控制相关度
相关度评分背后的理论
如何计算评分的
Lucene 使用布尔模型(Boolean model) 查找匹配文档 并主要的借鉴了 词频/逆向文档频率(term frequency/inverse document frequency) 和 向量空间模型(vector space model),同时加入 协调因子 字段长度归一化 以及词或查询语句权重提升
- 布尔模型
就是在查询中使用 AND 、 OR 和 NOT (与、或和非) 来匹配文档 - 词频/逆向文档频率(TF/IDF)
一个文档的相关度评分部分取决于每个查询词在文档中的 权重
词的权重由三个因素决定 -
词频
词在文档中出现的频度是多少? 频度越高,权重 越高
tf(t in d) = √frequency 词 t 在文档 d 的词频( tf )是该词在文档中出现次数的平方根 -
逆向文档频率
词在集合所有文档里出现的频率是多少?频次越高,权重 越低
vidf(t) = 1 + log ( numDocs / (docFreq + 1)) 词 t 的逆向文档频率( idf )是:索引中文档数量除以所有包含该词的文档数,然后求其对数 -
字段长度归一值
字段的长度是多少? 字段越短,字段的权重 越高 。
norm(d) = 1 / √numTerms 字段长度归一值( norm )是字段中词数平方根的倒数
对于 not_analyzed 字符串字段的归一值默认是禁用的
** 通过实例查询,来看评分是如何计算的**
GET product/base/_search
{
"size": 1,
"explain": true,
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "上海"
}
}
}展示出的explanation 内容
{
"took": 17,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 19,
"max_score": 4.266216,
"hits": [
{
"_shard": "[product_v3][3]",
"_node": "N_gFl4xjTNmIxr9SY9FAQw",
"_index": "product_v3",
"_type": "base",
"_id": "1-134473",
"_score": 4.266216,
"_source": {
"productSource": 1,
"departureCitys": [
"上海"
],
"keywords": [
"上海",
"哈哈"
],
"pattern": "101",
"buyQuantity": 34,
"managerRecommend": "111。",
"averageScore": 0,
"themes": [
{
"category": "游玩景点",
"items": [
{
"code": 4724,
"name": "太原+五台山+大同+平遥"
}
]
}
],
"installmentFlag": 0,
"madeType": 0,
"bussinessProductId": "1-134473",
"attribute": 91,
"supplierName": "春秋旅游",
"passbyCities": [
"上海"
],
"pictureLabels": [],
"productId": 134473,
"weight": 22,
"picture": "http://webresourcetest.springtour.com/Images/gallery/201702/43362c75-91ae-43af-8cfd-85b43ec9199e_201702211501_500_350.jpg",
"productThemes": [
"太原+五台山+大同+平遥"
],
"brandId": 2,
"name": "上海3日2晚上海名牌",
"dayNum": 3,
"online": 1
},
"_explanation": {
"value": 4.266216,
"description": "sum of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 4.266216,
"description": "weight(name:上海 in 54) [PerFieldSimilarity], result of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 4.266216,
"description": "score(doc=54,freq=2.0 = termFreq=2.0
), product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 2.730029,
"description": "idf, computed as log(1 + (docCount - docFreq + 0.5) / (docFreq + 0.5)) from:",
"details": [
{
"value": 4,
"description": "docFreq",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 68,
"description": "docCount",
