->table[index] = entry; 34 ht->used++; 35 36 /* Set the hash entry fields. */ 37 dictSetKey(d, entry, key); 38 39 return entry; 40 }
dictAdd:添加新的键值对到字典
1 /* Add an element to the target hash table */ 2 int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val) 3 { 4 dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key); 5 6 // 键已存在,添加失败 7 if (!entry) return DICT_ERR; 8 9 // 键不存在,设置节点的值 10 dictSetVal(d, entry, val); 11 12 return DICT_OK; 13 }
dictReplace:更新键值对,原来没有就添加,原来有就更新值
1 /* Add an element, discarding the old if the key already exists. 2 * Return 1 if the key was added from scratch, 0 if there was already an element with such key and dictReplace() just performed a value update operation. 3 */ 4 int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val) 5 { 6 dictEntry *entry, auxentry; 7 8 /* Try to add the element. If the key 9 * does not exists dictAdd will suceed. */ 10 if (dictAdd(d, key, val) == DICT_OK) 11 return 1; 12 13 /* It already exists, get the entry */ 14 entry = dictFind(d, key); 15 16 auxentry = *entry; 17 18 dictSetVal(d, entry, val); 19 20 dictFreeVal(d, &auxentry); 21 22 return 0; 23 }
dictGenericDelete:删除指定key对应的一个元素
1 /* Search and remove an element */ 2 static int dictGenericDelete(dict *d, const void *key, int nofree) 3 { 4 unsigned int h, idx; 5 dictEntry *he, *prevHe; 6 int table; 7 8 if (d->ht[0].size == 0) return DICT_ERR; /* d->ht[0].table is NULL */ 9 10 if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); 11 12 // 计算哈希值 13 h = dictHashKey(d, key); 14 15 // 遍历哈希表 16 for (table = 0; table <= 1; table++) { 17 18 // 计算索引值 19 idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask; 20 // 指向该索引上的链表,就是链表的第一个元素 21 he = d->ht[table].table[idx]; 22 prevHe = NULL; 23 24 while(he) { 25 26 if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key)) { 27 28 /* Unlink the element from the list */ 29 // 就是删除一个就得了 30 if (prevHe) 31 prevHe->next = he->next; 32 else 33 d->ht[table].table[idx] = he->next; 34 35 if (!nofree) { 36 dictFreeKey(d, he); 37 dictFreeVal(d, he); 38 } 39 40 zfree(he); 41 42 d->ht[table].used--; 43 44 return DICT_OK; 45 } 46 47 prevHe = he; 48 he = he->next; 49 } 50 51 if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) break; 52 } 53 54 return DICT_ERR; /* not found */ 55 }
_dictClear:释放hash
1 /* Destroy an entire dictionary */ 2 int _dictClear(dict *d, dictht *ht, void(callback)(void *)) { 3 unsigned long i; 4 5 /* Free all the elements */ 6 for (i = 0; i < ht->size && ht->used > 0; i++) { 7 dictEntry *he, *nextHe; 8 9 if (callback && (i & 65535) == 0) callback(d->privdata); 10 11 // 跳过空索引 12 if ((he = ht->table[i]) == NULL) continue; 13 14 // 遍历整个链表 15 while(he) { 16 nextHe = he->next; 17 dictFreeKey(d, he); 18 dictFreeVal(d, he); 19 zfree(he); 20 21 ht->used--; 22 23 he = nextHe; 24 } 25 } 26 27 /* Free the table and the allocated cache structure */ 28 zfree(ht->table); 29 30 /* Re-initialize the table */ 31 _dictReset(ht); 32 33 return DICT_OK; /* never fails */ 34 }
关于dictGetIterator、dictGetSafeIterator、dictNext、dictReleaseIterator具体应用暂时分析一下:
首先先看用到这几个函数的地方吧
