1. Overview
- What is the Internet?
- What is a protocol?
- Network edge网络边缘: hosts, access network接入网, physical media
- Network core网络核心: packet/circuit switching, internet structure
- Internet structure
2. The internet
There are different ways【俩】 to describe what is the internet:
“nuts and bolts” view,具体细节
“devices” view,设备
2.1 A “nuts and bolts”(components, essentials)具体细节 view
We can describe the nuts and bolts of the Internet, that is, the basic hardware and software components that make up the Internet.
组成部分/具体细节的视角:描述组成因特网的硬件和软件
2.1.1 What is computer network?
A computer network is a group of computers that use a set of common communication protocols over digital interconnections for the purpose of sharing resources.
计算机网络是一组使用了一系列在数字交互上common传输协议的计算机。
2.1.2 What is the Internet?
The internet is a computer network that interconnects billions of computing devices(called hosts or end systems) using communication links and packet switches.
因特网是一个通过传输链路和分组交换机连接了数十亿计算设备的计算机网络。
Internet is the best-known computer network.
因特网是最著名的计算机网络
(1) Billions of connected computing devices:
hosts = end systems主机 = 端系统
End systems are connected together by a network of communication links and packet switches
端系统由传输链路和分组交换机组成的网络连接
A packet switch is used to forward packets. It takes a packet arriving on one of its incoming links and forwards that packet on one of its outgoing links. The two most prominent types of packet switches in today’s Internet are routers and link-layer switches. Routers are typically used in network core, and Link-layer switches are typically used in access networks.
分组交换机用于发送数据包。它在数据包到达它的接收链路时接收数据然后将数据包推向它的一个outgoing链路(发送/传递数据)。现在应用最广泛的两类分组交换机是:路由器和连链路层交换机。其中,路由器多用于网络核心、链路层交换机多用于接入网。
running network apps at Internet’s “edge”【computing devices】运行在因特网的“边缘”(比如手机、电脑等)
(2) Packets switches
Forward packets(chunks of data): routers, switches
【功能】发送数据包:路由器、交换机【例子】
(3) Communication links
Fiber, copper, radio, satellite
光纤、铜线【双绞线】、声音【电波】、卫星【无线电】
Transmission rate: bandwidth
传输速率:带宽
(4) Networks
Collection of devices, routers, links: managed by an organization
设备、路由器和链路的集合体:由一个组织【ISPs,Internet Service Providers网络服务提供商】统一管理
2.1.3 ISP, Internet Service Provider
(1) Internet: “network of network”
因特网:网络中的网络
End systems access the Internet through Internet Service Providers (ISPS). Each ISP itself is a network of packet switches and communication links. The Internet is all about connecting end systems to each other, so the ISPs that provide access to end systems must be interconnected.(因此,Internet is the network of network)
端系统通过ISP接入因特网。每一个ISP本身也是由分组交换机和传输链路构成的网络。因特网也在连接着各个端系统,所以提供网络接入【服务】的ISP也必须相互连接。
(2) Protocols are everywhere
Control sending, receiving of messages
E.g. HTTP(Web), streaming video, Skype, TCP, IP, WiFi, 4G, Ethernet
(3) Internet standards
Internet standards are developed by IETF, its document are called RFC, in which, protocols such as TCP, IP, HTTP are defined.
因特网标准由IETF互联网工程任务组组织制定(develop),其中的文档是RFC(是由互联网工程任务组(IETF)发布的一系列备忘录),其中包括(contains) TCP、IP、HTTP等多种协议。
RFC: Request for Comments
IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force
2.2 A “devices” view设备的角度
We can also describe the Internet in terms of a networking infrastructure that provides services to distributed applications.
网络基础设置的视角:描述为各种应用提供的服务
2.2.1 description
(1) Infrastructure that provides services to applications
向应用提供设备的基础设施
【服务了以下这些应用(未列举完)】
Web, streaming video, multimedia teleconferencing, email, games, e-commerce, social media, inter-connected appliances
(2) Provides programming interface to distributed applications
向distributed应用提供了程序接口
【用以下比喻说明】
* “hooks” allowing sending/receiving apps to “connect” to, use Internet transport service
* provides service options, analogous【类似】 to postal service
3. Protocol
All communication activity in Internet governed by protocols
3.1 What’s a protocol?
Protocols define the format, order of messages sent and received among network entities, and actions taken on msg transmission, receipt.
