题意
两个企鹅,一个从地图的右下角走右上角,一个从另一个地图的左下角走到左上角,我们操控左边的企鹅,右边的企鹅与左边企鹅运动规则如下。
- 左边企鹅向左,右边企鹅向右
- 左边企鹅向右,右边企鹅向左
- 左边企鹅向上,右边企鹅向上
- 左边企鹅向下,右边企鹅向下
与此同时,如果左右企鹅遇到了障碍,或者遇到了越界情况,那么这一步就作废。
求最小步数,并且给出字典序最小的方向变化,以及用('A')来体现运动路径。
解题:
说实话真的没见过(bfs)还能这样玩的,假设只有一只企鹅那么设状态就(d[x][y]),那么两只企鹅就是(d[x1][y1][x2][y2])就好了呀,剩下的就是正常的(bfs)过程,对于队列的类型我是用的结构体,看北大大佬的代码使用的元组类型,至于记录路径以及方向,那么就是老套路了,用g数组记录就行。
细节:
- 要求输出方向字典序最小,那么就是轮询的方向就是下、左、右、上了。
- 对于切换方向,如果1异或3等于2,2异或3等于1,很巧妙。
- 处理输入,题目直接给了这样一个输入,两个地图用空格隔开,我可能直接用字符数组一次性保存两个了,处理起来肯定贼麻烦。

但是可以这样,直接保存两个地图。
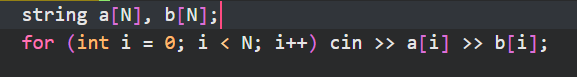
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 20;
#define x first
#define y second
string a[N], b[N];
int d[N][N][N][N];
int dx[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1}, dy[4] = {0, -1, 1, 0};
struct node {
int x1, y1, x2, y2, i;
}rem[N][N][N][N];
int another(int i) {
if (i == 1 || i == 2) return i ^ 3;
else return i;
}
PII move(string g[], int x, int y, int i) {
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if (xx < 0 || xx >= N || yy < 0 || yy >= N || g[xx][yy] == '#') return {x, y};
return {xx, yy};
}
void bfs() {
memset(d, -1, sizeof d);
queue<node> q;
q.push({N - 1, N - 1, N - 1, 0});
d[N - 1][N - 1][N - 1][0] = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
PII leftP = move(a, t.x1, t.y1, i);
PII rightP = move(b, t.x2, t.y2, another(i));
if (d[leftP.x][leftP.y][rightP.x][rightP.y] == -1) {
d[leftP.x][leftP.y][rightP.x][rightP.y] = d[t.x1][t.y1][t.x2][t.y2] + 1;
rem[leftP.x][leftP.y][rightP.x][rightP.y] = {t.x1, t.y1, t.x2, t.y2, i};
q.push({leftP.x, leftP.y, rightP.x, rightP.y});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
string a[N], b[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
bfs();
cout << d[0][N - 1][0][0] << endl;
int ex1 = 0, ey1 = N - 1, ex2 = 0, ey2 = 0;
string res = "";
while (true) {
a[ex1][ey1] = b[ex2][ey2] = 'A';
if (ex1 == N - 1 && ey1 == N - 1 && ex2 == N - 1 && ey2 == 0) break;
auto t = rem[ex1][ey1][ex2][ey2];
int x1 = t.x1, y1 = t.y1, x2 = t.x2, y2 = t.y2, i = t.i;
string dir = "DLRU";
res += dir[i];
ex1 = x1, ey1 = y1, ex2 = x2, ey2 = y2;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
cout << res << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " " << b[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}