Graph constructive problems are back! This time the graph you are asked to build should match the following properties.
The graph is connected if and only if there exists a path between every pair of vertices.
The diameter (aka "longest shortest path") of a connected undirected graph is the maximum number of edges in the shortest path between any pair of its vertices.
The degree of a vertex is the number of edges incident to it.
Given a sequence of nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an construct a connected undirected graph of nn vertices such that:
- the graph contains no self-loops and no multiple edges;
- the degree didi of the ii-th vertex doesn't exceed aiai (i.e. di≤aidi≤ai);
- the diameter of the graph is maximum possible.
Output the resulting graph or report that no solution exists.
The first line contains a single integer nn (3≤n≤5003≤n≤500) — the number of vertices in the graph.
The second line contains nn integers a1,a2,…,ana1,a2,…,an (1≤ai≤n−11≤ai≤n−1) — the upper limits to vertex degrees.
Print "NO" if no graph can be constructed under the given conditions.
Otherwise print "YES" and the diameter of the resulting graph in the first line.
The second line should contain a single integer mm — the number of edges in the resulting graph.
The ii-th of the next mm lines should contain two integers vi,uivi,ui (1≤vi,ui≤n1≤vi,ui≤n, vi≠uivi≠ui) — the description of the ii-th edge. The graph should contain no multiple edges — for each pair (x,y)(x,y) you output, you should output no more pairs (x,y)(x,y) or (y,x)(y,x).
3 2 2 2
YES 2 2 1 2 2 3
5 1 4 1 1 1
YES 2 4 1 2 3 2 4 2 5 2
3 1 1 1
NO
Here are the graphs for the first two example cases. Both have diameter of 22.
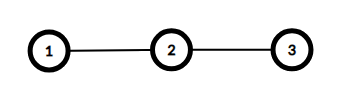 d1=1≤a1=2d1=1≤a1=2
d1=1≤a1=2d1=1≤a1=2
d2=2≤a2=2d2=2≤a2=2
d3=1≤a3=2d3=1≤a3=2
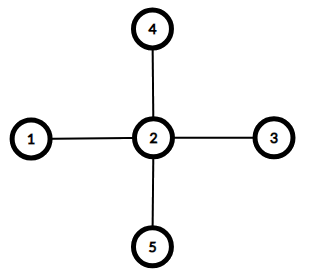 d1=1≤a1=1d1=1≤a1=1
d1=1≤a1=1d1=1≤a1=1
d2=4≤a2=4d2=4≤a2=4
d3=1≤a3=1d3=1≤a3=1
d4=1≤a4=1
这个题无语,自己打比赛的时候看错题,求成最短的了,mdzz。。。
直接构造一条最长链就可以。从大到小连,为1的两边最多能连2个,其他的中间连,然后就可以了。
代码:
1 //D 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cstring> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cassert> 8 #include<cctype> 9 #include<cmath> 10 #include<cstdlib> 11 #include<ctime> 12 #include<deque> 13 #include<iomanip> 14 #include<list> 15 #include<map> 16 #include<queue> 17 #include<set> 18 #include<stack> 19 #include<vector> 20 using namespace std; 21 typedef long long ll; 22 typedef long double ld; 23 typedef pair<int,int> pii; 24 25 const double PI=acos(-1.0); 26 const double eps=1e-6; 27 const ll mod=1e9+7; 28 const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f; 29 const int maxn=500+10; 30 const int maxm=100+10; 31 #define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); 32 33 int n,m,t,p,ans; 34 int d[maxn*2],first[maxn*2],v[maxn*2],w[maxn*2],nextt[maxn*2]; 35 36 struct node{ 37 int p,d; 38 39 bool operator <(const node &a)const{ 40 return d<a.d; 41 } 42 43 }a[maxn]; 44 45 vector<pair<int,int> > ve; 46 47 ll pre[maxn]; 48 49 int main() 50 { 51 int n; 52 cin>>n; 53 int flag=0; 54 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 55 cin>>a[i].d,a[i].p=i; 56 if(a[i].d!=1)flag=1; 57 } 58 if(flag==0) {cout<<"NO"<<endl;return 0;} 59 sort(a+1,a+1+n); 60 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 61 pre[i]=pre[i-1]+a[i].d; 62 int i=n-1,con=n,tail=n,len=0,flag1=0,flag2=0; 63 while(1){ 64 if(a[con].d&&a[i].d) {ve.push_back(make_pair(a[con].p,a[i].p));a[con].d--;a[i].d--;con--;i--;len++;} 65 else if(!a[con].d&&flag1==0) {ve.push_back(make_pair(a[tail].p,a[i].p));a[tail].d--;a[i].d--;i--;len++;flag1=1;if(a[tail].d==0) tail--;} 66 else{ 67 if(a[tail].d!=0) {ve.push_back(make_pair(a[tail].p,a[i].p));a[tail].d--;a[i].d--;i--;if(a[tail].d==0) tail--;} 68 else {flag2=1;break;} 69 } 70 if(i==0) break; 71 } 72 if(flag2==1) {cout<<"NO"<<endl;return 0;} 73 vector<pair<int,int> >::iterator it; 74 cout<<"YES "<<len<<endl; 75 cout<<ve.size()<<endl; 76 for(it=ve.begin();it!=ve.end();it++){ 77 cout<<(*it).first<<" "<<(*it).second<<endl; 78 } 79 }