协议规定了网络实体间数据发送和接收的格式和顺序,以及信息传输、接收的行为
Distributed entities involved exchanging msgs (governed by protocols)
分布式实体涉及交换数据(由协议管控)
4. Network Edge
Terminology: hosts, access network, physical media
4.1 Hosts: clients and servers, where servers often in data center
网络边缘,就是字面意思,位于网络的边缘,所有(手机、电脑等clients+servers)host都处于/属于网络边缘,同时服务器位于/是数据核心(data center)
4.2 Access network
Access network is the network that physically connects an end system to the first router(also known as the “edge router”) on a path from the end system to any other distant end system
接入网是通过物理方式(有线/无线)连接到端系统和(从这个端系统到任意其他端系统方向的)第一个路由器(也称为边缘路由器,edge router)的。
Access network may use wired or wireless communication links. For wired links, different kinds of physical media can be used. For wireless communications, radio spectrum is used to transmit data.
对于有线连接/接入(方式),使用了不同材质的物理媒介;而对于无线连接/接入(方式),使用了无线电频谱传输数据
4.2.1 How to connect end systems to edge router
怎样连接端系统与边缘路由器【network edge,~的第一个路由器】
(1) 以下列举了接入网的三种类别
Residential access networks家庭接入
Institutional access networks(school, company)企业接入
Mobile access networks(WiFi, 4G/5G)移动设备接入
(2) 我们要考虑:
What is the transmission rate(传输速率,bps, bits per second,不是bytes,而是bits!)
Are there shared or dedicated access among users使用者之间的接入网是共享的还是专用的
(3) Access networks: cable-based access基于电缆的接入
FDM, frequency division multiplexing频分复用
Two most prevalent types of broadband residential access are cable and digital subscriber line(DSL)
两种最流行的宽带家庭接入方式是电缆-因特网和数字用户线(DSL)接入:
- 方式一
Cable-based Internet access makes use of the cable television company’s existing infrastructure, where data and TV signals are transmitted at different frequencies over shared cable distribution network.
电缆因特网接入【共享】使用的是已经存在的电视线基础设施,这里data(传输的数据)和TV signal使用频分复用的方式进行共享,a shared broadcast medium一种共享广播介质
HFC, hybrid fiber coax混合光纤同轴电缆
This cable-based access is often called hybrid fiber coax(HFC) network, because both fiber and coaxial cable are used in this system.电缆-因特网接入常被称为混合光光纤同轴电缆接入,因为这种方式同时用到了光纤和同轴电缆
Cable modem【电缆调制解调器】 and splitter【分路器】 are needed in one family. A cable modem divide the HFC system into upstream channel and downstream channel, a splitter is used to separate the signal into data ans TV signal.
A downstream channel typically has a higher transmission rate than the upstream channel【下行:因特网到PC的信号,上行:PC到因特网的信号】
CMTs【cable-based termination system,中心局(电视)】, 分频用的,将混合信号重新分成data和TV signal
- 方式二
DSL, Digital Subscriber Ling数字用户线接入
Using existing telephone line to central office DSLAM
* data over DSL phone line goes to Internet
* voice over DSL phone goes to telephone net
DSL modem turn data into digital signal (with high frequency), when the combined data arrives central office, the DSLAM will separates the data and telephone signals.
When data arrives home, the splitter will separate the data and telephone signal.
