问题
如何访问数据集中的特定数据?
Python 和 Pandas 如何帮助我分析数据?
目标
描述什么是基于 0 的索引。
使用列标题和索引位置操作和提取数据。
使用切片从 DataFrame 中选择数据集。
使用标签和基于整数的索引来选择数据帧中的数据范围。
在 DataFrame 的子集中重新分配值。
创建 DataFrame 的副本。
使用以下运算符使用一组条件查询/选择数据子集:
==,!=,>,<,>=,<=。使用掩码定位数据子集。
在 Python 中描述 BOOLEAN 对象并使用 BOOLEAN 操作数据。
在本课的第一集中,我们将一个 CSV 文件读入 Pandas 的 DataFrame。我们学会了如何:
- 将 DataFrame 保存到命名对象,
- 对数据进行基础数学运算,
- 计算汇总统计数据,以及
- 根据我们加载到 Pandas 中的数据创建绘图。
在本课中,我们将探索使用以下方法访问数据不同部分的方法:
- 索引,
- 切片,和
- 子集。
加载我们的数据
我们将继续使用我们在上一集中使用的调查数据集。让我们重新打开并再次读入数据:
# Make sure pandas is loaded import pandas as pd # Read in the survey CSV surveys_df = pd.read_csv("data/surveys.csv")
Python 中的索引和切片
我们经常想使用DataFrame对象的子集。有多种方法可以实现这一点,包括:使用标签(列标题)、数字范围或特定的 x,y 索引位置。
使用标签(列标题)选择数据
我们使用方括号[]来选择 Python 对象的子集。例如,我们可以species_id从surveys_df DataFrame 按名称命名的列中选择所有数据。有两种方法可以做到这一点:
# TIP: use the .head() method we saw earlier to make output shorter # Method 1: select a 'subset' of the data using the column name surveys_df['species_id'] # Method 2: use the column name as an 'attribute'; gives the same output surveys_df.species_id
我们还可以创建一个仅包含species_id列中数据的新对象, 如下所示:
# Creates an object, surveys_species, that only contains the `species_id` column surveys_species = surveys_df['species_id']
我们也可以传递列名列表,作为按该顺序选择列的索引。当我们需要重新组织数据时,这很有用。
注意:如果 DataFrame 中不包含列名,则会引发异常(错误)。
# Select the species and plot columns from the DataFrame surveys_df[['species_id', 'plot_id']] # What happens when you flip the order? surveys_df[['plot_id', 'species_id']] # What happens if you ask for a column that doesn't exist? surveys_df['speciess']
Python 在回溯中告诉我们它是什么类型的错误,在底部它说 KeyError: 'speciess'这意味着这speciess不是有效的列名(也不是相关 Python 数据类型字典中的有效键)。
提醒
Python 语言及其模块(例如 Pandas)定义了在分配对象和变量名称时不应用作标识符的保留字。的在Python保留字实例包括布尔值