"details": []
}
]
},
{
"value": 1.5626998,
"description": "tfNorm, computed as (freq * (k1 + 1)) / (freq + k1 * (1 - b + b * fieldLength / avgFieldLength)) from:",
"details": [
{
"value": 2,
"description": "termFreq=2.0",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1.2,
"description": "parameter k1",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 0.75,
"description": "parameter b",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 12.411765,
"description": "avgFieldLength",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 7.111111,
"description": "fieldLength",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
}
]
},
{
"value": 0,
"description": "match on required clause, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0,
"description": "# clause",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1,
"description": "_type:base, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "boost",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 1,
"description": "queryNorm",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
}
]
}
}由于展示的内容过多,我们将其简化 就会简化到下面这样的主干
weight(text:上海 in 0) [PerFieldSimilarity]: 0.15342641 // 词 fox 在文档的内部 Lucene doc ID 为 0 ,字段是 text 里的最终评分
result of:
fieldWeight in 0 0.15342641
product of:
tf(freq=1.0), with freq of 1: 1.0 //词 上海 在该文档 text 字段中只出现了一次。
idf(docFreq=1, maxDocs=1): 0.30685282 //上海 在所有文档 text 字段索引的逆向文档频率。
fieldNorm(doc=0): 0.5 // 该字段的字段长度归一值。- 但是问题来了,我们通常来说都不是一个字段查询,而是多个字段。这样我们就有一个合并多词权重----- 向量空间模型(vector space model )
向量空间模型是将文档和查询都以向量的形式表示
向量实际上就是包含多个数的一维数组
[1,2,5,22,3,8]
在向量空间模型里, 向量空间模型里的每个数字都代表一个词的 权重 。
如果我们查询 happy hippopotamus 因为happy 比较常见,所以这个词的权重较低假设为2。另外一个词hippopotamus 不经常见,所以权重交大假设为5 。所以我们创建一个二维向量[2,5] ——在坐标系下作条直线,线的起点是 (0,0) 终点是 (2,5)
happy hippopotamus” 的二维查询向量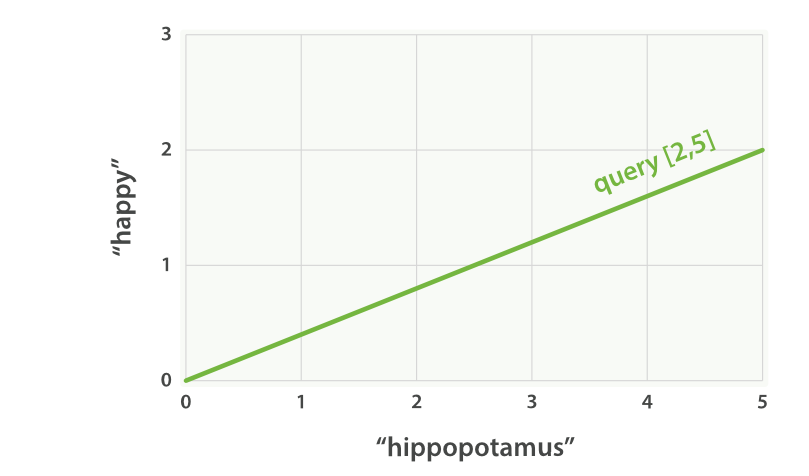
假设我们有三个文档
- I am happy in summer 。
- After Christmas I’m a hippopotamus 。
- The happy hippopotamus helped Harry 。
我们为每个文档创建包含每个查询此 的权重向量
- 文档 1: (happy,____________) —— [2,0]
- 文档 2: ( ___ ,hippopotamus) —— [0,5]
- 文档 3: (happy,hippopotamus) —— [2,5]
happy hippopotamus” 查询及文档向量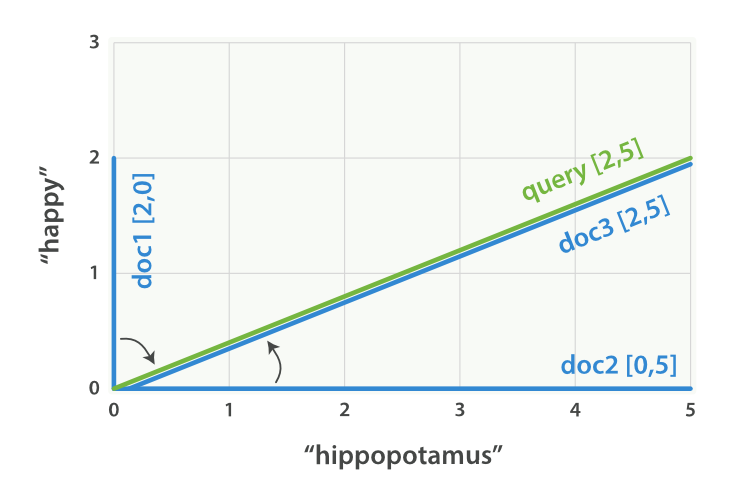
向量之间是可以比较的,只要测量查询向量和文档向量之间的角度就可以得到每个文档的相关度
我们只是利用二维的演示这个原理,其实在现实中 肯定有多于两个的。这样的我们可以使用线性代数 ——作为数学中处理向量的一个分支——为我们提供了计算两个多维向量间角度工具
为什么向量之间的角度可以表示他们的相关度 使用了 余弦近似度(cosine similarity)。
Lucene 的实用评分函数
在一个多词查询中,ES是如何对这些多词进行处理的呢?
