在没有subprocess这个模块的时候,我们怎么去跟我们的操作系统做交互的呐?下面我们先说说这三个模块:os.system()、os.popen()、commands。
1. os.system()
作用:执行系统命令,完成后退出,只返回命令的执行状态(0:成功,非0:失败),不返回命令的执行结果。
>>> import os
>>> os.system("ls -l")
total 16708
-rw-------. 1 root root 1350 Jan 4 01:51 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8017 Jan 4 01:51 install.log
0 #执行返回的状态
>>> res = os.system("ls -l")
total 16708
-rw-------. 1 root root 1350 Jan 4 01:51 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8017 Jan 4 01:51 install.log
>>> res
0 #0: 表示成功
>>> res = os.system("lm")
sh: lm: command not found
>>> res
32512 #非0:表示失败
2. os.popen()
作用:执行系统命令,不返回命令的执行状态,实现一个“管道”可以用来返回命令的执行结果。
>>> import os
>>> os.popen("ls -l")
<open file 'ls -l', mode 'r' at 0x7f5ded070540>
>>> cmd = os.popen("ls -l")
>>> res = res.read()
>>> print(res) #打印返回结果
total 16708
-rw-------. 1 root root 1350 Jan 4 01:51 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8017 Jan 4 01:51 install.log
注:执行popen()不是直接返回命令的执行结果的,而是需要read一下,这是因为popen相当于打开了一个文件,它把结果存到文件中,只不过它是相当于存在内存中了,但是你好像打开文件的样子去取一样。
3. commands模块
作用:既可以获取命令的执行状态,也可以获取命令的执行结果,但是只能在python2.7有这个命令,在python3.5之后就没有,还有就是这个模块功能只支持Linux,Windows不支持,这边知道这个命令就行了,先忘记它吧。
>>> import commands #导入commands命令
>>> commands.getstatusoutput("ls -l")
(0, 'total 16708 -rw-------. 1 root root 1350 Jan 4 01:51 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8017 Jan 4 01:51 install.log') #元组的形式返回
>>> res = commands.getstatusoutput("ls -l")
>>> res[0] #执行状态
0
>>> print(res[1]) #执行结果
total 16708
-rw-------. 1 root root 1350 Jan 4 01:51 anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 8017 Jan 4 01:51 install.log
4. subprocess模块
上面说commands模块在python3.5以后的版本就没有了,而且它又不支持Windows,那怎么办呢?不用担心,python3.5之后又出来新的模块更为强大,subprocess模块,下面我们就来说说它是运作的。
1、subprocess.run()
作用:运行命令,返回命令执行的结果(python3.5以后的版本才会有这个命令)
>>> import subprocess
# python 解析则传入命令的每个参数的列表
>>> subprocess.run(["df","-h"])
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-LogVol00
289G 70G 204G 26% /
tmpfs 64G 0 64G 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 283M 27M 241M 11% /boot
CompletedProcess(args=['df', '-h'], returncode=0)
# 需要交给Linux shell自己解析,则:传入命令字符串,shell=True
>>> subprocess.run("df -h|grep /dev/sda1",shell=True)
/dev/sda1 283M 27M 241M 11% /boot
CompletedProcess(args='df -h|grep /dev/sda1', returncode=0)
注:看到上面run函数的使用,这边有很多小伙伴有点不解,这边我解释一下:第1种情况是:执行的命令需要让python去解释执行这个命令,执行的命令以及参数,需要以列表的形式传入。第二种情况:但是如果需要交给Linux shell环境去解析的还,这传入命令的字符串,并且声明shell=True即可。
2、subprocess.call()
作用:执行命令,返回命令的状态,0或者非0
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.call(["ls","-l"])
total 26976
-rw-r--r-- 1 1000 1000 10914 Jan 17 15:57 aclocal.m4
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 May 12 14:21 build
-rwxr-xr-x 1 1000 1000 43940 Jan 17 15:57 config.guess
>>> res #返回命令的状态
0
3、subprocess.check_call()
作用:执行命令,如果执行结果为0,正常返回,否则抛异常
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.check_call(["ls","-l"])
total 26976
-rw-r--r-- 1 1000 1000 10914 Jan 17 15:57 aclocal.m4
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 May 12 14:21 build
>>> res
0
4、subprocess.getstatusoutput()
作用:接收字符串形式的命令,返回元组形式,第1个元素是执行状态,第二个是命令结果
>>> import subprocess
>>> subprocess.getstatusoutput('ls /bin/ls')
(0, '/bin/ls') #0:执行状态,'bin/ls':执行结果
5、subprocess.getoutput()
作用:接收字符串形式的命令,并且返回命令的结果
>>> import subprocess
>>> subprocess.getoutput('ls /bin/ls')
'/bin/ls' #返回命令的结果
6、subprocess.check_output()
作用:执行命令,并且返回结果,不是打印
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.check_output(["ls","-l"])
>>> res
b'total 26976 -rw-r--r-- 1 1000 1000 10914 Jan 17 15:57 aclocal.m4
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 May 12 14:21 build
-rwxr-xr-x 1 1000 1000 43940 Jan 17 15:57 config.guess
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 756903 May 12 14:18 config.log ' #这边是以字节类型返回的
1) subprocess.Popen()
其实以上subprocess使用的方法,都是对subprocess.Popen的封装,下面我们就来看看这个Popen方法。
1、stdout
作用:标准输出
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("df -h",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE) #需要管道标准输出
>>> res.stdout.read() #标准输出
b'Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/VolGroup-
LogVol00 289G 70G 204G 26% / tmpfs 64G 0 64G
0% /dev/shm /dev/sda1 283M 27M 241M 11% /boot '
>>> obj.stdout.close() #关闭标准输出
2、stdin
作用:标准输入
>>> import subprocess
>>> obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> obj.stdin.write(b"hello world") #标准输入
>>> obj.stdin.close() #关闭标准输入
#这里输入完成了是不是的把他的输出读出来?
