教材学习内容总结
- 第一周要点:
- 要点1:vim编辑器的基本操作;
- 要点2:正则表达式基础;
- 要点3:Linux C编程基础:
- 编译器GCC;
- 调试器GDB;
- Makefile。
- 要点4:教材第一章、第七章。
- 教材第一章 “计算机系统漫游” 要点:
- 要点1:信息就是位+上下文;
- 要点2:存储设备形成层次结构;
- 要点3:重要主题(概念):
- Amdahl 定律;
- 并发和并行;
- 抽象。
- 教材第七章 “链接” 要点:
- 要点1:静态链接两个主要任务:
- 符号解析;
- 重定位。
- 要点2:目标文件:
- 要点3:符号和符号表;
- 要点4:符号解析:
- 链接器如何解析多重定义的全局符号;
- (未完)
- 要点1:静态链接两个主要任务:
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
1. 生成二进制文件时命令错误。
根据PPT中:

的命令出错。
在如下项目结构中:

使用 gcc -c -I/include src/say_hello.c 命令出错。
src/say_hello.c:2:11: 致命错误:say_hello.h:没有那个文件或目录
2 | # include "say_hello.h"
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~
编译中断。
-
问题原因分析:
gcc命令格式出错,-I应与头文件所在目录分离。 -
问题解决方案:
-I 与 头文件所在目录 分离,再将生成文件导出到 include 文件夹下,命令如下:
gcc -c -I include src/say_hello.c -o include/say_hello.o
可生成:
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ tree
.
├── bin
├── include
│ ├── say_hello.h
│ └── say_hello.o
├── libs
├── makefile
├── Readme.md
└── src
├── main.c
└── say_hello.c
4 directories, 6 files
2. 在最终链接时报错。
输入命令 gcc src/main.c -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main 报错。
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ gcc src/main.c -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main
src/main.c: 在函数‘main’中:
src/main.c:5:2: 警告:隐式声明函数‘say_hello’ [-Wimplicit-function-declaration]
5 | say_hello();
| ^~~~~~~~~
/usr/bin/ld: /tmp/ccKSn7Vo.o: in function `main':
main.c:(.text+0xa): undefined reference to `say_hello'
collect2: 错误:ld 返回 1
-
问题原因分析:
发生"undefined reference to"错误有多种原因(点击查看)。在这里是由于链接时缺失了二进制文件(say_hello.o)。 -
问题解决方案:
方法一:
将命令中最开始的 "src/main.c" 改为"src/*.c" ,直接将所有的源文件一起重新汇编成二进制文件,再一起编译。
gcc src/*.c -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main
方法二:
直接将缺少的二进制文件加入编译命令,在 src/main.c -I 中间添加 include/say_hello.o 。
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ gcc src/*.c -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ bin/main
hello word
3. 静态函数库、动态函数库命令编译步骤。
- 静态库
gcc -c -I include/ src/say_hello.c -o include/say_hello.o
ar rcvs libs/libsay_h.a include/say_hello.o
# 屏幕输出提示:r - include/say_hello.o
gcc src/*.c -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main
# 运行可执行文件即可:
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ bin/main
hello word
- 动态库
gcc -fPIC -c -I include/ src/say_hello.c -o include_so/say_hello.o
gcc -shared -o include_so/libsay_h.so include_so/say_hello.o
gcc src/main.c include_so/say_hello.o -I include/ -L libs/ -o bin/main_so
# 运行可执行文件即可:
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ bin/main_so
hello word
- 创建的项目结构
项目结构
[yogile@yogile-pc gcc_test]$ tree . ├── bin │ ├── main │ └── main_so ├── include │ ├── say_hello.h │ └── say_hello.o ├── include_so │ └── say_hello.o ├── libs │ ├── libsay_h.a │ └── libsay_h.so ├── makefile ├── Readme.md └── src ├── main.c └── say_hello.c
5 directories, 11 files
4. 对链接器解析多重定义全局符号 规则 的疑惑。
强弱符号解析处理规则有三:
- 不允许多个同名的强符号;
- 若有一个强符号和多个弱符号同名,则则选择强符号;
- 若有多个弱符号同名,则任取一个。
疑惑1:对于规则2,若在 main.c 文件中,定义弱符号 x;在 module_2.c 文件中,定义强符号 x=3,在 main.c 中输出显示 x 为多少?