Lucene 使用 布尔模型(Boolean model) 、 TF/IDF 以及 向量空间模型(vector space model) ,然后将它们组合到单个高效的包里以收集匹配文档并进行评分计算
我们使用例子来看多词查询 是怎么转化为基本查询的
GET /my_index/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"text": "quick fox"
}
}
}
会在内部被重写为
GET /my_index/doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{"term": { "text": "quick" }},
{"term": { "text": "fox" }}
]
}
}
}bool 查询实现了布尔模型
- 要是匹配到数据 我们使用实用评分函数 进行计算评分
实用评分函数 计算公式
score(q,d) = //文档 d 与查询 q 的相关度评分。
queryNorm(q) //查询归一化 因子
· coord(q,d) //协调 因子
· ∑ ( //查询 q 中每个词 t 对于文档 d 的权重和
tf(t in d) //词 t 在文档 d 中的 词频 。
· idf(t)² //词 t 的 逆向文档频率
· t.getBoost() //查询中使用的 boost(
· norm(t,d) //是 字段长度归一值 ,与 索引时字段层 boost (如果存在)的和
) (t in q) 查询归一因子 queryNorm
查询归一因子 ( queryNorm )试图将查询 归一化 , 这样就能将两个不同的查询结果相比较。
查询协调
协调因子 ( coord ) 可以为那些查询词包含度高的文档提供奖励,文档里出现的查询词越多,它越有机会成为好的匹配结果。
索引时字段层权重提升
在索引时对这个字段上的数据进行权重的提升
不推荐这样使用
- 会丢失长度归一值的精度
- 索引后的文档不可更改,需要重新创建文档
- 索引时权重提升的字段有多个值,提升值会按照每个值来自乘,这会导致该字段的权重急剧上升。
查询时权重提升
查询脚本
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "quick brown fox",
"boost": 2
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"content": "quick brown fox"
}
}
]
}
}
}** 将 boost 设置为 2 ,并不代表最终的评分 _score 是原值的两倍;实际的权重值会经过归一化和一些其他内部优化过程**
-
提升索引权重
当在多个索引中搜索时, 可以使用参数 indices_boost 来提升整个索引的权重GET /docs_2014_*/_search
{
"indices_boost": {
"docs_2014_10": 3,
"docs_2014_09": 2
},
"query": {
"match": {
"text": "quick brown fox"
}
}
} -
t.getBoost()
权重提升不会被应用于它在查询表达式中出现的层,而是会被合并下转至每个词中。 t.getBoost() 始终返回当前词的权重或当前分析链上查询的权重
使用查询结构修改相关度
假如一个业务场景,我们想搜索Apple,但是我们可能会返回水果 食谱和公司,我们可以使用must_not语句来排除我们不想要的,而将结果范围缩小在Apple公司的相关的结果
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"text": "apple"
}
},
"must_not": {
"match": {
"text": "pie tart fruit crumble tree"
}
}
}
}
}但是我们会不会发现,使用这种方法是不是过于严格了?会不会使我们遗漏一些我们所需要的数据呢?
我们乐意使用 权重提升查询 方法
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"match": {
"text": "apple"
}
},
"negative": {
"match": {
"text": "pie tart fruit crumble tree"