>>> cmd_out = obj.stdout.read() #获取启动的进程的标准输出
>>> obj.stdout.close() #关闭标准输出
>>> cmd_error = obj.stderr.read() #获取启动的进程的标准错误
>>> obj.stderr.close() #关闭启动程序的标准错误
3、stderr
作用:标准错误
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("lm -l",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> res.stderr.read() #标准输出错误
'/bin/sh: lm: command not found '
>>> obj.stderr.close() #关闭启动程序的标准错误
注意:上面的提到的标准输出都为啥都需要等于subprocess.PIPE,这个又是啥呢?原来这个是一个管道,这个需要画一个图来解释一下:
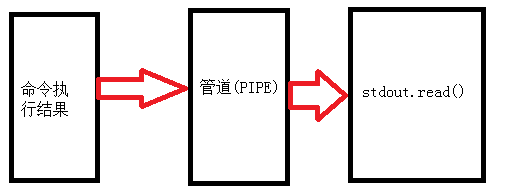
4、poll()
作用:定时检查命令有没有执行完毕,执行完毕返回0,没有完毕返回None
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("sleep 20;echo 'hello'",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> print(res.poll())
None #没有执行完毕
>>> print(res.poll())
0 #执行完毕
5、wait()
作用:等待命令执行完成,并且返回结果状态
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("sleep 20;echo 'hello'",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> res.wait()
############
漫长等待中
############
0 #等待结束,返回执行结果状态
6、terminate()
作用:杀掉启动进程
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("sleep 20;echo 'hello'",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> res.terminate() #杀掉启动的进程
>>> res.stdout.read() #杀掉后,标准输出为空
b''
7、communicate()
作用:执行的过程传数据,没什么用,先忘记它吧!以后用到再说
>>> import subprocess
>>> obj = subprocess.Popen(["python"], stdin=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> obj.stdin.write(b"hello world") #标准输入
>>> out_error_list = obj.communicate(timeout=10)
>>> print(out_error_list) #输入的结果
('', ' File "<stdin>", line 1 hello world ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax ')
8、pid
作用:获取当前执行子shell的程序的进程号
>>> import subprocess
>>> res = subprocess.Popen("sleep 20;echo 'hello'",shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> res.pid #获取这个Linux shell的环境的进程号
30225
9、可用参数
args:shell命令,可以是字符串或者序列类型(如:list,元组)
bufsize:指定缓冲。0 无缓冲,1 行缓冲,其他 缓冲区大小,负值 系统缓冲
stdin, stdout, stderr:分别表示程序的标准输入、输出、错误句柄
preexec_fn:只在Unix平台下有效,用于指定一个可执行对象(callable object),它将在子进程运行之前被调用
close_sfs:在windows平台下,如果close_fds被设置为True,则新创建的子进程将不会继承父进程的输入、输出、错误管道。所以不能将close_fds设置为True同时重定向子进程的标准输入、输出与错误(stdin, stdout, stderr)。
shell:同上
cwd:用于设置子进程的当前目录
env:用于指定子进程的环境变量。如果env = None,子进程的环境变量将从父进程中继承。
universal_newlines:不同系统的换行符不同,True -> 同意使用
startupinfo与createionflags只在windows下有效将被传递给底层的CreateProcess()函数,用于设置子进程的一些属性,如:主窗口的