JDBC,它主要是连接数据库的操作,是一个可以连接各种数据库和程序的接口
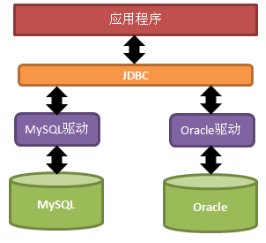
连接数据库的前提是,将整个包放入文件的lib文件夹中。然后再上面的包里面复制一下整个jar包。
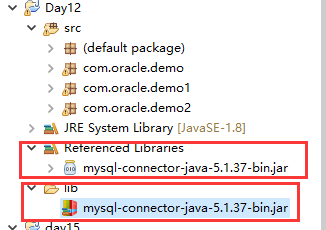
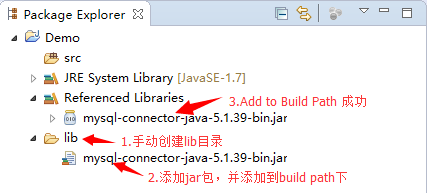
接着,
- 注册驱动.
- 告知JVM使用的是哪一个数据库的驱动
- 获得连接.
- 使用JDBC中的类,完成对MySQL数据库的连接
- 获得语句执行平台
- 通过连接对象获取对SQL语句的执行者对象
- 执行sql语句 获取sql语句,用字符串接收
- 使用执行者对象,向数据库执行SQL语句
- 获取到数据库的执行后的结果
- 处理结果集
- 释放资源.
虽然是这些东西,但是可以封装成一个JDBC工具类,这个工具类主要是把注册驱动,获得连接对象,释放资源放在一个类里面,使用的时候再调用即可。上面的黄字标注的全部被封装。
package com.oracle.demo1; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; public class JDBCUtils { //获取连接对象,工具类都是静态,调取方法只需要类名.静态方法 public static Connection getConn(){ //获得链接对象 String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java0611?characterEncoding=utf8"; String username="root"; String password="123456"; //为了返回值,必须把它作为全局变量 Connection conn=null; try { //注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //获得连接对象 conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; } //释放资源 //1.增删改 public static void close(Statement pst ,Connection conn){ if(pst!=null){ try { pst.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //查询释放资源(方法重载) public static void close(ResultSet rs,Statement pst,Connection conn){ if(rs!=null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(pst!=null){ try { pst.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
有了工具类之后,就可以执行剩下的操作了。
于是剩下的流程就变成了这样。
①获得连接对象(直接获取JDBC工具类)→②获得数据库语句→③运行结果集→④释放资源(调取JDBC工具类的查询方法)
②
获得数据库语句:
insert 增加
select 查询
delete 删除
update 修改
重点:如果是正常的数据库语句操作,如

可能会出现黑客攻击行为,而解决这个注入问题的话就采用?

而采取了注入之后,需要将占位符?赋值
//给占位符?赋值 给第几个问号赋值 pst.setString(1,uname); pst.setString(2,pwd);
如果是模糊查询的话,数据库语句需要拼串,语句上还用?号,但是占位符赋值用‘%’?‘%’、
//年报表 方法重载 public List< cost> getBaobiao(int year ) throws SQLException{ //获得连接对象 Connection conn=JDBCUtils.getConn(); //数据库语句 String sql="SELECT username,cost.`room_num`,cost.usercard,SUM(cost) " + "FROM cost JOIN userinfo ON cost.`usercard`=userinfo.`usercard` " + "WHERE TIME LIKE ? GROUP BY usercard"; PreparedStatement pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql); //运行结果集 pst.setString(1, "%"+year+"%"); ResultSet rs=pst.executeQuery(); //处理结果集 List<cost> list=new ArrayList<cost>(); while(rs.next()){ cost cost=new cost(); cost.setUsername(rs.getString("username")); cost.setUsercard(rs.getString("usercard")); cost.setRoom_num(rs.getInt("room_num")); cost.setCost(rs.getDouble("sum(cost)")); list.add(cost); }
③
运行结果集:
它的原理
rs.next();//指向第一行 rs.getInt(1);//获取第一行第一列的数据 常用方法: Object getObject(int index) / Object getObject(String name) 获得任意对象 String getString(int index) / Object getObject(String name) 获得字符串 int getInt(int index) / Object getObject(String name) 获得整形 double getDouble(int index) / Object getObject(String name) 获得双精度浮点型
如何是查询, ResultSet rs=pst.executeQuery();
如果是增删改:int row=pst.executeUpdate
处理结果集:
如果是查询:
while(rs.next){
rs.getString(1);
}
增删改:int row=pst.executeUpdate。
public List< cost> getBaobiao(String month ) throws SQLException{ //获得连接对象 Connection conn=JDBCUtils.getConn(); //数据库语句 String sql="SELECT username,usercard,room_num,(SELECT SUM(cost) FROM cost
WHERE cost.usercard=userinfo.usercard AND TIME LIKE '%' ? '%' GROUP BY usercard ) price FROM userinfo"; PreparedStatement pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql); //运行结果集 pst.setString(1, month); ResultSet rs=pst.executeQuery(); //处理结果集 List<cost> list=new ArrayList<cost>(); while(rs.next()){ cost cost=new cost(); cost.setUsername(rs.getString(1)); cost.setUsercard(rs.getString(2)); cost.setRoom_num(rs.getInt(3)); cost.setPrice(rs.getString(4)); list.add(cost); }//释放资源 JDBCUtils.close(rs, pst, conn); //返回一个list集合给前台 return list ; }