response响应对象也为我们提供了字节输出流,字节输出流可以输出任意的数据,接下来我们来进行简单的演示。
代码:
@WebServlet("/servlet01")
public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取字节输出流
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
//写出数据
os.write("你好".getBytes());
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}
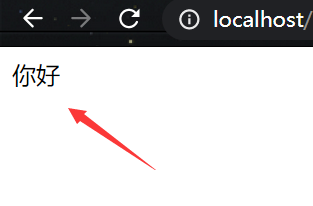
结果:
可以看出我们将字符串转变成字节数组后输出浏览器,并没有产生乱码,说明浏览器和字符串的获取字符数组的编解码方式是相同的:
我们知道浏览器的编解码格式在默认情况下适合操作系统默认相同的,在中国也就是gbk,其实字符串的获取字节数组的方法的编码格式也是和当前操作系统的编解码格式相同的。
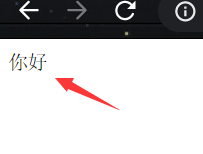
我们可以将字符串获得字节数组的编码格式修改成utf-8,然后进行输出,不出意外会乱码:
@WebServlet("/servlet01")
public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取字节输出流
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
//写出数据
os.write("你好".getBytes("utf-8"));
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}
结果:
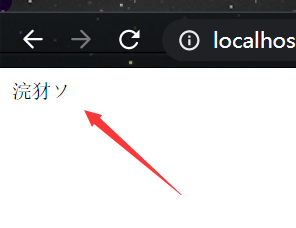
解决办法就是告诉浏览器该怎么解码:
@WebServlet("/servlet01")
public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
//获取字节输出流
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
//写出数据
os.write("你好".getBytes("utf-8"));
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
}
结果: