项目需要画一个类似知识图谱的节点关系图。
一开始用的是echart画的。
根据https://gallery.echartsjs.com/editor.html?c=xH1Rkt3hkb,成功画出简单的节点关系。
如图:
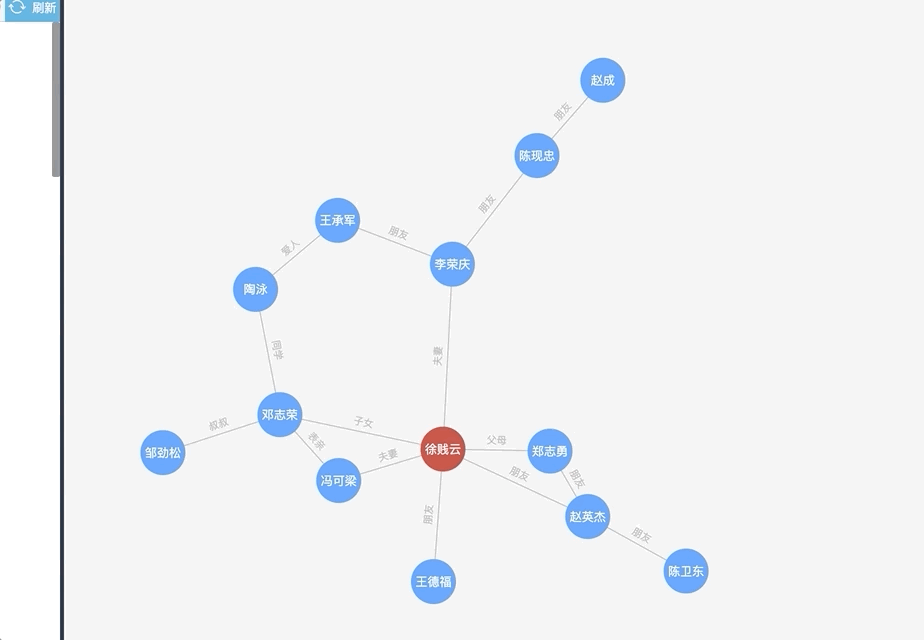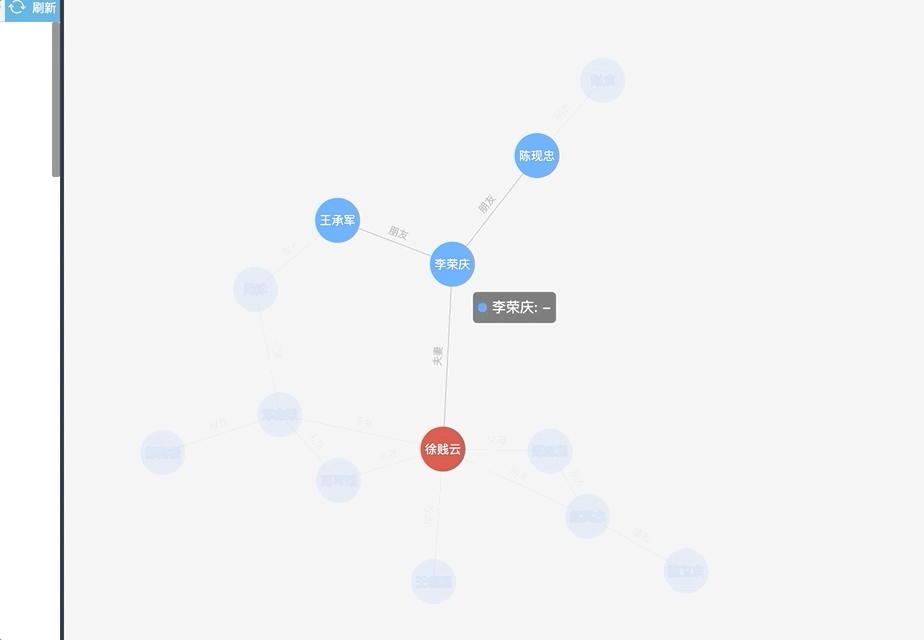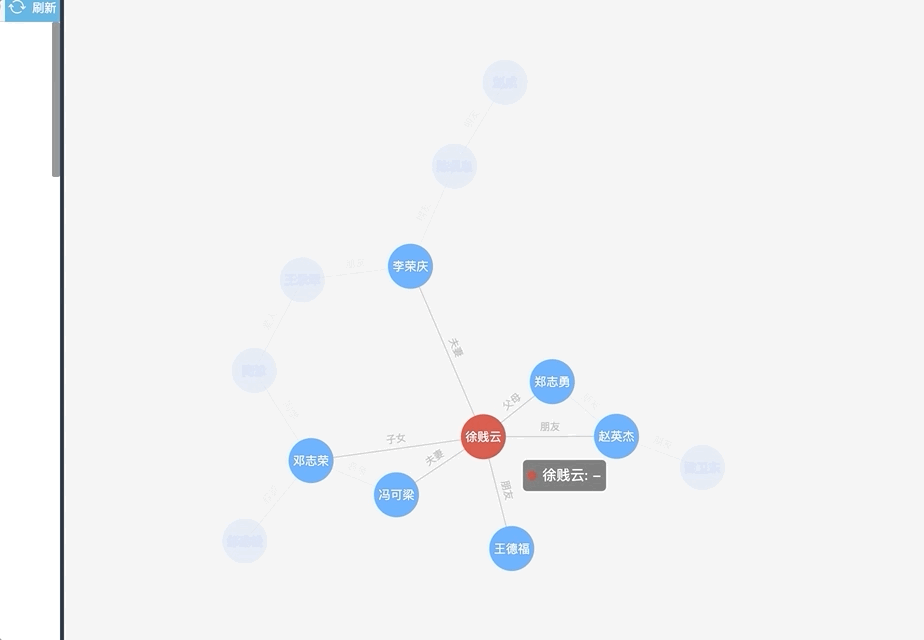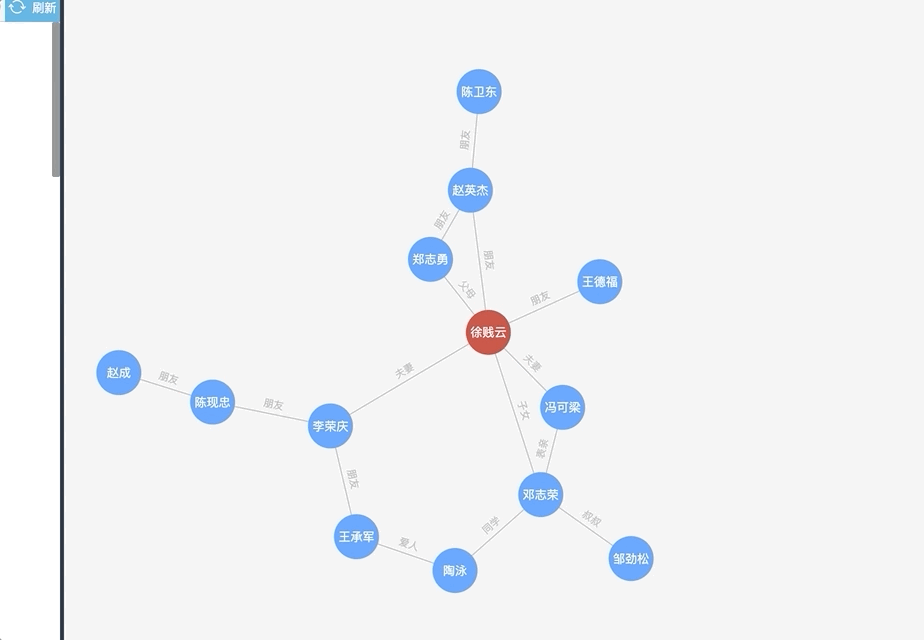
总结——
【优点】:关系一目了然,可以鼠标悬浮查看相邻节点,其他节点淡化。
【缺点】:拖动结果不理想,尤其是数据过多时,一旦拖动一个,整个页面所有的节点都在动,很久都无法停止(可能是我配置方法不对,但是后续没找到解决方法)
于是转而使用d3力导图。
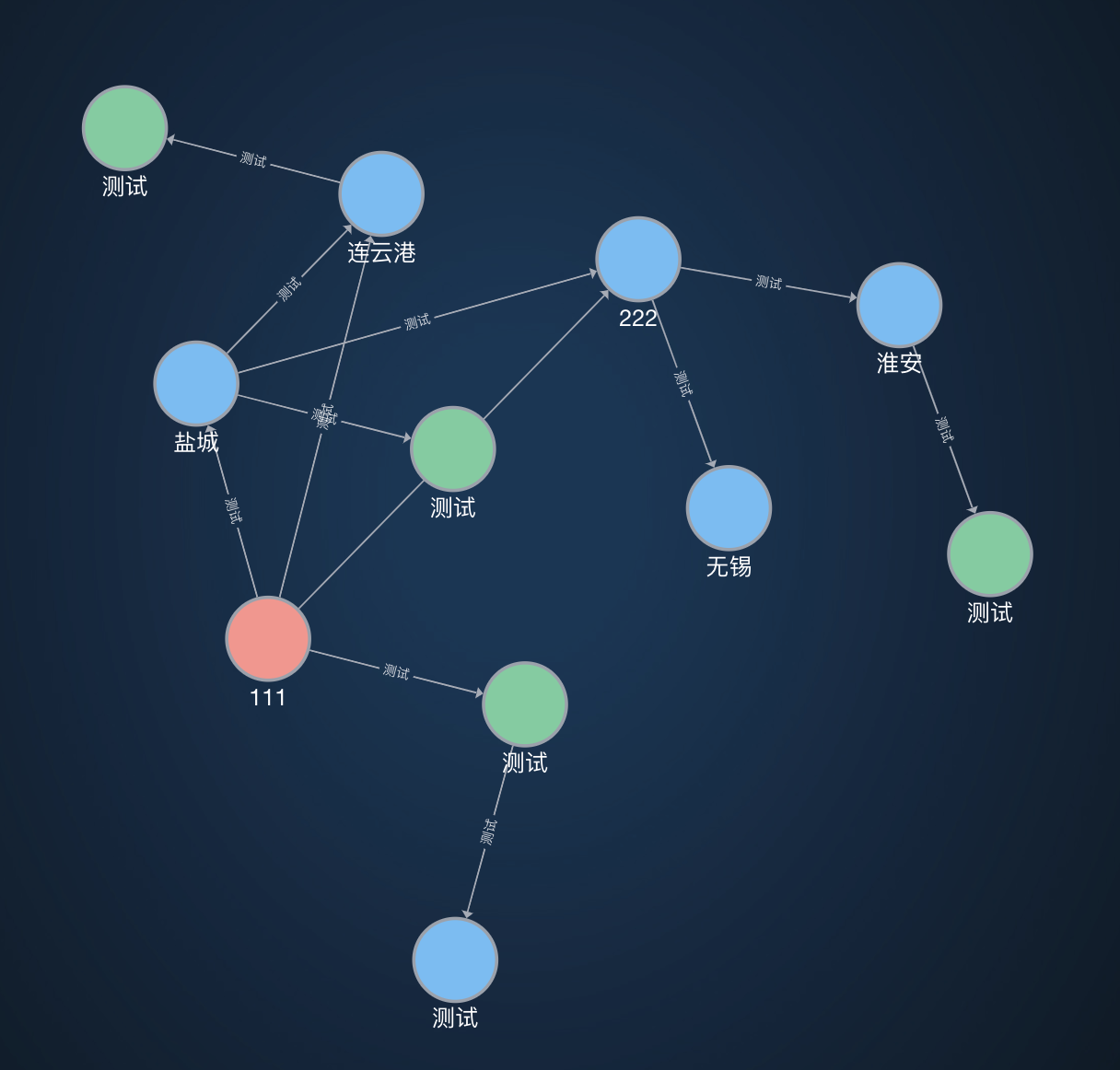
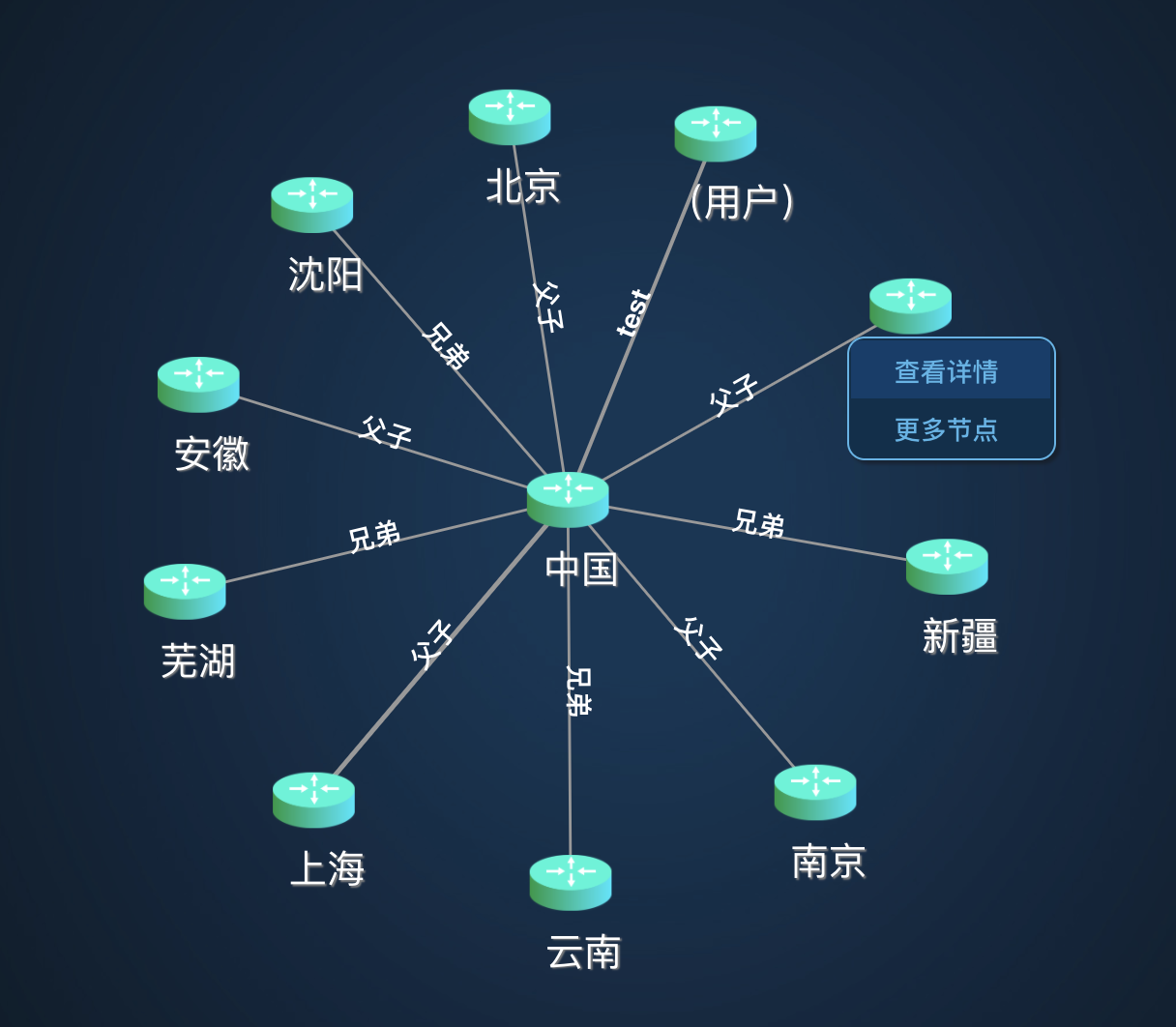
除了基本的节点展示和拖动之外,还可以双击新增节点,以及右击展示节点详情。
核心操作有以下:
1、绘制graph力