True和False,运营商and,or和not,等等。在https://docs.python.org/3/reference/lexical_analysis.html#identifiers 中提供了 Python 版本 3 的完整保留字列表 。在命名对象和变量时,避免使用内置数据结构和方法的名称也很重要。例如,列表是一种内置数据类型。例如,可以使用单词“list”作为新对象的标识符
list = ['apples', 'oranges', 'bananas']。但是,您将无法使用创建空列表list()或使用将元组转换为列表list(sometuple)。
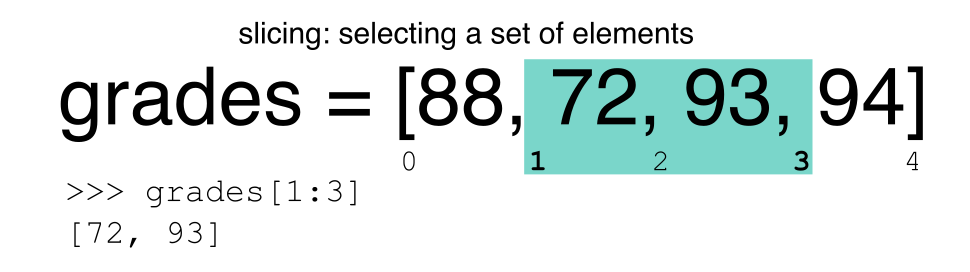
提取基于范围的子集:切片
提醒
Python 使用基于 0 的索引。
让我们提醒自己,Python 使用基于 0 的索引。这意味着对象中的第一个元素位于位置 0。这与其他工具(如 R 和 Matlab)不同,它们在对象中索引从 1 开始的元素。
# Create a list of numbers:
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
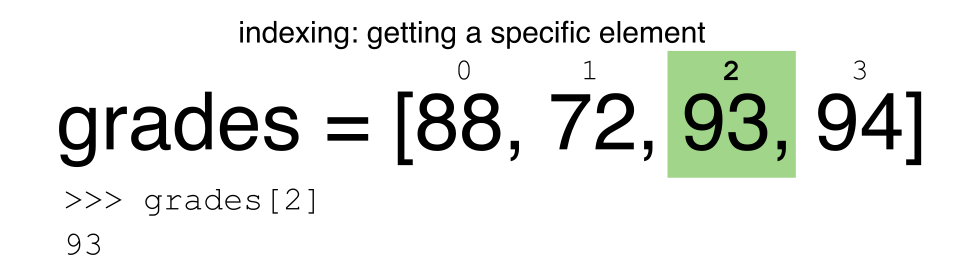
挑战 - 提取数据
下面的代码返回什么值?
a[0]这个怎么样:
a[5]在上面的例子中,调用
a[5]返回一个错误。这是为什么?关于什么?
a[len(a)]
在 Python 中对行的子集进行切片
使用[]运算符切片从 DataFrame 中选择一组行和/或列。要切出一组行,请使用以下语法: data[start:stop]. 在 Pandas 中切片时,起始边界包含在输出中。停止边界是您要选择的行之外的一步。因此,如果您想选择第 0、1 和 2 行,您的代码将如下所示:
# Select rows 0, 1, 2 (row 3 is not selected)
surveys_df[0:3]
Python 中的停止边界与您在 Matlab 和 R 等语言中可能习惯的不同。
# Select the first 5 rows (rows 0, 1, 2, 3, 4)
surveys_df[:5]
# Select the last element in the list
# (the slice starts at the last element, and ends at the end of the list)
surveys_df[-1:]
我们还可以在 DataFrame 的子集中重新分配值。
但在此之前,让我们先看看 Python 中复制对象的概念和引用对象的概念之间的区别。
在 Python 中复制对象与引用对象
让我们从一个例子开始:
# Using the 'copy() method' true_copy_surveys_df = surveys_df.copy() # Using the '=' operator ref_surveys_df = surveys_df
您可能认为该代码ref_surveys_df = surveys_df创建了surveys_dfDataFrame 对象的新副本。但是,= 在简单语句y = x中使用运算符不会创建我们的 DataFrame 的副本。相反,y = x创建一个新变量y,该变量引用所引用的 同一对象x。为了说明这一点的另一种方式,只有 一个对象(数据帧),都x和y参考。
相比之下,copy()DataFrame的方法创建了 DataFrame 的真实副本。
让我们看看当我们重新分配引用另一个 DataFrame 对象的 DataFrame 子集中的值时会发生什么:
# Assign the value `0` to the first three rows of data in the DataFrame ref_surveys_df[0:3] = 0
让我们试试下面的代码:
# ref_surveys_df was created using the '=' operator ref_surveys_df.head() # surveys_df is the original dataframe surveys_df.head()
这两个数据框有什么区别?