1 void keysCommand(redisClient *c) { 2 dictIterator *di; 3 dictEntry *de; 4 5 sds pattern = c->argv[1]->ptr; 6 7 int plen = sdslen(pattern), allkeys; 8 unsigned long numkeys = 0; 9 void *replylen = addDeferredMultiBulkLength(c); 10 11 /* 首先先搞一个迭代器出来 */ 12 di = dictGetSafeIterator(c->db->dict); 13 allkeys = (pattern[0] == '*' && pattern[1] == '�'); 14 15 /* 开始遍历迭代器 */ 16 while((de = dictNext(di)) != NULL) { 17 sds key = dictGetKey(de); 18 robj *keyobj; 19 20 if (allkeys || stringmatchlen(pattern,plen,key,sdslen(key),0)) { 21 22 keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key)); 23 24 if (expireIfNeeded(c->db,keyobj) == 0) { 25 addReplyBulk(c,keyobj); 26 numkeys++; 27 } 28 29 decrRefCount(keyobj); 30 } 31 } 32 33 /* 释放迭代器 */ 34 dictReleaseIterator(di); 35 36 setDeferredMultiBulkLength(c,replylen,numkeys); 37 }
有了上面的应用场景,我们再来看上面几个函数的实现就好办了。
先看dictIterator结构体:
1 /* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call 2 * dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while 3 * iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext() 4 * should be called while iterating. */ 5 typedef struct dictIterator { 6 7 // 被迭代的字典 8 dict *d; 9 10 // table :正在被迭代的哈希表号码,值可以是 0 或 1 。 dictht ht[2];中的哪一个 11 // index :迭代器当前所指向的哈希表索引位置。 对应具体的桶槽位号 12 // safe :标识这个迭代器是否安全 13 int table, index, safe; 14 15 // entry :当前迭代到的节点的指针 16 // nextEntry :当前迭代节点的下一个节点 17 dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry; 18 19 long long fingerprint; /* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection */ 20 } dictIterator;
dictGetIterator:创建迭代器
1 dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d) 2 { 3 dictIterator *iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter)); 4 5 iter->d = d; 6 iter->table = 0; 7 iter->index = -1; 8 iter->safe = 0; 9 iter->entry = NULL; 10 iter->nextEntry = NULL; 11 12 return iter; 13 }
dictNext:迭代,遍历桶中的所有节点,第一次遍历该函数的时候直接获取具体桶首元素,否则使用nextEntry。这个函数比较难理解……
1 dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter) 2 { 3 while (1) { 4 5 // 进入这个循环有两种可能: 6 // 1) 这是迭代器第一次运行 7 // 2) 当前索引链表中的节点已经迭代完(NULL 为链表的表尾) 8 if (iter->entry == NULL) { 9 10 // 指向被迭代的哈希表 11 dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table]; 12 13 // 初次迭代时执行 14 if (iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0) { 15 // 如果是安全迭代器,那么更新安全迭代器计数器 16 if (iter->safe) 17 iter->d->iterators++; 18 // 如果是不安全迭代器,那么计算指纹 19 else 20 iter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d); 21 } 22 // 更新索引 23 iter->index++; //默认值为-1,自加后刚好为0,即第一个桶 24 25 // 如果迭代器的当前索引大于当前被迭代的哈希表的大小 26 // 那么说明这个哈希表已经迭代完毕 27 if (iter->index >= (signed) ht->size) { 28 // 如果正在 rehash 的话,那么说明 1 号哈希表也正在使用中 29 // 那么继续对 1 号哈希表进行迭代 30 if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == 0) { 31 iter->table++; 32 iter->index = 0; 33 ht = &iter->d->ht[1]; 34 // 如果没有 rehash ,那么说明迭代已经完成 35 } else { 36 break; 37 } 38 } 39 40 // 如果进行到这里,说明这个哈希表并未迭代完 41 // 更新节点指针,指向下个索引链表的表头节点 42 iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index]; 43 } else { 44 // 执行到这里,说明程序正在迭代某个链表 45 // 将节点指针指向链表的下个节点 46 iter->entry = iter->nextEntry; 47 } 48 49 if (iter->entry) { 50 /* We need to save the 'next' here, the iterator user 51 * may delete the entry we are returning. */ 52 iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next; 53 return iter->entry; 54 } 55 } 56 57 // 迭代完毕 58 return NULL; 59 }
dictReleaseIterator:释放迭代器,没有什么好说的了
1 void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter) 2 { 3 4 if (!(iter->index == -1 && iter->table == 0)) { 5 // 释放安全迭代器时,安全迭代器计数器减一 6 if (iter->safe) 7 iter->d->iterators--; 8 // 释放不安全迭代器时,验证指纹是否有变化 9 else 10 assert(iter->fingerprint == dictFingerprint(iter->d)); 11 } 12 zfree(iter); 13 }
关于迭代器里面,安全和非安全迭代器还不是特别明白;另外dictScan暂时没有深入研究,后续再深入研究吧。