var simulation = d3 .forceSimulation(nodes) .force( 'collide', d3 .forceCollide() .radius(() => 30) .iterations(2) ) .force( 'charge', d3 .forceManyBody() // .distanceMax(300) .strength(-400) ) .force( 'link', d3 .forceLink(links) .id(d => d.id) .distance(100) ) .force('center', d3.forceCenter(this.width / 2, this.height / 2)) // .force('x', d3.forceX(this.width / 2)) // .force('y', d3.forceY(this.height / 2))
2、绘制存放节点和关系的svg
var svgArea = d3 .select('.containers') .append('svg') .attr('viewBox', [0, 0, this.width, this.height]) .attr('class', 'd3Test') .call( d3.zoom().on('zoom', function() { g.attr('transform', d3.event.transform) }) ) .on('dblclick.zoom', () => {}) // 禁止双击放大
const g = this.svgArea.append('g').attr('class', 'content')
3、绘制节点关系
var links = g .append('g') .attr('class', 'links') .selectAll('path') .data(links, function(d) { if (typeof d.source === 'object') { return d.source.name + '_' + d.relationship + '_' + d.target.name } else { return d.source + '_' + d.relationship + '_' + d.target } }) .join('path') .attr('stroke-width', d => Math.sqrt(d.value)) .attr('class', 'link') .attr('id', function(d) { if (typeof d.source === 'object') { return d.source.name + '_' + d.relationship + '_' + d.target.name } else { return d.source + '_' + d.relationship + '_' + d.target } })