当我们为前 3 列分配0使用 ref_surveys_dfDataFrame的值时,surveys_dfDataFrame 也被修改。请记住,我们在执行ref_surveys_df时创建了上面的引用对象 ref_surveys_df = surveys_df。请记住surveys_df并ref_surveys_df 引用相同的 DataFrame 对象。如果其中任何一个更改了对象,另一个将看到对参考对象的相同更改。
回顾和回顾:
-
复制使用数据框的
copy()方法true_copy_surveys_df = surveys_df.copy() -
甲参考被使用所创建的
=操作员ref_surveys_df = surveys_df
好了,这就够了。让我们从原始数据 CSV 文件创建一个全新的干净数据框。
surveys_df = pd.read_csv("data/surveys.csv")
在 Python 中对行和列的子集进行切片
我们可以使用标签或基于整数的索引在行和列方向上选择特定范围的数据。
loc主要是基于标签的索引。可以使用整数,但它们被解释为标签。iloc主要是基于整数的索引
要从我们的 DataFrame 中选择行和列的子集,我们可以使用该 iloc方法。例如,我们可以选择月、日和年(如果我们从 1 开始计数,则为第 2、3 和 4 列),如下所示:
# iloc[row slicing, column slicing] surveys_df.iloc[0:3, 1:4]
这给出了输出
month day year
0 7 16 1977
1 7 16 1977
2 7 16 1977
请注意,我们要求从 0:3 获取切片。这产生了 3 行数据。当您要求 0:3 时,您实际上是在告诉 Python 从索引 0 开始并选择行 0, 1, 2直到但不包括 3。
让我们探索一些其他方法来索引和选择数据子集:
# Select all columns for rows of index values 0 and 10 surveys_df.loc[[0, 10], :] # What does this do? surveys_df.loc[0, ['species_id', 'plot_id', 'weight']] # What happens when you type the code below? surveys_df.loc[[0, 10, 35549], :]
注意:必须在 DataFrame 中找到标签,否则您将获得一个KeyError.
按标签索引loc不同于按整数索引iloc。使用 时loc,起始边界和终止边界都包含在内。使用时loc,可以使用 整数,但整数指的是索引标签而不是位置。例如,使用loc和选择 1:4 将获得与使用iloc1:4 选择行不同的结果。
我们还可以使用 DataFrame 中的行和列位置和iloc索引来选择特定的数据值:
# Syntax for iloc indexing to finding a specific data element dat.iloc[row, column]
在这个iloc例子中,
surveys_df.iloc[2, 6]
给出输出
'F'
请记住,Python 索引从 0 开始。因此,索引位置 [2, 6] 选择 DataFrame 中向下 3 行和 7 列的元素。
挑战 - 范围
执行时会发生什么:
surveys_df[0:1]surveys_df[:4]surveys_df[:-1]调用时会发生什么:
surveys_df.iloc[0:4, 1:4]surveys_df.loc[0:4, 1:4]
- 这两个命令有何不同?
使用标准对数据进行子集化
我们还可以使用标准选择数据的子集。例如,我们可以选择年份值为 2002 的所有行:
surveys_df[surveys_df.year == 2002]
产生以下输出:
record_id month day year plot_id species_id sex hindfoot_length weight
33320 33321 1 12 2002 1 DM M 38 44
33321 33322 1 12 2002 1 DO M 37 58
33322 33323 1 12 2002 1 PB M 28 45
33323 33324 1 12 2002 1 AB NaN NaN NaN
33324 33325 1 12 2002 1 DO M 35 29
...
