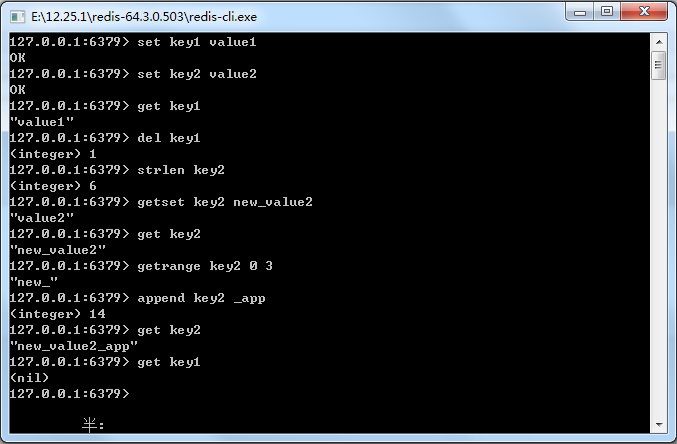
18-1 字符串的一些基本命令
18-1 :配置Spring关于Redis字符串的运行环境
<bean id="poolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <property name="maxIdle" value="50"></property> <property name="maxTotal" value="100"></property> <property name="maxWaitMillis" value="20000"></property> </bean> <bean id="stringRedisSerializer" class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"></bean> <bean id="connectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory"> <property name="hostName" value="localhost"></property> <property name="port" value="6379"></property> <property name="poolConfig" ref="poolConfig"></property> </bean> <bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate"> <property name="connectionFactory" ref="connectionFactory"></property> <property name="defaultSerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer"></property> <property name="keySerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer"></property> <property name="valueSerializer" ref="stringRedisSerializer"></property> </bean>
18-2 Redis支持的简单运算
图18-3 操作浮点数和整数

18-2 使用Spring测试Redis字符串操作
public static void testString(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); // 设值 redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key1", "value1"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key2", "value2"); // 通过key获取值 String value1 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key1"); System.out.println(value1); // 通过key删除值 redisTemplate.delete("key1"); // 求长度 Long length = redisTemplate.opsForValue().size("key2"); System.out.println(length); // 设值新值并返回旧值 String oldValue2 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().getAndSet("key2", "new_value2"); System.out.println(oldValue2); // 通过key获取值 String value2 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key2"); System.out.println(value2); // 求子串 String rangeValue2 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key2", 0, 3); System.out.println(rangeValue2); // 追加字符串到末尾,返回新串长度 int newLen = redisTemplate.opsForValue().append("key2", "_app"); System.out.println(newLen); String appendValue2 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("key2"); System.out.println(appendValue2); }
18-3 使用Spring测试Redis运算