4、绘制节点
var nodes = g .append('g') .attr('class', 'nodes') .selectAll('circle') .data(nodes, d => d.name) .join('circle') .attr('r', d => (d.number ? d.number : 20)) .attr('class', 'node') .attr('stroke', '#fff') .attr('stroke-width', 1.5) .attr('fill', this.color) .on('dblclick', this.dbclickNode)//双击节点事件 .on('click', this.clickNode)//单击节点触发事件 // .on('mouseover', this.mouseoverNode) // .on('mouseout', this.mouseoutNode) .call(this.drag(this.simulation))
nodes.append('title').text(d => d.name)
5、然后还有个让节点缓慢停止下来的tick
this.simulation.on('tick', () => { this.links.attr('d', function(d) { if (d.source.x < d.target.x) { return ( 'M ' + d.source.x + ' ' + d.source.y + ' L ' + d.target.x + ' ' + d.target.y ) } else { return ( 'M ' + d.target.x + ' ' + d.target.y + ' L ' + d.source.x + ' ' + d.source.y ) } }) this.nodes .attr('cx', function(d) { if (d.fixed) { d.fx = nodes[d.index].x } return d.x }) .attr('cy', function(d) { if (d.fixed) { d.fy = nodes[d.index].y } return d.y }) this.nodesName.attr('x', d => d.x).attr('y', d => d.y) })
附上官网案例:https://observablehq.com/@d3/force-directed-graph
这个案例的版本好像比较老,个人建议用新版,不过新版的API有改动。
参考案例:https://eisman.github.io/neo4jd3/
知识点汇总:
关于x,y,vx,vy,fx,fy