35544 35545 12 31 2002 15 AH NaN NaN NaN
35545 35546 12 31 2002 15 AH NaN NaN NaN
35546 35547 12 31 2002 10 RM F 15 14
35547 35548 12 31 2002 7 DO M 36 51
35548 35549 12 31 2002 5 NaN NaN NaN NaN
[2229 rows x 9 columns]
或者我们可以选择所有不包含 2002 年的行:
surveys_df[surveys_df.year != 2002]
我们也可以定义一组标准:
surveys_df[(surveys_df.year >= 1980) & (surveys_df.year <= 1985)]
Python 语法备忘单
当从 DataFrame 按条件查询数据时,我们可以使用以下语法。尝试选择“调查”数据的各种子集。
- 等于:
== - 不等于:
!= - 大于、小于:
>或< - 大于或等于
>= - 小于或等于
<=
挑战 - 查询
在
surveys_dfDataFrame 中选择包含 1999 年数据且权重值小于或等于 8的行子集。您最终得到了多少行?你的邻居得到了什么?您可以使用
isinPython 中的命令根据值列表查询 DataFrame,如下所示:surveys_df[surveys_df['species_id'].isin([listGoesHere])]使用该
isin函数在“调查”数据框中查找包含特定物种的所有图。有多少记录包含这些值?
尝试其他查询。创建一个查询,查找权重值 > 或等于 0 的所有行。
~Python 中的符号可用于返回您在 Python 中指定的选择的 OPPOSITE。它相当于不在 中。编写一个查询,选择“surveys”数据中性别不等于“M”或“F”的所有行。
使用掩码识别特定情况
甲掩模可以是有用的,可找到存在值的特定子集或不存在-例如,NaN时,或“不是数”的值。要理解掩码,我们还需要理解BOOLEANPython 中的对象。
布尔值包括True或False。例如,
# Set x to 5
x = 5
# What does the code below return?
x > 5
# How about this?
x == 5
当我们询问 Python 是否x大于 5 时,它返回False。这是 Python 说“不”的方式。确实,的值为x5,5不大于5。
创建布尔掩码:
- 设置真/假标准(例如
values > 5 = True) - 然后 Python 将评估对象中的每个值,以确定该值是否符合条件 (True) 或不符合 (False)。
- Python 创建一个与原始对象形状相同的输出对象,但每个索引位置都有一个
True或False值。
让我们试试这个。让我们确定调查数据中具有空(缺失或 NaN)数据值的所有位置。我们可以使用isnull方法来做到这一点。该isnull方法将每个单元格与空值进行比较。如果元素具有空值,则将True在输出对象中为其分配值 。
pd.isnull(surveys_df)
输出的片段如下:
record_id month day year plot_id species_id sex hindfoot_length weight
0 False False False False False False False False True
1 False False False False False False False False True
2 False False False False False False False False True
3 False False False False False False False False True
4 False False False False False False False False True
[35549 rows x 9 columns]
要选择有空值的行,我们可以使用掩码作为索引来对数据进行子集,如下所示:
# To select just the rows with NaN values, we can use the 'any()' method surveys_df[pd.isnull(surveys_df).any(axis=1)]
请注意,weight我们 DataFrame的列包含许多null或NaN 值。我们将在下一集中的数据类型和格式中探讨处理这个问题的方法。
我们也可以isnull在特定的列上运行。下面的代码有什么作用?
# What does this do? empty_weights = surveys_df[pd.isnull(surveys_df['weight'])]['weight'] print(empty_weights)
让我们花一点时间来看看上面的语句。我们使用 Boolean 对象pd.isnull(surveys_df['weight'])作为 的索引surveys_df。我们要求 Python 选择具有NaN权重值的行。
挑战 - 把一切放在一起
创建一个新的 DataFrame,它只包含性别值不是女性或男性的观察值。将新 DataFrame 中的每个性别值分配给新值“x”。确定子集中空值的数量。
创建一个仅包含性别为男性或女性且权重值大于 0 的观测值的新 DataFrame。
关键点
在 Python 中,可以使用索引、切片、列标题和基于条件的子集来访问部分数据。
Python 使用基于 0 的索引,其中列表、元组或任何其他数据结构中的第一个元素的索引为 0。
Pandas 支持常见的数据探索步骤,例如数据索引、切片和条件子集。