/** * 测试Redis运算. */ public static void testCal(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("i", "9"); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("i", 1); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().decr(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize("i")); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().decrBy(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize("i"), 6); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("i", 2.3); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); } /** * 打印当前key的值 * * @param redisTemplate * spring RedisTemplate * @param key键 */ public static void printCurrValue(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, String key){ String i = (String) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); System.err.print(i+"/"); }
所有关于减法的方法,原有值都必须是整数,否则就会引发异常
18-4 通过操作浮点数减法产生异常
public static void testCal(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("i", "9"); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("i", 1); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().decr(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize("i")); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().decrBy(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize("i"), 6); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("i", 2.3); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("i", "8.9"); redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().decr(redisTemplate.getKeySerializer().serialize("i")); printCurrValue(redisTemplate, "i"); }
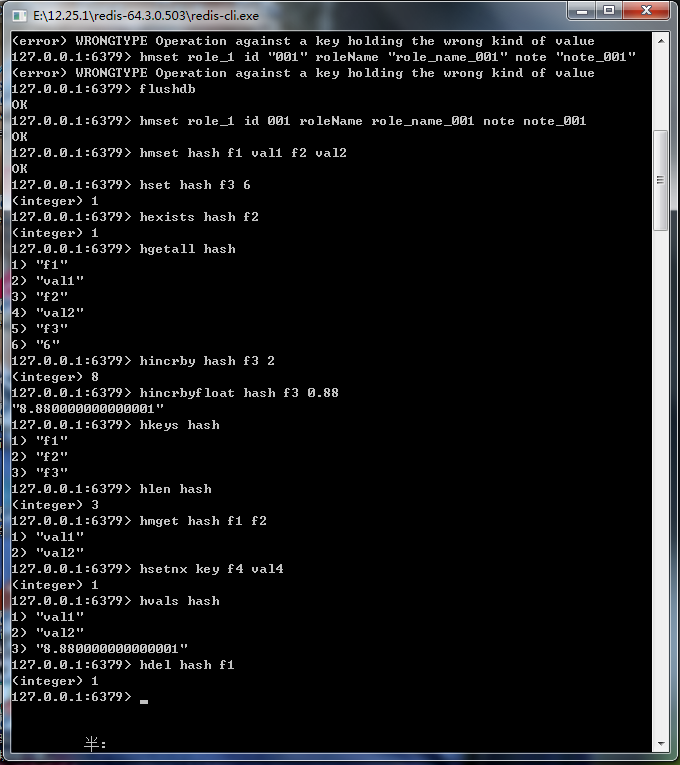
图18-4 使用Redis命令保存角色对象
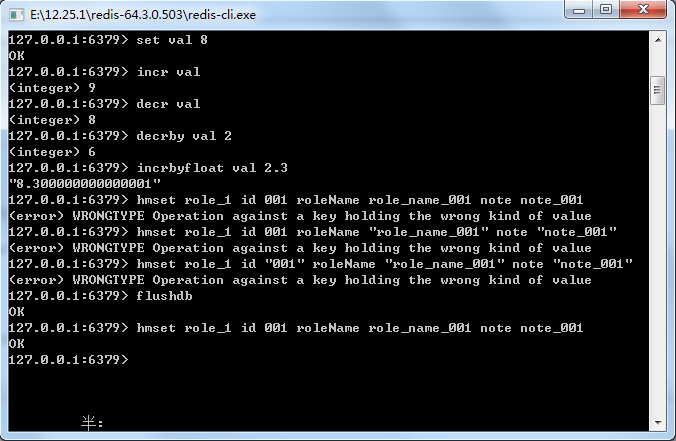
图18-5 Redis的hash结构命令展示
18-5 修改默认的序列化器为字符串序列化
18-6 使用Spring操作hash结构
public static void testRedisHash(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); String key = "hash"; Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put("f1", "val1"); map.put("f2", "val2"); // 相当于hmset命令 redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map); // 相当于hset命令 redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "f3", "6"); printValueForhash(redisTemplate, key, "f3"); // 相当于 hexists key filed命令 boolean exists = redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(key, "f3"); System.out.println(exists); // 相当于hgetall命令 Map keyValMap = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key); // 相当于hincrby命令 redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, "f3", 2); printValueForhash(redisTemplate, key, "f3"); // 相当于hincrbyfloat命令 redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, "f3", 0.88); printValueForhash(redisTemplate, key, "f3"); // 相当于hvals命令 List valuesList = redisTemplate.opsForHash().values(key); // 相当于hkeys命令 Set keyList = redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys(key); List<String> fieldList = new ArrayList<String>(); fieldList.add("f1"); fieldList.add("f2"); // 相当于hmget命令 List valueList2 = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, keyList); // 相当于hsetnx命令 boolean success = redisTemplate.opsForHash().putIfAbsent(key, "f4", "val4"); System.out.println(success); // 相当于hdel命令 Long result = redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, "f1","f2"); System.out.println(result); } private static void printValueForhash(RedisTemplate redisTemplate,String key,String field){ // 相当于hget命令 Object value = redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, field); System.out.println(value); }
18-3 Redis数据结构——链表(linked-list)
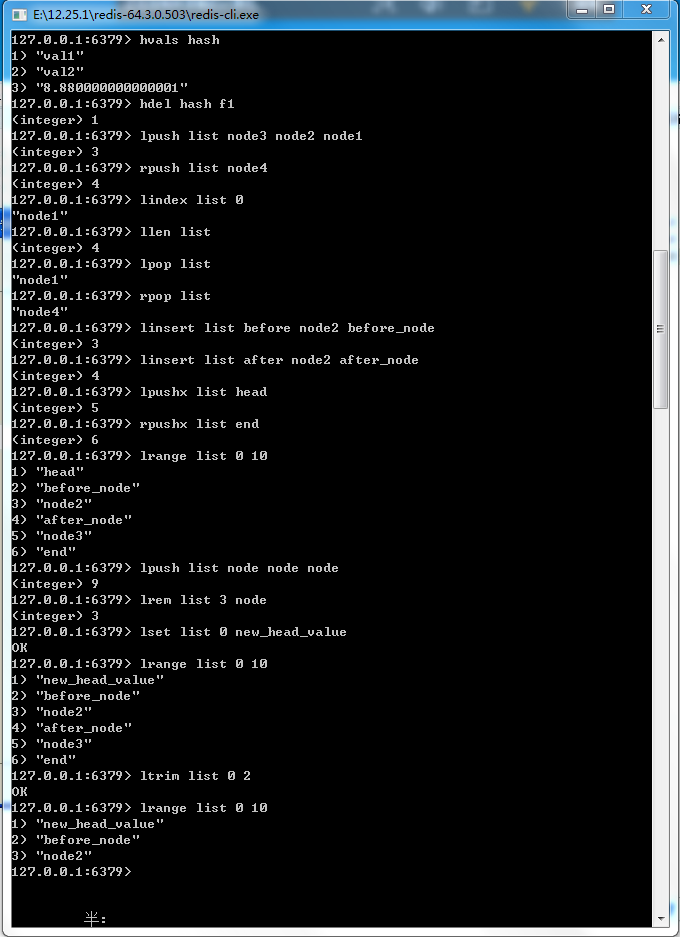
图18-8 Redis关于链表的操作命令
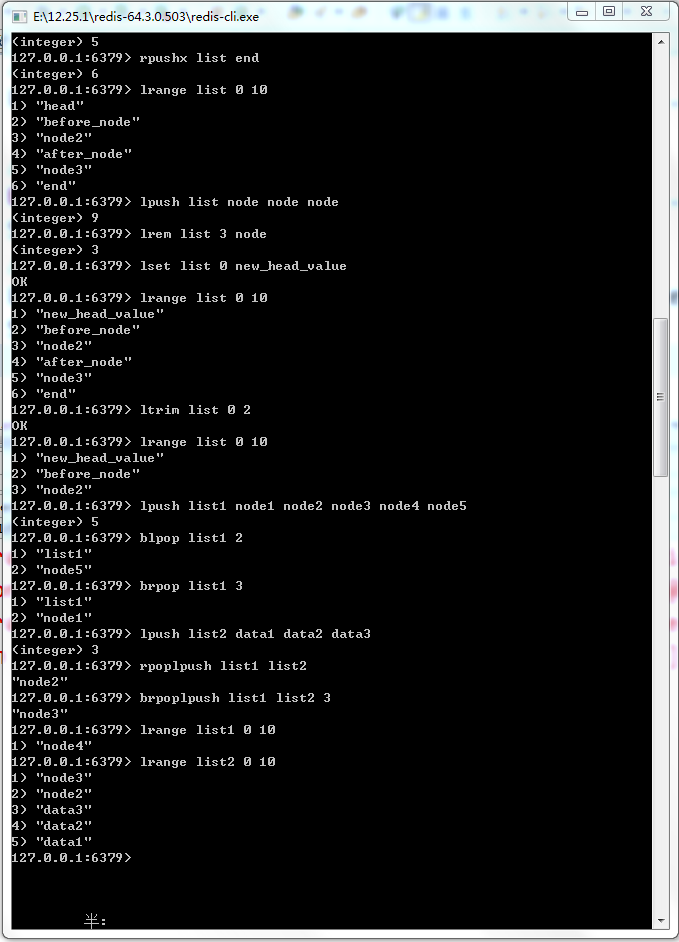
图18-9 Redis链表阻塞操作命令
18-7 :通过Spring操作Redis的链表结构
public static void testList(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); try { // 删除链表,以便我们可以反复测试 redisTemplate.delete("list"); // 把node3插入链表list redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("list", "node3"); List<String> nodeList = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i >= 1; i--) { nodeList.add("node" + i); } // 相当于lpush把多个价值从左插入链表 redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("list", nodeList); // 从右边插入一个节点 redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush("list", "node4"); // 获取下标为0的节点 String node1 = (String) redisTemplate.opsForList().index("list", 0); // 获取链表长度 long size = redisTemplate.opsForList().size("list"); // 从左边弹出一个节点 String lPop = (String) redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop("list"); // 从右边弹出一个节点 String rPop = (String) redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("list"); // 注意,需要使用更为底层的命令才能操作insert命令 // 使用linsert命令在node2前插入一个节点 redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().lInsert("list".getBytes("utf-8"), RedisListCommands.Position.BEFORE, "node2".getBytes("utf-8"), "before_node".getBytes("utf-8")); // 使用linsert命令在node2后插入一个节点 redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().lInsert("list".getBytes("utf-8"), RedisListCommands.Position.AFTER, "node2".getBytes("utf-8"), "after_node".getBytes("utf-8")); // 判断list是否存在,如果存在则从左边插入head节点 redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushIfPresent("list", "head"); // 判断list是否存在,如果存在则从右边插入end节点 redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushIfPresent("list", "end"); // 从左到右,或者下标从0到10的节点元素 List valueList = redisTemplate.opsForList().range("list", 0, 10); nodeList.clear(); for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { nodeList.add("node"); } // 在链表左边插入三个值为node的节点 redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("list", nodeList); // 从左到右删除至多三个node节点 redisTemplate.opsForList().remove("list", 3, "node"); // 给链表下标为0的节点设置新值 redisTemplate.opsForList().set("list", 0, "new_head_value"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } //打印链表数据 printList(redisTemplate, "list"); }
public static void printList(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, String key){ // 链表长度 Long size = redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key); // 获取整个链表的值 List valueList = redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, 0, size); // 打印 System.out.println(valueList); }
18-8 Spring对Redis阻塞命令的操作
public static void testBList() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); RedisTemplate redisTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RedisTemplate.class); // 清空数据,可以重复测试 redisTemplate.delete("list1"); redisTemplate.delete("list2"); // 初始化链表list1 List<String> nodeList = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { nodeList.add("node" + i); } redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("list1", nodeList); // Spring使用参数超时时间作为阻塞命令区分,等价于blpop命令,并且可以设置时间参数 redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop("list1", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // Spring使用参数超时时间作为阻塞命令区分,等价于brpop命令,并且可以设置时间参数 redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop("list1", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); nodeList.clear(); // 初始化链表list2 for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { nodeList.add("data" + i); } redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("list2", nodeList); // 相当于rpoplpush命令,弹出list1最右边的节点,插入到list2最左边 redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush("list1", "list2"); // 相当于brpoplpush命令,注意在Spring中使用超时参数区分 redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush("list1", "list2", 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 打印链表数据 printList(redisTemplate, "list1"); printList(redisTemplate, "list2"); }
18.4 Redis数据结构——集合


图18-10 通过命令行客户端演示这些命令
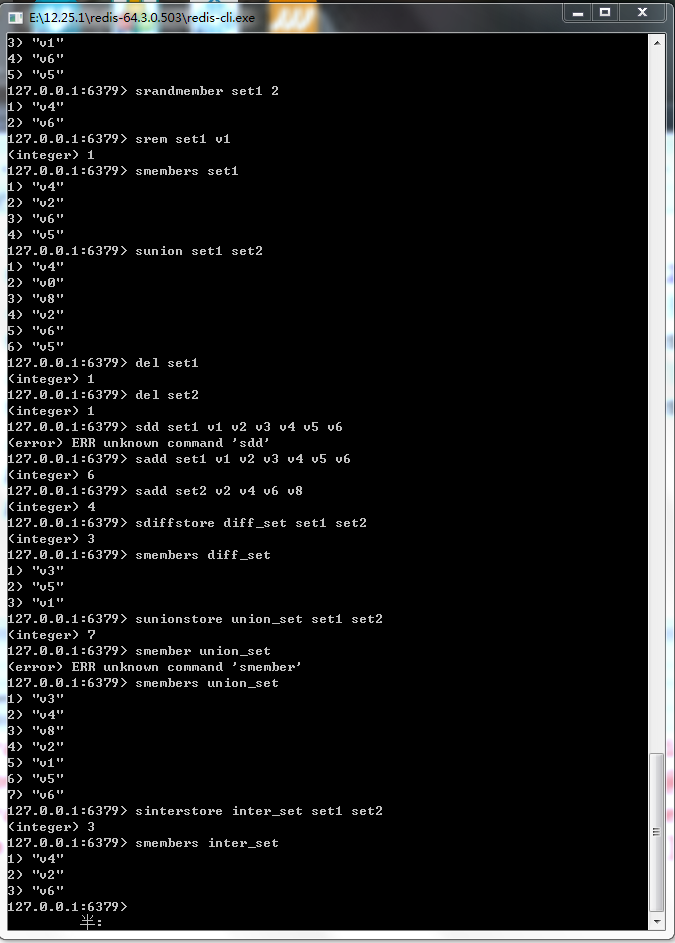
图18-11 交集、并集和差集保存命令的用法
18.5 Redis数据结构——有序集合