哈夫曼树及哈夫曼编码
-
哈夫曼树是判定过程最优的决策树,又称最优二叉树。
-
哈夫曼树的每个结点有权值,一个结点的权值实际上就是这个结点子树在整个树中所占的比例,通常指字符对应的二进制编码出现的概率。权值大的结点距离根结点近。
-
树的带权路径长度(WPL):如果树中每个叶子上都带有一个权值,则把树中所有叶子的带权路径长度之和称为树的带权路径长度。哈弗曼树就是带权路径长度最小的二叉树。设某二叉树有n个带权值的叶子结点,则该二叉树的带权路径长度记为(Wk为第k个叶子结点的权值;Lk为该结点的路径长度):
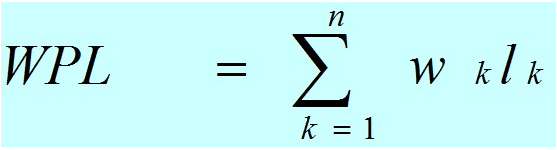
-
哈弗曼树是自底向上构建的,二叉树的左子树编码为0,右子树编码为1,然后从根到每个叶结点依次写出叶结点的编码,即哈夫曼编码。
-
哈夫曼编码是已知的最佳无损压缩算法,并且满足前缀码的性质,可以随时解码。
-
具体过程:
- 给定字符集设为S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h},计算各个字符出现的概率,即权值。
- 将字符转换为树结点并根据权值大小将字符由小到大排序
- 依次将权值最小的两个字符的权值相加,得到新的权值,为那两个字符的父结点,删除那两个字符,并将形成的树添加到排序列表中,父结点的权值按大小排序,在序列中找到合适的位置,然后再将最小的两个字符进行以上操作...
- 最终只剩一个结点,并形成了一棵树,即哈弗曼树。
-
编码:在哈夫曼树中规定左分支表示符号0,右分支表示符号1。对于每个叶子结点,从根结点到此叶子结点形成的编码就是这个结点表示字符的哈夫曼编码。
-
解码:译码过程是分解、识别各个字符,还原数据的过程。从字符串头开始扫描到尾,依次去匹配。
-
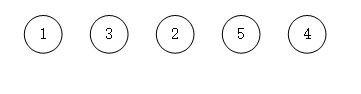
图示过程
- 首先是带权值的数
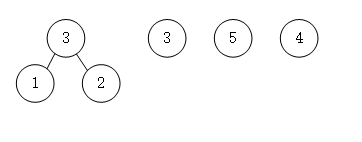
- 第二步将最小的1和2组合相加形成父结点,并删除1和2
- 依次进行
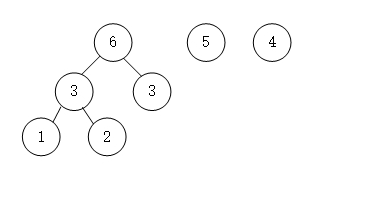

