一,EL 表达式概述(EL主要从域中取数据)
EL(Express Lanuage)表达式可以嵌入在jsp页面内部,减少jsp脚本的编写,EL出现的目的是要替代jsp页面中脚本的编写。
二,EL从域中取出数据(EL最重要的作用)
jsp脚本:
<%=request.getAttribute(name)%>
EL表达式替代上面的脚本:
${requestScope.name}
EL最主要的作用是获得四大域中的数据
格式:${ EL表达式 }
|
EL获得pageContext域中的值 |
${pageScope.key}; |
|
EL获得request域中的值 |
${requestScope.key}; |
|
EL获得session域中的值 |
${sessionScope.key}; |
|
EL获得application域中的值 |
${applicationScope.key}; |
EL从四个域中获得某个值:${key};
EL表达式语句在执行时,会调用pageContext.findAttribute方法,用标识符为关键字,分别从page、request、session、application四个域中查找相应的对象,找到则返回相应对象,找不到则返回"" (注意,不是null,而是空字符串)。
例如:
User实体类:
public class User { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; public User(int id, String name, String pwd) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.pwd = pwd; } public User() { } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPwd() { return pwd; } public void setPwd(String pwd) { this.pwd = pwd; } }
Index.jsp:
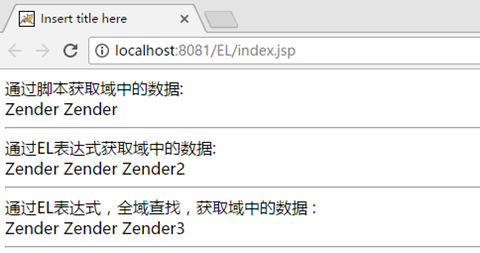
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ page import="com.zender.*,java.util.*"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 模拟域中的数据 --> <% //存储字符串 request.setAttribute("name","Zender"); //存储一个对象 User user = new User(1, "Zender", "123"); session.setAttribute("user", user); //存储一个集合 User user1 = new User(1, "Zender", "123"); User user2 = new User(2, "Zender2", "1234"); User user3 = new User(3, "Zender3", "1235"); List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); list.add(user1); list.add(user2); list.add(user3); application.setAttribute("list", list); %> 通过脚本获取域中的数据:<br/> <!-- 通过脚本获取域中的数据 --> <%=request.getAttribute("name") %> <% User sessionUser = (User)session.getAttribute("user"); out.write(sessionUser.getName()); %> <hr/> 通过EL表达式获取域中的数据:<br/> <!-- 通过EL表达式获取域中的数据 --> ${requestScope.name} ${sessionScope.user.name} ${applicationScope.list[1].name} <hr/> 通过EL表达式,全域查找,获取域中的数据 :<br/> <!-- 通过EL表达式,全域查找,获取域中的数据 --> ${name} ${user.name} ${list[2].name} <hr/> </body> </html>
访问index.jsp结果如下:
三,EL表达式执行运算
语法:${运算表达式},EL表达式支持如下运算符:
1、关系运算符
2、逻辑运算符
3、empty运算符:检查对象是否为null(空)
4、二元表达式:${user!=null?user.name :""}
5、[ ] 和 . 号运算符
例如:
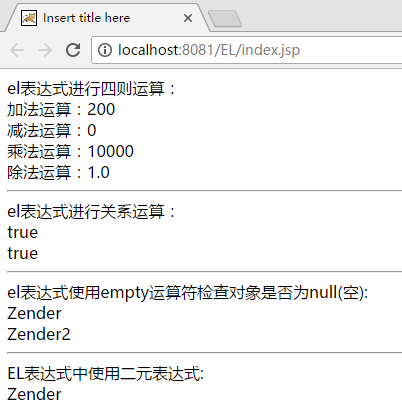
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@ page import="com.zender.*,java.util.*"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> el表达式进行四则运算:<br/> 加法运算:${100+100}<br/> 减法运算:${100-100}<br/> 乘法运算:${100*100}<br/> 除法运算:${100/100}<hr/> el表达式进行关系运算:<br/> <%--${user == null}和 ${user eq null}两种写法等价--%> ${user == null}<br/> ${user eq null}<hr/> el表达式使用empty运算符检查对象是否为null(空):<br/> <%--使用empty运算符检查对象是否为null(空) --%> <% List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); list.add("Zender"); list.add("Zender2"); request.setAttribute("list",list); %> <c:if test="${!empty(list)}"> <c:forEach var="str" items="${list}"> ${str}<br/> </c:forEach> </c:if> <hr/> EL表达式中使用二元表达式:<br/> <% session.setAttribute("user1",new User(1,"Zender","123")); %> ${user1 == null ? "对不起,您没有登陆 " : user1.name} </body> </html>
运行结果如下:
四,EL的内置11个对象
|
pageScope,requestScope,sessionScope,applicationScope |
用于获取JSP中域中的数据 |
|
param,paramValues |
用于接收参数,相当于request.getParameter(),rquest.getParameterValues() |
|
header,headerValues |
用于获取请求头信息,相当于request.getHeader(name),request.getHeaders() |
|
initParam |
用于获取全局初始化参数,相当于this.getServletContext().getInitParameter(name) |
|
cookie |
用于WEB开发中的cookie,相当于request.getCookies()--->cookie.getName()--->cookie.getValue() |
|
pageContext |
用于WEB开发中的pageContext |
注意:
测试header和headerValues时,如果头里面有"-" ,例Char-Encoding,则需要header["Char-Encoding"]、headerValues["Char-Encoding"]
测试cookie时,例${cookie.key}取的是cookie对象,如访问cookie的名称和值,必须${cookie.key.name}或者${cookie.key.value}
五,EL表达式保留关键字
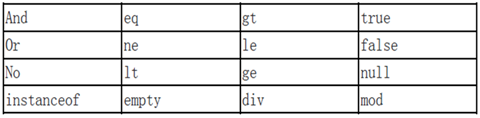
所谓保留字的意思是指变量在命名时,应该避开上述的名字,以免程序编译时发生错误。