4.2.2 接入网例子
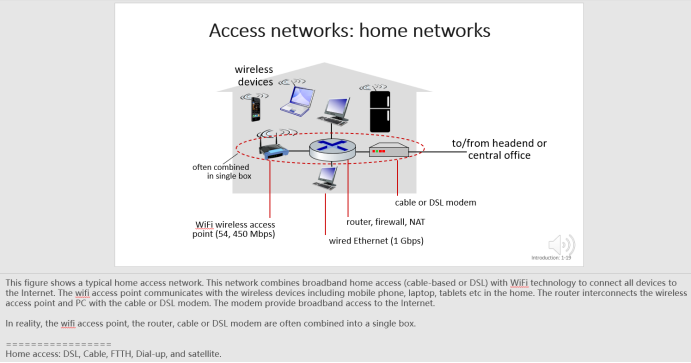
家庭接入网
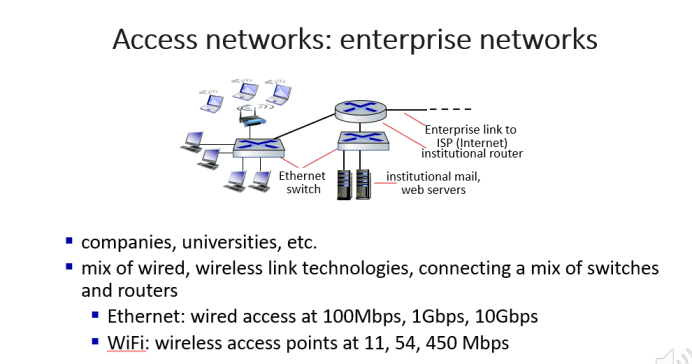
企业接入网
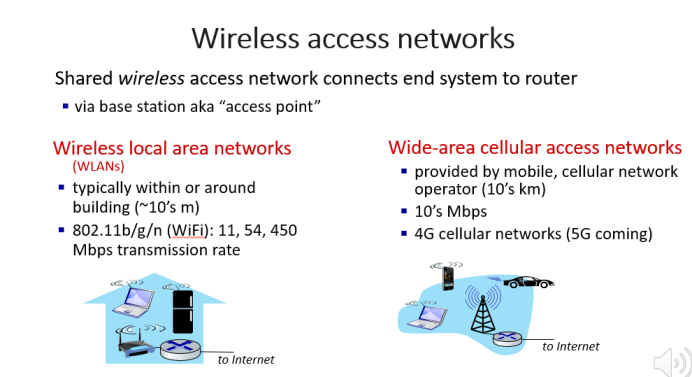
无线接入网
4.2.3 Host: sends packets of data
Host send function:
(1) Takes application msg
(2) Breaks into smaller chunks, known as packets, of length L bits
(3) Transmits packet into access network at transmission rate R
* link transmission rate, aka link capacity, aka link bandwidth
4.2.4 物理媒体
Guided media:
Signals propagate in solid media: copper, fiber, coax.
(1) Twisted pair(TP) 双绞线:two insulated copper wires
(2) Coaxial cable: 同轴电缆
* two concentric copper conductors
* bidirectional
* broadband
Coaxial cable is quite common in cable television system and cable Internet access.
(3) Fiber: 光纤
Fiber optics are the preferred long-distance guided transmission media, especially for overseas links. They are also prevalent in the backbone of the Internet. However, the oprical devices are quite expensive.
Unguided media
Signals propagate freely: radio
Wireless radio: 无线电
(1) 特点
* signal carried in electromagnetic spectrum
* no physical “wire”
* broadcast and “half-duplex”单工
* propagation environment effect:
Reflection
Obstruction by objects
Interference
(2) Radio link types
* terrestrial microwave微波
* Wireless LAN(WiFi)局域网
* wide-area(e.g. cellular)广域网
* satellite卫星
5. Network core
The network core is a mess of Interconnected routers【一堆相互连接的路由器】
Network of networks【Internet:network of network】
5.1 Packet-switching
分组交换,共享资源,就像是没有预定而直接到餐厅就餐一样,你可能一个人享有所有的参观资源(one source host)、也可能与其他顾客一起吃饭(over one source hosts)、也可能没有空位只能等待有人出来或者放弃(packet queuing, loss)
hosts break application-layer msgs into packets
* forward packet from one router to the next, across links on path from source to destination
* each packet transmitted at full link capacity
What is packet switching?
To send a message from a source host to a destination host, the source host breaks long application-layer msgs into smaller chunks of data known as packets. Packets are forwarded from one router to the next, across links on path from source to destination. Packets are transmitted over each communication link at a rate equal to the full transmission rate or full link capacity.
为了从源主机向目标主机发送数据,源主机将(较长的)应用层数据分为几个(较短的)数据段(称为packet,分组)。分组从一个路由器被推向另一个,经过从源主机到目的地的所有路段。分组以满传输速率或满链路容量的速度在交互链路之间传输。
5.1.1 Delay
(1) Transmission delay
Takes L/R seconds to transmit (push out) L-bit packet into link at R bps.
将一个L比特的分组推入传输速率为R bps的链路的传输时延为L/R秒
(2) Store and forward
存储转发
Entire packet must arrive router before it can be transmitted on next link
整个分组在向下一个链路传输前必须全部到达“这一个”路由器
(3) End to end delay for one packet
端到端传输时延
如果不考虑传播时延和处理时延等(只考虑传输时延),则P个L-bit分组经过N条R-bps链路传输的总时延为:(N-1)L/R+PL/R = (P+N-1)L/R秒
(4) Propagation delay
传播时延 = 长度/光速(3*10^8m/s)
(5) Processing delay
处理时延
(6) Queue delay, loss
For each output link, the packet switch has an output buffer (or output queue), which stores packets that the router is about to send into that link.
对于每一个输出连接,分组交换都有一个输出缓冲区(或称输出队列),这个队列存储着“这个”路由器要发送向给这个链路的分组
(7) Packet queuing and loss
If arrival rate (in bps) to link exceeds transmission rate (bps) of link for a period of time:
* packets will queue, waiting to be transmitted on output link
* packet can be dropped (lost) if memory (buffer) in router fills up
如果分组到达的速率要大于传输链路所能传输的速率,那么:
* 分组需要排队【此时产生排队时延】,等待被传输给输出链路
* 如果内存(缓冲区)已经满了,后来的分组或者已经在队列中的分组可能会丢失
5.2 Two key network-core functions
(1) Forwarding
转发
Local action:
Move arriving packets from router’s input link to appropriate router output link
将分组从输入链路准确地转移至输出分组
(2) Routing
路由
Global action:
Determine source-destination paths taken by packets
决定源地址到目标地址的路线
* routing algorithm
路由算法
Routing protocol路由选择协议
一个路由选择协议可以决定从每台路由器到目的地的最短路径,并用这些最短路径结构来配置路由器中的转发表
5.3 circuit switching
电路交换,专用资源,相当于吃饭前提前预约,即使是你不来的时间其他的顾客也不能坐你的位置(带宽等资源)
End-to-end resources allocated to, reserved for “call” between source and destination.
* establish a connection between source and destination before transmission
Connection: called “circuit”(virtual)
* dedicated resources: no sharing专用资源
Circuit-like (guarantee) performance
* circuit segment idle if not used by call (no sharing)
没有使用就保持静止(不工作状态)
* commonly used in traditional telephone networks
多用于传统电话机网络
5.3.1 FDM and TDM
(1) FDM
Frequency Division Multiplexing频分复用
* optical, electromagnetic frequencies divided into (narrow) frequency bands
* each circuit allocated its own band, can transmit at max rate of that narrow band
(2) TDM
Time Division Multiplexing时分复用
* time divided into frames of fixed duration where one frame contains a fixed number time slots
时间被分成固定数量和固定长度的帧
* each circuit assigned periodic slot(s), can transmit at maximum rate of (wider) frequency band, but only during its time slot(s)
每个电路都分配到了指定的时间段,他们可以在这段时间段中以最大速率传输,但是也仅限于指定的一端时间
5.3.2 Example
How long it takes to transfer a file of 640,000 bits through two hosts by circuit switching with each link has a transmission rate of 1.536M bps, having 24 circuits? (circuit establishment time is 500ms, propagation delay ignored)
Answer: Time = 640,000/(1.536M bps/24) + 0.5 = 10.5s
Note that
The transmission time is independent of the number of links
* the time will still be 10 s even if there are 100 links between the two hosts, coz the ene-to-end resources are reserved for a call between source and destination in circuit-switched networks. It is different from the sore-and-forward in pack switching.
5.4 Packet switching Versus Circuit switching
Circuit switching完败!
5.4.1 The packet switching
- optical
*Offers better sharing of transmission capacity than circuit switching. It allows more users to use networks
* Is simpler, more efficient, and less costly to implement than circuit switching.
- Shortage
Excessive congestion possible:
Packet delay and loss to buffer overflow so that protocol needed for reliable data transfer, like congestion control
5.4.2 The circuit switching
The dedicated circuits are idle during silent periods.
Establishing end-to-end circuits and reserving end-to-end transmission capacity is complicated and requires complex signaling software to coordinate the operation of the switches along the end-to-end path.
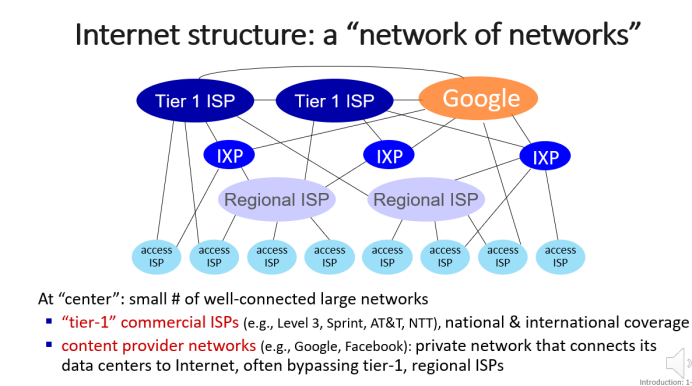
6. Internet structure
A network of networks
6.1 Overview
(1) Host connect to Internet via access Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
ISPs provide the wire and wireless networks.
互联网服务供应商【后称“供应商”】提供有线/无线的网络【服务】
* residential, enterprise(company, university, commercial) ISPs
(2) Access ISPs in turn must be interconnected
So that any two hosts can send packets to each other
接入网供应商之间必须互联以支持任意两个主机之间可以互相交换分组【通信】
(3) Resulting network of networks is very complex
Evolution was driven by economics and national policies
6.2 Current Internet structure
以下由简入繁呈现现在互联网的结构关系
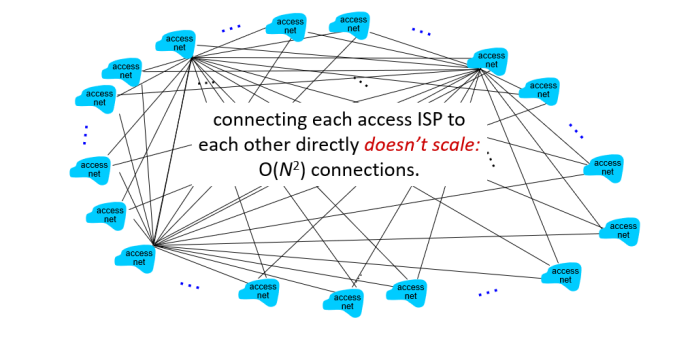
(1) Given millions of access ISPs, how to connect them together?
The simplest approach is directly connect each access ISP to each other. But its scale is too large.(O(N^2))
将所有供应商直接相连,但是繁琐【也很费钱】
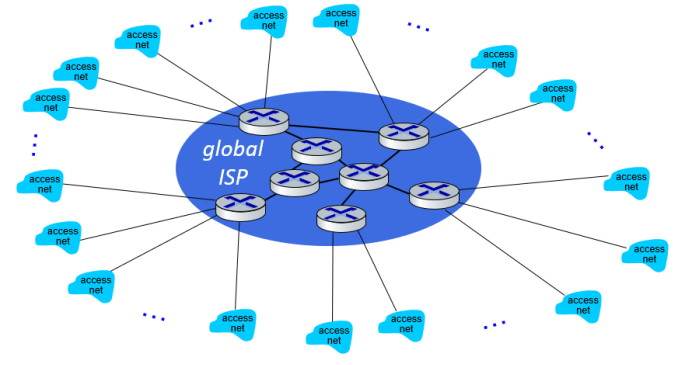
(2) Use global transit ISPs
Connect each access ISP to one global transit ISP, customer and provider ISPs have economis agreement.
将接入网连入多个全球运营供应商提供的服务,这些个全球运营供应商再互相连接,这其中的customer是access ISP,而provider是the global transit ISP
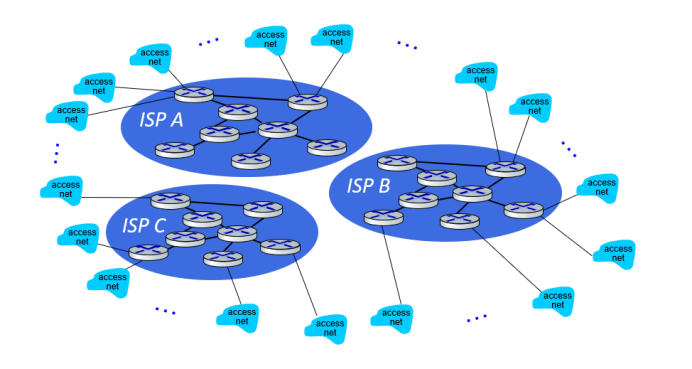
(3) 多个“(2)”方案结合——structure 2
It is natural for other companies to build their own global transit ISPs and compete with the original global transit ISP.