- 这是只剩下一个结点,同时也形成了一棵树,这就是哈夫曼树。
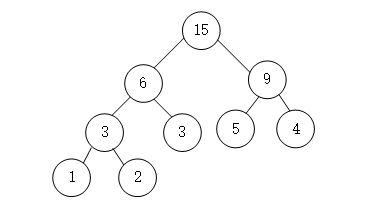
- 首先是带权值的数
代码实现
-
首先构造结点类,每个结点需要有哈夫曼编码,字符本身,权值,以及左结点和右结点。
public class TreeNode { public String code = "";// 节点的哈夫曼编码 public String data = "";// 节点的字符 public int count;// 节点的权值 public TreeNode lChild;//左结点 public TreeNode rChild;//右结点 public TreeNode(String data, int count) { this.data = data; this.count = count; } public TreeNode(int count, TreeNode lChild, TreeNode rChild) { this.count = count; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; } } -
计算每个字符的权重,flag用来判定取出的字符串是否存在,若不存在为true,如果存在那么就在出现次数统计上加一,即权重加一,如果没有出现过,就将它加入到存储字符的链表中。
// 统计出现的字符及出现次数 private void getCharNum(String str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); // 从字符串中取出字符 flag = true; for (int j = 0; j < charList.size(); j++) { CharData data = charList.get(j); // 遍历字符链表,若有相同字符则将个数加1 if(ch == data.chardata){ data.num++; flag = false; totalcount++; break; } } // 字符对象链表中没有相同字符则将其加到链表中 if(flag){ charList.add(new CharData(ch)); totalcount++; } } } -
将字符链表中的字符构建为结点,利用循环将字符链表中的字符和其权值创建为TreeNode结点,并加入到结点链表中。
//将字符创建为结点 private void creatNodes() { for (int i = 0; i < charList.size(); i++) { String data = charList.get(i).chardata + ""; int count = charList.get(i).num;//权值 TreeNode node = new TreeNode(data, count); // 创建节点对象 NodeList.add(node); // 加入到节点链表 } } -
构建哈弗曼树,根据上文提到的哈夫曼编码的规则,将最小的两个节点分别设置为左右子结点,左边编码为0,右边为1,然后依据父结点创建新的TreeNode结点,将新的结点放到链表首位并重新排序。一次循环进行,直到结点链表中的节点数不大于1,这时树就形成了。
//构建哈夫曼树 private void creatTree() { // 当节点数目大于一时,将权值最小的两个节点生成一棵新树,父结点为两者之和,并删除两个结点将新树放到列表中 while (NodeList.size() > 1) { TreeNode left = NodeList.poll(); TreeNode right = NodeList.poll(); // 设置各个结点的哈夫曼编码 left.code = "0"; right.code = "1"; setCode(left); setCode(right); int parentWeight = left.count + right.count;// 父节点权值等于子节点权值之和 TreeNode parent = new TreeNode(parentWeight, left, right); NodeList.addFirst(parent); // 暂时将父节点置于首位 Sort(NodeList); // 重新排序将父结点放到合适位置 } } -
在构建哈夫曼树的过程中每次将最小的两个相加构造新结点时,需要对新的链表进行排序,所以用到升序排序法,将链表从左开始依次与其右边的所有字符比较权值,将权值小的字符放到左边,这样就形成升序链表。
//升序排序 private void Sort(LinkedList<TreeNode> nodelist) { for (int i = 0; i < nodelist.size() - 1; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < nodelist.size(); j++) { TreeNode temp; if (nodelist.get(i).count > nodelist.get(j).count) { temp = nodelist.get(i); nodelist.set(i, nodelist.get(j)); nodelist.set(j, temp); } } } } -
设置每个结点的哈夫曼编码,从根结点开始,分别对做孩子和右孩子的编码添加0/1,左结点为0,右结点为1。这样每个叶子节点都有独一无二的01编码。
//设置结点的哈夫曼编码 private void setCode(TreeNode root) { if (root.lChild != null) { root.lChild.code = root.code + "0"; setCode(root.lChild); } if (root.rChild != null) { root.rChild.code = root.code + "1"; setCode(root.rChild); } } -
利用以上方法,根据哈夫曼编码的规则构建哈夫曼树
//构建哈夫曼树 public void creatHuffmanTree(String str) { this.str = str; NodeList = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); charList = new LinkedList<CharData>(); // 统计字符串中字符以及字符的出现次数 getCharNum(str); // 创建节点 creatNodes(); // 对节点升序排序 Sort(NodeList); // 将权值最小的两个节点相加生成一个新的父节点并删除权值最小的两个节点,将父节点存放到列表中,形成树 creatTree(); // 将最后的一个节点赋给根节点 root = NodeList.get(0); } -
遍历节点输出字符的编码,通过判断左右孩子是否为空的情况,找到叶子结点,即字符,然后输出其编码和出现次数。
//遍历结点 private void output(TreeNode node) { if (node.lChild == null && node.rChild == null) { System.out.println(node.data + " 的编码为:" + node.code+ " 出现次数为:"+ node.count + " 出现概率为:"+ (node.count)/totalcount); } if (node.lChild != null) { output(node.lChild); } if (node.rChild != null) { output(node.rChild); } } -
编码,定义字符串hfmCodeStr,将叶子结点的编码依次添加到编码字符串中,返回hfmCodeStr字符串。
//编码 public String creHufmCode(String str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { String string = str.charAt(i) + ""; search(root, string); } return hfmCodeStr; } //找到叶子结点,添加其编码 private void search(TreeNode root, String c) { if (root.lChild == null && root.rChild == null) { if (c.equals(root.data)) { hfmCodeStr += root.code; } } if (root.lChild != null) { search(root.lChild, c); } if (root.rChild != null) { search(root.rChild, c); } } -
解码,通过遍历叶子结点找到相匹配的字符编码,定义编码后的字符串从第一个数字开始,用substring方法截取字符串,如果找到相匹配的叶子结点编码,就进行解码,当解码失败时,说明编码不匹配,end向后移,当解码成功时,first向后移,对下一段字符进行解码,最后输出解码后的字符串。
//解码 public String decode(String codeStr) { int first = 0; int end = 1; while(end <= codeStr.length()){ target = false; String s = codeStr.substring(first, end); matchCode(root, s); // 解码 // 每解码一个字符,first向后移 if(target){ first = end; } end++; } return result; } //匹配字符哈夫曼编码,找到对应的字符 private void matchCode(TreeNode root, String code){ if (root.lChild == null && root.rChild == null) { if (code.equals(root.code)) { result += root.data; // 找到对应的字符,拼接到解码字符串后 target = true; // 标志为true } } if (root.lChild != null) { matchCode(root.lChild, code); } if (root.rChild != null) { matchCode(root.rChild, code); } } -
读取文件中的字符串,并构造哈夫曼树
BufferedReader a = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("wen.txt")); String data = a.readLine(); huff.creatHuffmanTree(data);// 构造树 -
将编码解码后的内容写入文件
//写入文件 File file = new File("wen2"); Writer write = new FileWriter(file); write.write(hufmCode); write.flush(); write.write(huff.decode(hufmCode)); write.close( -
运行结果

-
英文文件
-
将编码解码后的结果存入文件

码云链接
https://gitee.com/CS-IMIS-23/20172314/blob/master/src/新第十四周/Huffman.java