}
},
"negative_boost": 0.5
}
}
}操作的过程就是那些匹配 positive 查询的文档罗列出来,对于那些同时还匹配 negative 查询的文档将通过文档的原始 _score 与 negative_boost 相乘的方式降级
function_score 查询 的作用
- 允许为每个与主查询匹配的文档应用一个函数, 以达到改变甚至完全替换原始查询评分 _score
- 也可使用过滤器对结果的子集应用不同的函数
- 预定义的函数有下面这些
- weight 权重,提升值
- field_value_factor 使用这个值来修改_score
- random_score ,每个用户产生随机排序,对具体用户,看到的顺序始终是一致的
- 预定义的函数有下面这些
- 衰减函数 -- lineear exp gauss
- script_score 也可以自己使用自定义脚本完全控制平均分计算、
根据产品的属性来提升权重
下面我们使用下面的这个查询来演示我们提升权重的过程
使用function_score
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {//function_score 查询将主查询和函数包括在内
"query": {//先查询主查询
"multi_match": {
"query": "上海",
"fields": ["name", "keywords"]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {field_value_factor 函数会被应用到每个与主 query 匹配的文档
"field": "averageScore"//使用这个字段对score值进行计算
}
}
}
}
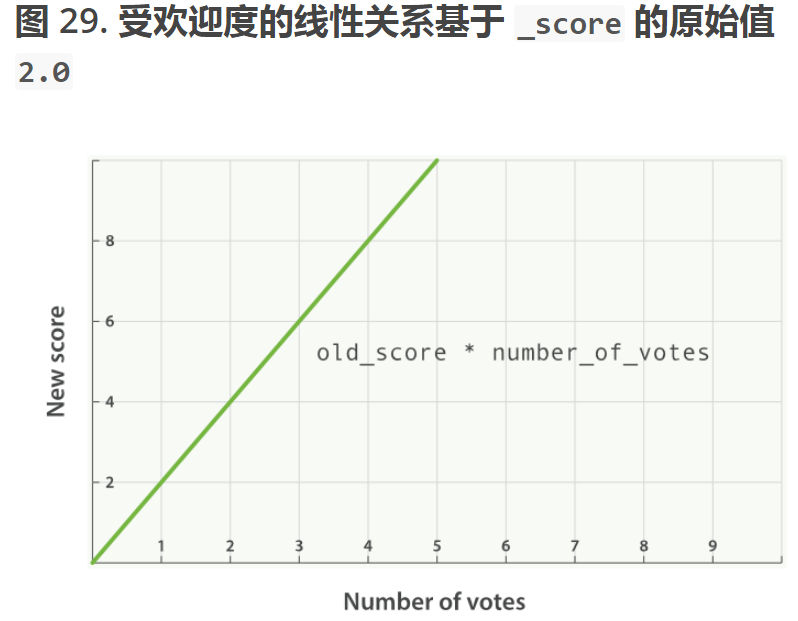
//每个文档的最终评分score做了下面的修改
new_score = old_score * number_of_votes-
这样的话,我们的score值会根据成这样的比例增长
- 我们可以根据更改modifyer 属性来更改变换score函数的 类型
- 假如我们使用log1p 参数值,那么我们的公式会如下的
- new_score = old_score * log(1 + number_of_votes)
我们的score值的变化趋势将是这样的
- new_score = old_score * log(1 + number_of_votes)
带modifyer 参数的请求
GET /blogposts/post/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "popularity",
"fields": [ "title", "content" ]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "votes",
"modifier": "log1p"
}
}
}
}修饰词 modifyer 值可以为多种
- none 默认
- log 取对数值
- log1p 加1 取对数值
- log2p 加2 取对数值
- ln 去自然对数
- ln1p 加一 取自然对数
- ln2p 加2 取自然对数
- square 取平方
- sqrt 开根号
- reciprocal 倒数
factor
-
使用指定字段与factor 的积来调节score的值
我们通过在factor属性添加值来改变scoreGET product/_search
使用过factor 的计算是这样的
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "上海",
"fields": ["name","keywords" ]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "buyQuantity",
"modifier": "ln2p",
"factor": 2
}
}
}
}
new_score = old_score * log(2 + factor * buyQuantity) -
在函数图表上显示的话,就是这样的

boost_mode
- 此属性控制 来控制函数和查询评分score合并后的结果