疑惑2:对于规则3,到底会选用哪个弱符号?
- 分析回答:
回答疑惑1:
对于规则2,无论强符号在哪个模块定义,在其他模块调用同名符号时,链接器都会选择该模块的强符号,测试如下。
测试1
**main.c**
```
# include
# include "mod.h"
int x;
int main()
{
printf("x_start = %d
", x);
x=1;
mod_2();
printf("x = %d
", x);
return 0;
}
**module_2.c**
include <stdio.h>
include "mod.h"
int x=3;
void mod_2()
{
printf(" x_2 = %d
", x);
}
编译运行结果为:
[yogile@yogile-pc 7.6.1]$ ./mod.out
x_start = 3
x_2 = 1
x = 1
</code></pre>
</details>
回答疑惑2:
对于规则三,若都是弱符号(即:未初始化,编译时初值为0),根据资料,所谓“随机选定的”是指占用空间最大的,选定后不会更改,测试如下。
<details>
<summary><mark><font color=darkred>测试2</font></mark></summary><pre><code>
**main.c**
include <stdio.h>
include "mod.h"
int x;
int main()
{
printf("x_start = %d
", x);
mod_2();
x=1;
mod_2();
printf("x = %d
", x);
return 0;
}
**module_2.c**
include <stdio.h>
include "mod.h"
int x;
void mod_2()
{
printf(" x_2 = %d
", x);
}
编译运行结果为:
[yogile@yogile-pc 7.6.1]$ ./mod.out
x_start = 0
x_2 = 0
x_2 = 1
x = 1
</code></pre>
</details>
****
## [代码托管]
已更改 `statistics.sh(ssss.sh)` 中 `find . -name "*.java"` 更改为 `find . -name "*.c"`。
对应仓库网页链接:https://gitee.com/Yogile/Cpt_System_Yogile
- 代码提交过程截图:
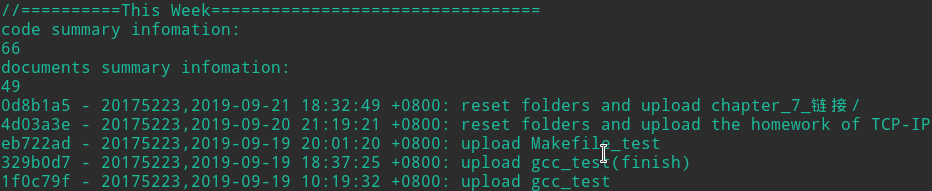
- 代码量截图:
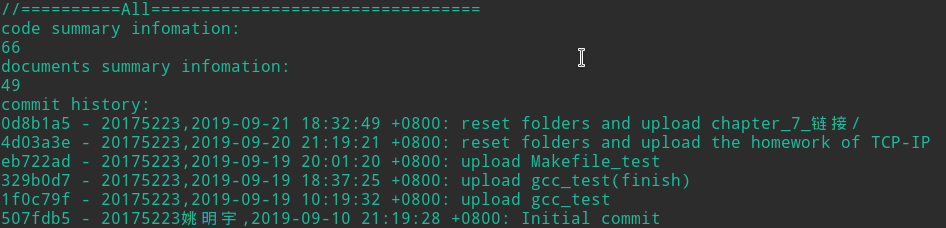
****
## 学习进度条
| | 代码行数(新增/累积)| 博客量(新增/累积)|学习时间(新增/累积)|重要成长|
| -------- | :----------------:|:----------------:|:---------------: |:-----:|
| 目标 | 4000行 | 20篇 | 280小时 | |
| 第一周 | 66/66 | 1/1 | 24/24 | |
- 计划学习时间:16小时
- 实际学习时间:24小时
****
## 参考资料
- ["undefined reference to" 问题解决方法](https://blog.csdn.net/u011244446/article/details/51519741)