使用CoreData [2]
此篇讲解CoreData处理关系型数据.
1. 先创建出Student于Teacher的实体.
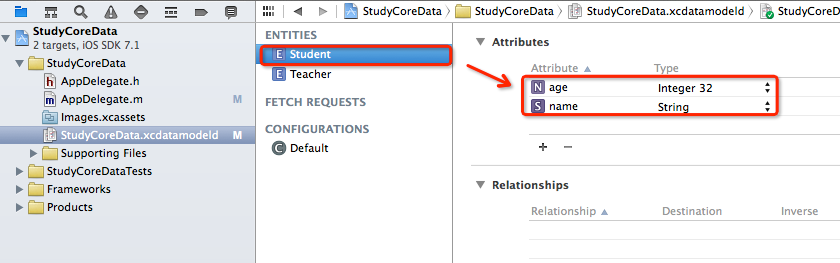

2. 确定关系,并修改描述
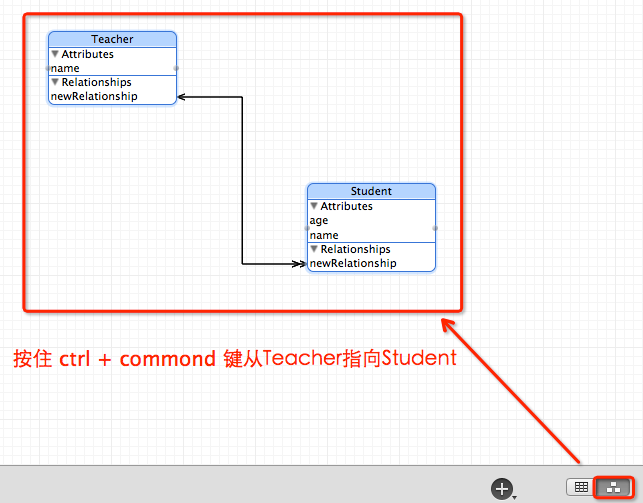
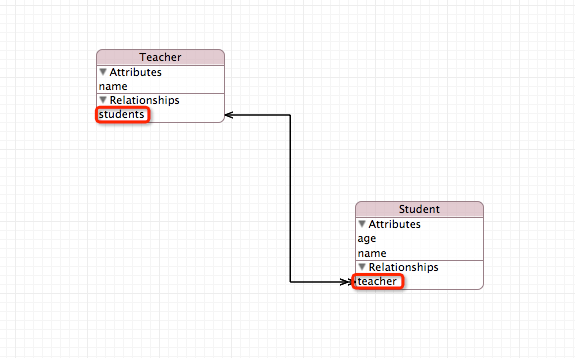
3. 创建对象,并查看一下关系(Teacher与Student之间是有着关联关系的哦)
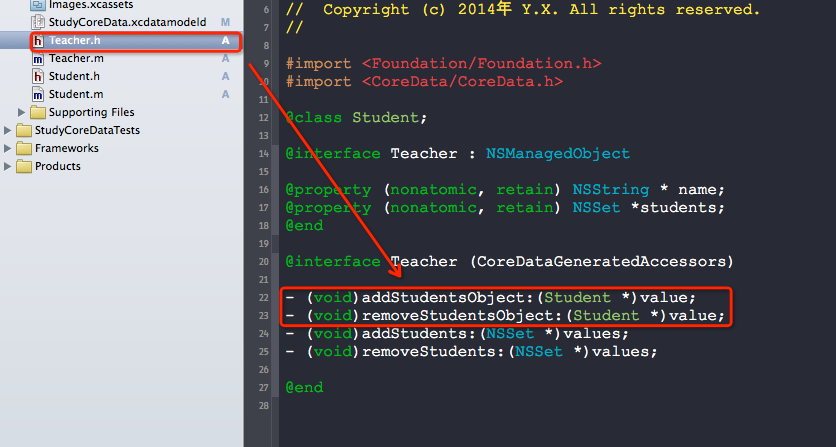
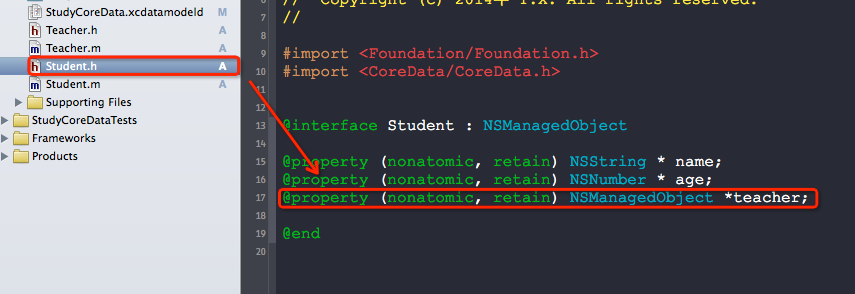
4. 测试代码.