- multiply 与 评分score函数值的积(默认)
- sum 和
- min 较小的值
- max 较大的值
- replace 代替score
请求参数
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "上海",
"fields": ["name","keywords" ]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "buyQuantity",
"modifier": "ln2p",
"factor": 2
},
"boost_mode": "sum" //修改此参数
}
}
}
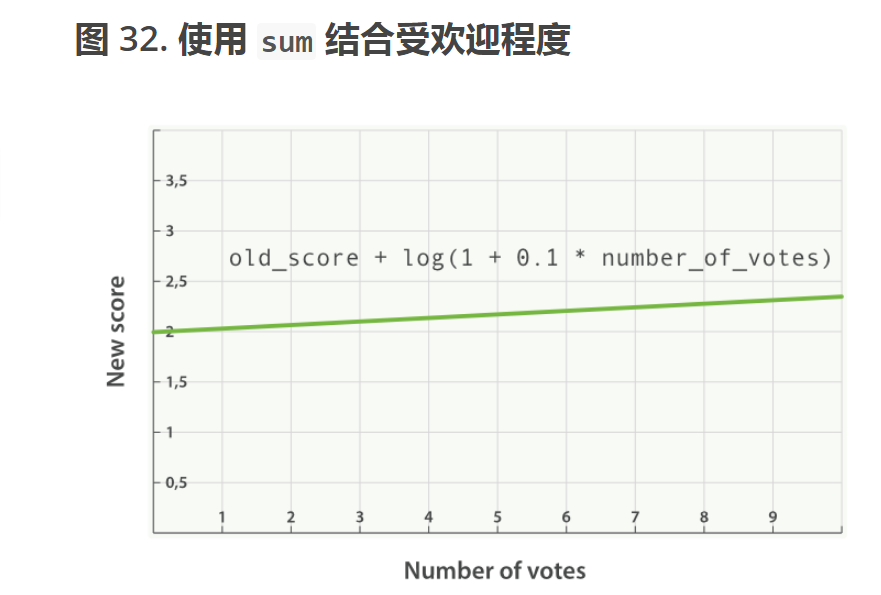
//现在我们的计算得分的函数是这样的
new_score = old_score + log(2 + 2 * buyQuantity)
max_boost
- 可以使用 max_boost 参数限制一个函数的最大效果
过滤集提升权重
通过整合多个函数,来提升权重信息
整合多个函数的查询
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"filter": { //function_score 查询有个 filter 过滤器而不是 query 查询
"term": { "name": "上海" }
},
"functions": [ //functions 关键字存储着一个将被应用的函数列表
{
"filter": { "term": { "name": "杭州" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "name": "北京" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "name": "三亚" }},
"weight": 2 //三亚 比其他特性更重要,所以它有更高 weight
}
],
"score_mode": "sum" score_mode 指定各个函数的值进行组合运算的方式。
}
}
}- 过滤和查询
- function_score 查询接受 query 或 filter ,如果没有特别指定,则默认使用 match_all 查询
- 函数functions
- functions 关键字保持着一个将要被使用的函数列表
- 函数只会被应用到那些与过滤器匹配的文档
- score_mode 评分模式
- multiply 函数结果 积
- sum 函数结果 和
- avg 函数结果 平均值
- max 函数结果 最大值
- min 函数结果 最小
- first 使用的首个函数的结构作为结果
随机评分
random_score 函数的作用
andom_score 函数会输出一个 0 到 1 之间的数, 当种子 seed 值相同时,生成的随机结果是一致的
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"filter": {
"term": { "city": "Barcelona" }
},
"functions": [
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "wifi" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "garden" }},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "term": { "features": "pool" }},
"weight": 2
},
{
"random_score": {
"seed": "the users session id"
}
}
],
"score_mode": "sum"
}
}
}
// 1 **random_score** 语句没有任何过滤器 filter ,所以会被应用到所有文档
// 2 将用户的会话 ID 作为种子 seed ,让该用户的随机始终保持一致,相同的种子 seed 会产生相同的随机结果。越近越好
function_score 查询会提供一组 衰减函数(decay functions) , 让我们有能力在两个滑动标准,如地点和价格,之间权衡
三种衰减函数
- linear 线性
