#-----------------写入到文本文件中----------------#
/*
01)包含头文件fstream
02)创建一个ofstream对象,名字可以任意取
03)将该ofstream对象和一个文件关联起来,方法之一就是用open()方法
04)就可以像使用cout一样去使用该ofstream对象了
05)必须知名名称空间std,例如,为引用元素ofstream,必须使用编译指令using或前缀std::
06)使用完文件后,应使用方法close()将其关闭
*/

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> //for file I/O 01) 包含头文件 3 4 int main() 5 { 6 using namespace std; 7 8 char automobile[50]; 9 int year; 10 double a_price; 11 double b_price; 12 13 ofstream outFile; // 02) 创建一个ofstream对象 14 outFile.open("carinfo.txt"); //03) 将该ofstream对象(outFile)和一个文件关联起来, 15 //此后就可以像使用cout一样使用outFlie 16 cout << "Enter the make and model of automobile:"; 17 cin.getline(automobile, 50); 18 cout << "Enter the model year: "; 19 cin >> year; 20 cout << "Enter the original asking price: "; 21 cin >> a_price; 22 b_price = 0.913 * a_price; 23 24 //display infomation on screen with cout 25 cout << fixed; //使用一般方式输出浮点数,而不是可科学计数法 26 cout.precision(2); //设置2为浮点数的精度值 27 cout.setf(ios_base::showpoint); //显示小数点后面的0 28 cout << "Make the model: " << automobile << endl; 29 cout << "Year: " << year << endl; 30 cout << "was asking $" << a_price << endl; 31 cout << "Now asking $" << b_price << endl; 32 33 //Now do exact same things using outFile instead of cout 34 //但是outFile将cout在屏幕上显示的内容写入到了carinfo.txt文件中 35 //如果原来没有carinfo.txt文件,那么会自动创建 36 //该代码将文件创建在了和main.cpp在同一个文件夹中,但是在编译环境中没有显示出该文件 37 //如果已存在该文件,那么会默认情况下会覆盖掉文件中所有的内容 38 outFile << fixed; //使用一般方式输出浮点数,而不是可科学计数法 39 outFile.precision(2); //设置2为浮点数的精度值 40 outFile.setf(ios_base::showpoint); //显示小数点后面的0 41 outFile << "Making and model: " << automobile << endl; 42 outFile << "Year: " << year << endl; 43 outFile << "was asking $" << a_price << endl; 44 outFile << "Now asking $" << b_price << endl; 45 outFile.close(); //关闭文本文件 46 47 system("pause"); 48 49 return 0; 50 }
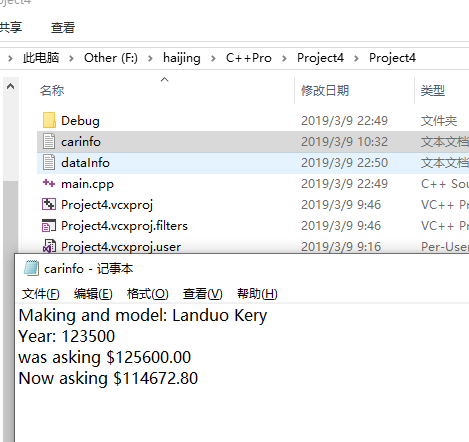
执行结果会在和main.cpp在同一个文件夹下创建一个carinfo.txt文件
其内容为:
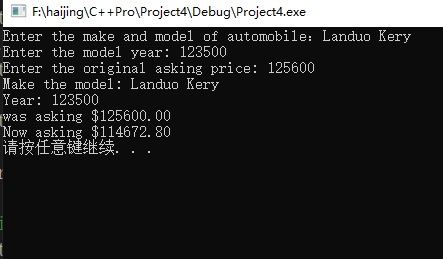
cout执行结果为:
读取文本文件
/*
01)包含头文件fstream
02)创建一个ifstream对象,名字可以任意取
03)将该ifstream对象和一个文件关联起来,方法之一就是用open()方法
04)就可以像使用cin一样去使用该ifstream对象了
05)必须知名名称空间std,例如,为引用元素ifstream,必须使用编译指令using或前缀std::
06)使用完文件后,应使用方法close()将其关闭
07)可以使用ifstream对象和get()方法来获取一个字符
08)可以使用ifstream对象和getline()方法来获取一行字符
09)可以结合ifstream对象和eof()、fail()等方法来判断输入是否成功
*/

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <cstdlib> //for exit() 4 5 const int SIZE = 60; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 using namespace std; 10 char filename[SIZE]; //刚刚使用size的小写,显示size不明确,现在用大写就没问题了 11 ifstream inFile; //02) 创建一个ifstream对象ifFile 12 cout << "Enter name of a data file: "; 13 cin.getline(filename, SIZE); 14 inFile.open(filename); //03) 将该ofstream对象(outFile)和一个文件关联起来, 15 //此后就可以像使用cout一样使用outFlie 16 if (!inFile.is_open()) //判断文件是否打开成功,如果打开成功,则inFile.is_open()返回true;否则返回false 17 { 18 cout << "Could not open the file " << filename << endl; 19 cout << "Program terminating" << endl; 20 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); //退出程序 21 } 22 double value; 23 double sum = 0.0; 24 int count = 0; 25 26 inFile >> value; //从文本文件中得到第一个数字,文件中的字符如果和value的类型不一样,下面的fail()方法就会返回true 27 while (inFile.good()) //1)good()方法指出最后一次读取输入是否成功,若成功,则返回true;否则,返回false 28 { //2)下面的eof()方法和fail()方法用于判断到底是因何错误导致读入数据发生错误 29 //3)也可以用while(inFile>>value)来代替,在正确输入的情况下,inFile>>value返回true,否则返回false 30 ++count; //对读取的次数进行计数,以便于接下来计算平均数 31 sum = sum + value; //进行文件中数据的累加 32 inFile >> value; //进行下一次的读取,并赋值给vlaue 33 } 34 if (inFile.eof()) //判断是否读到了文件的末尾,如果到了末尾,则eof()返回true 35 cout << "End of the file reached" << endl; 36 else if (inFile.fail()) //判断是否读到了和value类型不一样的字符,如果有,则fail()返回true 37 cout << "Input terminated by data mismatch" << endl; 38 else 39 cout << "Input terminated by unknow reason" << endl; 40 if (count == 0) //判断文件中是否有数字 41 cout << "No data readed" << endl; 42 else 43 { 44 cout << "Items read: " << count << endl; 45 cout << "Sum: " << sum << endl; 46 cout << "Average: " << sum / count << endl; 47 } 48 inFile.close(); 49 system("pause"); 50 return 0; 51 }
执行结果:
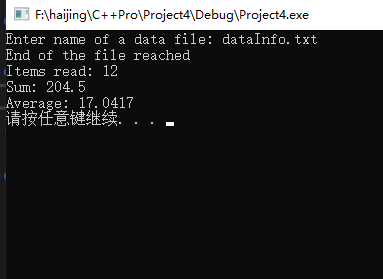
但是最开始的时候在最后一个字符中没有加换行符,导致最后一个字符没有被读入!!