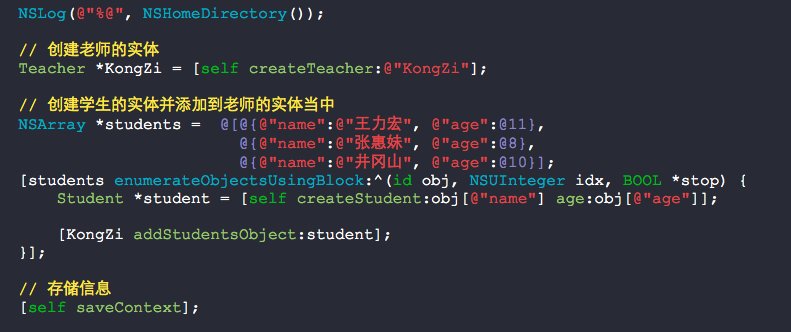
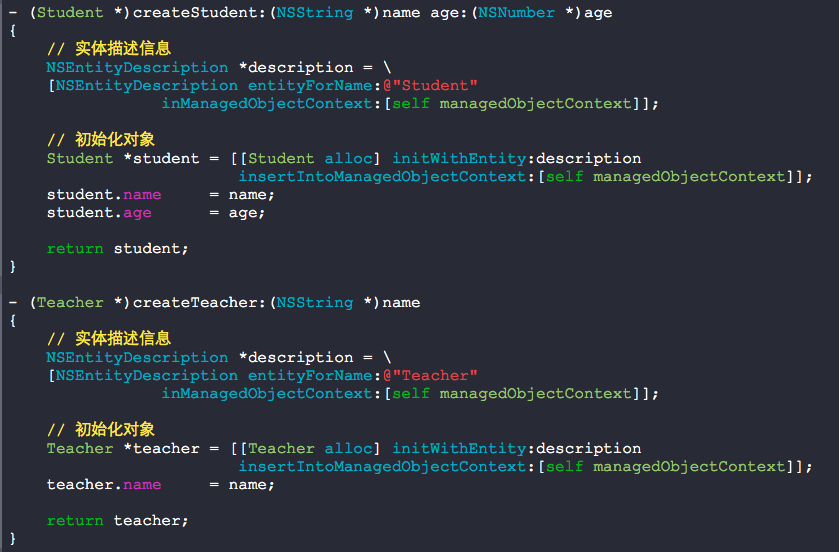
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { NSLog(@"%@", NSHomeDirectory()); // 创建老师的实体 Teacher *KongZi = [self createTeacher:@"KongZi"]; // 创建学生的实体并添加到老师的实体当中 NSArray *students = @[@{@"name":@"王力宏", @"age":@11}, @{@"name":@"张惠妹", @"age":@8}, @{@"name":@"井冈山", @"age":@10}]; [students enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { Student *student = [self createStudent:obj[@"name"] age:obj[@"age"]]; [KongZi addStudentsObject:student]; }]; // 存储信息 [self saveContext]; return YES; } - (Student *)createStudent:(NSString *)name age:(NSNumber *)age { // 实体描述信息 NSEntityDescription *description = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Student" inManagedObjectContext:[self managedObjectContext]]; // 初始化对象 Student *student = [[Student alloc] initWithEntity:description insertIntoManagedObjectContext:[self managedObjectContext]]; student.name = name; student.age = age; return student; } - (Teacher *)createTeacher:(NSString *)name { // 实体描述信息 NSEntityDescription *description = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Teacher" inManagedObjectContext:[self managedObjectContext]]; // 初始化对象 Teacher *teacher = [[Teacher alloc] initWithEntity:description insertIntoManagedObjectContext:[self managedObjectContext]]; teacher.name = name; return teacher; }
5. 验证关系型数据

- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { NSLog(@"%@", NSHomeDirectory()); // 设定要查询的实体 NSFetchRequest *fetch = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Teacher"]; // 取出查询结果 NSArray *teachers = [[self managedObjectContext] executeFetchRequest:fetch error:nil]; // 遍历出所有老师 [teachers enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { Teacher *teacher = obj; // 获取该老师所有的学生 [[teacher students] enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, BOOL *stop) { Student *student = obj; NSLog(@"%@ %@", student.age, student.name); Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)student.teacher; NSLog(@"老师是: %@", tmp.name); }]; }]; return YES; }
*6. 验证存在两个老师的情形
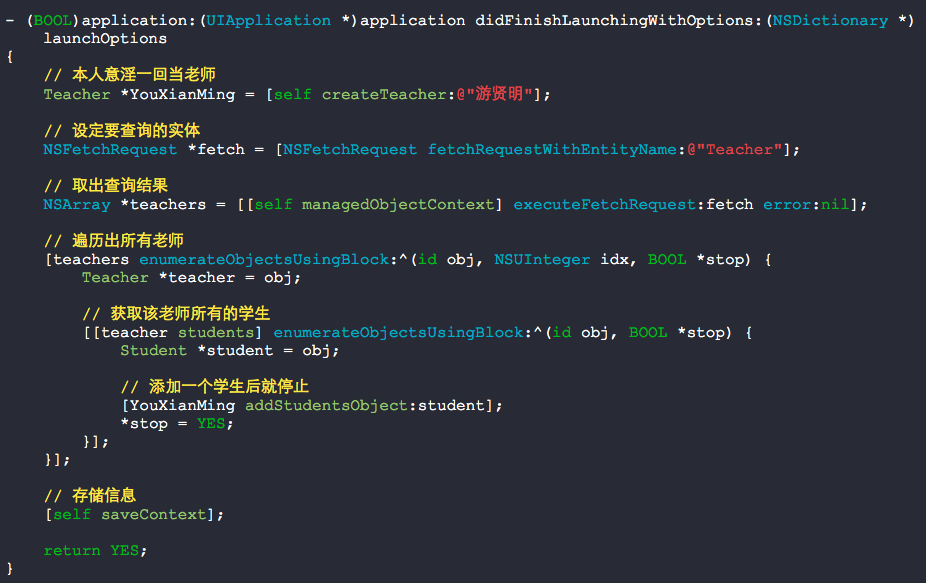
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { // 本人意淫一回当老师 Teacher *YouXianMing = [self createTeacher:@"游贤明"]; // 设定要查询的实体 NSFetchRequest *fetch = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Teacher"]; // 取出查询结果 NSArray *teachers = [[self managedObjectContext] executeFetchRequest:fetch error:nil]; // 遍历出所有老师 [teachers enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { Teacher *teacher = obj; // 获取该老师所有的学生 [[teacher students] enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, BOOL *stop) { Student *student = obj; // 添加一个学生后就停止 [YouXianMing addStudentsObject:student]; *stop = YES; }]; }]; // 存储信息 [self saveContext]; return YES; }
执行上述代码之后在执行下述代码.

下图表明了这个原因:
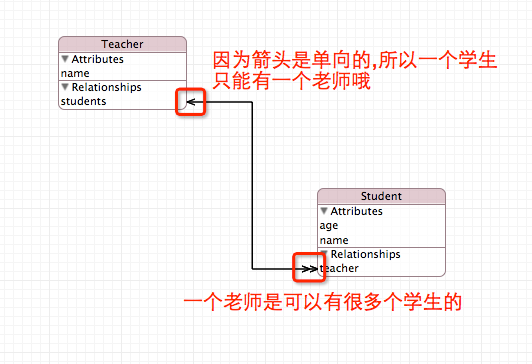
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { // 设定要查询的实体 NSFetchRequest *fetch = [NSFetchRequest fetchRequestWithEntityName:@"Teacher"]; // 取出查询结果 NSArray *teachers = [[self managedObjectContext] executeFetchRequest:fetch error:nil]; // 遍历出所有老师 [teachers enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, NSUInteger idx, BOOL *stop) { Teacher *teacher = obj; // 获取该老师所有的学生 [[teacher students] enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(id obj, BOOL *stop) { Student *student = obj; Teacher *tmp = (Teacher *)student.teacher; NSLog(@"%@ %@", student.age, student.name); NSLog(@"老师是: %@", tmp.name); }]; }]; return YES; }
附录:
如果想修改多对多,请以下图为参考
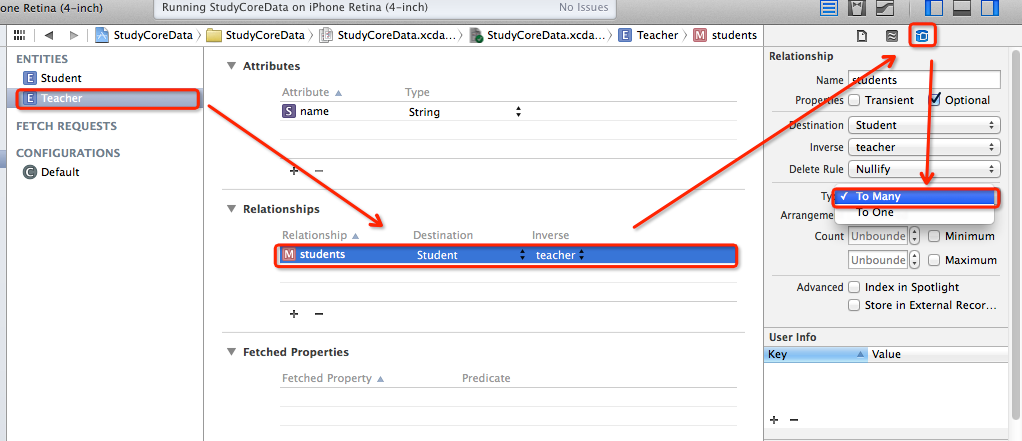
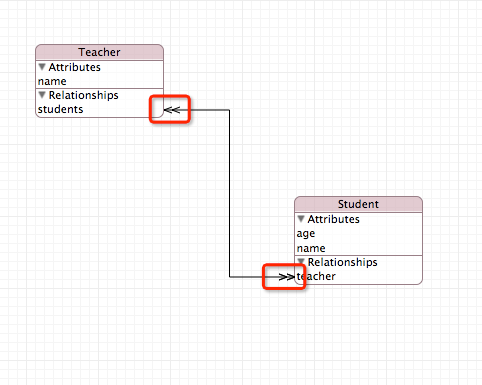
上图那么修改了之后就会变成下图所示的多对多了,一个学生也可以有好几个老师了.
以上就讲完了关系型数据:)