- exp 指数
- gauss 高斯函数
三个函数接受下面的参数,作为函数的变化曲线值
origin - 中心点 或字段可能的最佳值,落在原点 origin 上的文档评分 _score 为满分 1.0
scale - 衰减率,即一个文档从原点 origin 下落时,评分 _score 改变的速度
decay - 从原点 origin 衰减到 scale 所得的评分 _score ,默认值为 0.5
offset -
以原点 origin 为中心点,为其设置一个非零的偏移量 offset 覆盖一个范围,而不只是单个原点。在范围 -offset <= origin <= +offset 内的所有评分 _score 都是 1.0
下面的是衰减函数曲线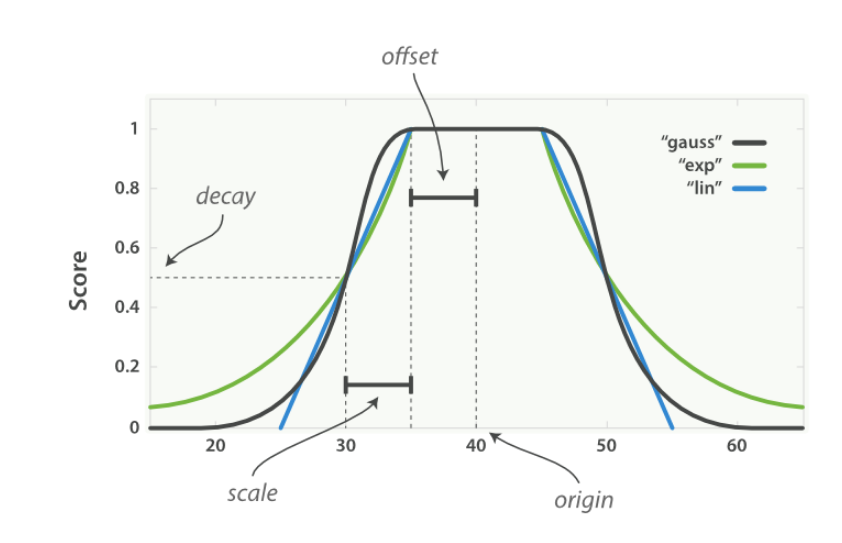
- linear 线性函数
- exp 指数函数 先快后慢
-
gauss 高斯函数 先慢后快最后慢
脚本实例
GET product/base/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {},
"functions": [
{
"gauss": {
"averageScore": {
"origin": "100",
"scale": "20",
"offset": "50"
}
}
},
{
"exp": {
"productId": {
"origin": "1500",
"scale": "100",
"offset": "50"
}
},
"weight": 2
}
]
}
}
}脚本评分
可插拔的相似算法
- ES默认使用 Lucene 的实用评分函数
- 也支持其他类型相似算法
- BM25
- Classic similarity
- DFR similarity
- DFI similarity
- IB similarity
- LM similarity
- Okapi BM25
- 此相似度算法是比较好的算法
- BM25 源自 概率相关模型(probabilistic relevance model) ,而不是向量空间模型
- 词频饱和度
- 某个词出现的次数对得分计算的作用
TF/IDF 与 BM25 的词频饱和度 的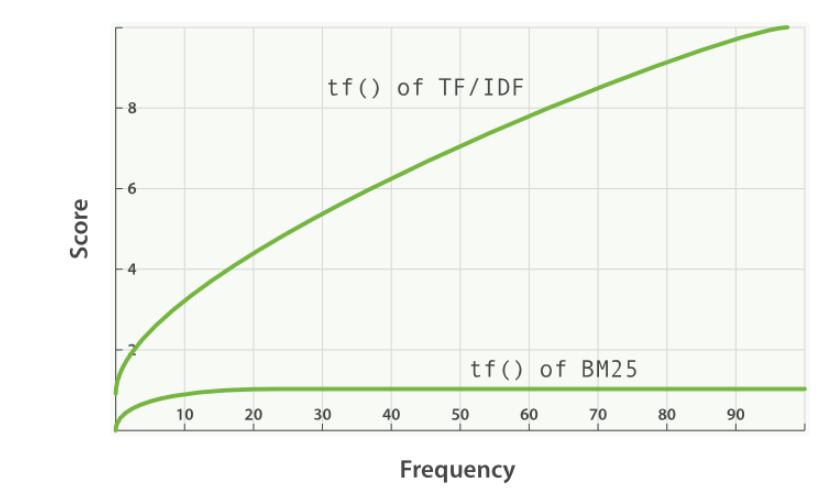
- 某个词出现的次数对得分计算的作用
- 字段长度归一化
- Lucene 会认为较短字段比较长字段更重要
- BM25 当然也认为较短字段应该有更多的权重,但是它会分别考虑每个字段内容的平均长度
- BM 25 调优
- BM 25 可以提供参数进行调优
- k1
- 这个参数控制着词频结果在词频饱和度中的上升速度。默认值为 1.2 。值越小饱和度变化越快,值越大饱和度变化越慢
- b
- 这个参数控制着字段长归一值所起的作用, 0.0 会禁用归一化, 1.0 会启用完全归一化。默认值为 0.75
更改相似度
在做字段映射的时候进行更改相似度
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "BM25" // title 字段使用 BM25 相似度算法
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "default"
// body 字段用默认相似度算法
}
}
}
}Elasticsearch 不支持更改已有字段的相似度算法 similarity 映射
配置BM25相似度
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"similarity": {
"my_bm25": { //创建一个基于内置 BM25 ,名为 my_bm25 的自定义相似度算法
"type": "BM25",
"b": 0
//禁用字段长度规范化(field-length normalization)
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "my_bm25"
//title 字段使用自定义相似度算法 my_bm25
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"similarity": "BM25"
//字段 body 使用内置相似度算法 BM25
}
}
}
}
}