Consists of hundreds of thousands of access ISPs and multiple global transit ISPs.
Its a two-tier hierarchy with global transit providers residing at the top tier and access ISP at the bottom tier.
这是一个两层的层次结构,全球运输提供商位于顶层,接入网供应商位于底层。
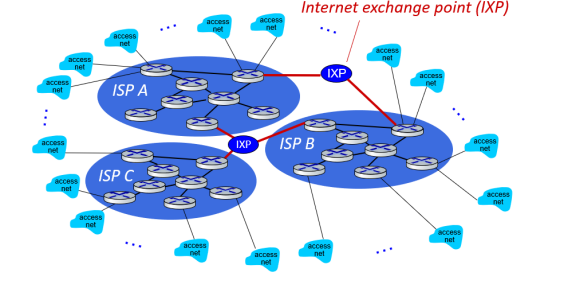
(4) Companies should be connected
IXPs are neutral entities that will connect multiple ISPs.
IXP: Internet exchange point, 互联网交换点
(5) The other way of connecting ISPs
除了通过IXP连接整个ISPs的company之外,ISP之间也可以通过peer link互相连接
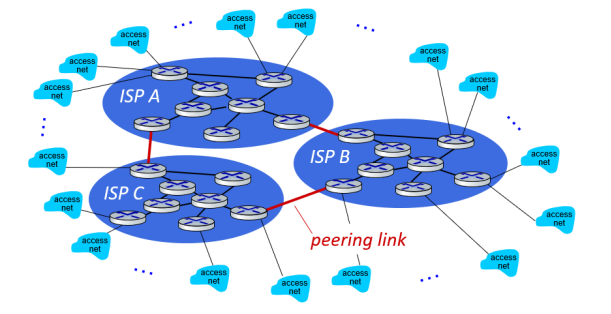
(6) Tier-1 ISPs
Tier-1 ISPs are similar to global transit ISP.
In reality, in any region, regional networks may arise to connect access nets to ISPs. Each regional ISP then connects to tier-1 ISPs.
In such a hierachy, each access ISP pays the connected regional ISP, and each regional ISP pays the connected tier-1 ISP.(An access ISP can also connect directly to a tier-1 ISP, in which case it pays the tier-1 ISP).
上面的付费关系:Access ISP -> connected regional ISP -> connected tier-1 ISP
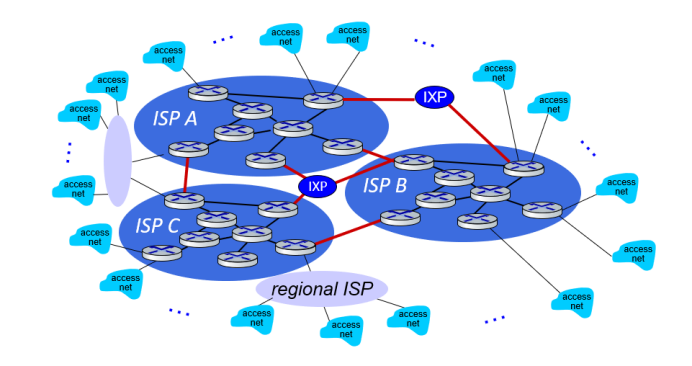
(7) Content network
They(Google, Microsoft, etc.) may run their own network, to bring services, content close to end users.
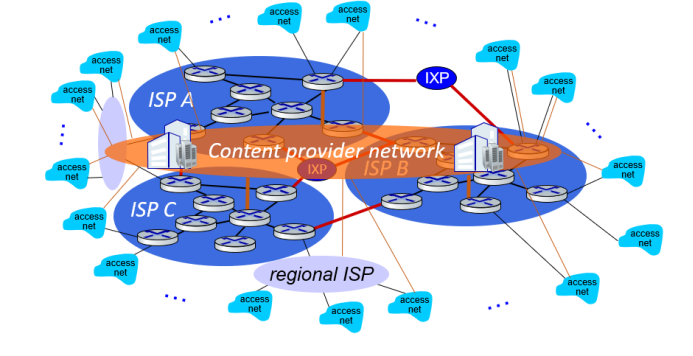
(8) 最终关系图