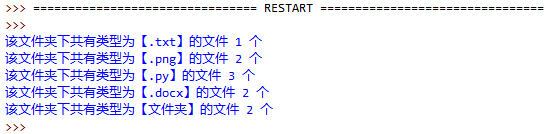
1. 编写一个程序,统计当前目录下每个文件类型的文件数,程序实现如图:
实现代码:
import os
all_files = os.listdir(os.chdir("D:\"))
type_dict = dict()
for each_file in all_files:
if os.path.isdir(each_file):
type_dict.setdefault('文件夹', 0)
type_dict['文件夹'] += 1
else:
ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1]
type_dict.setdefault(ext, 0)
type_dict[ext] += 1
for each_type in type_dict.keys():
print('该文件夹下共有类型为【%s】的文件 %d 个' % (each_type, type_dict[each_type]))
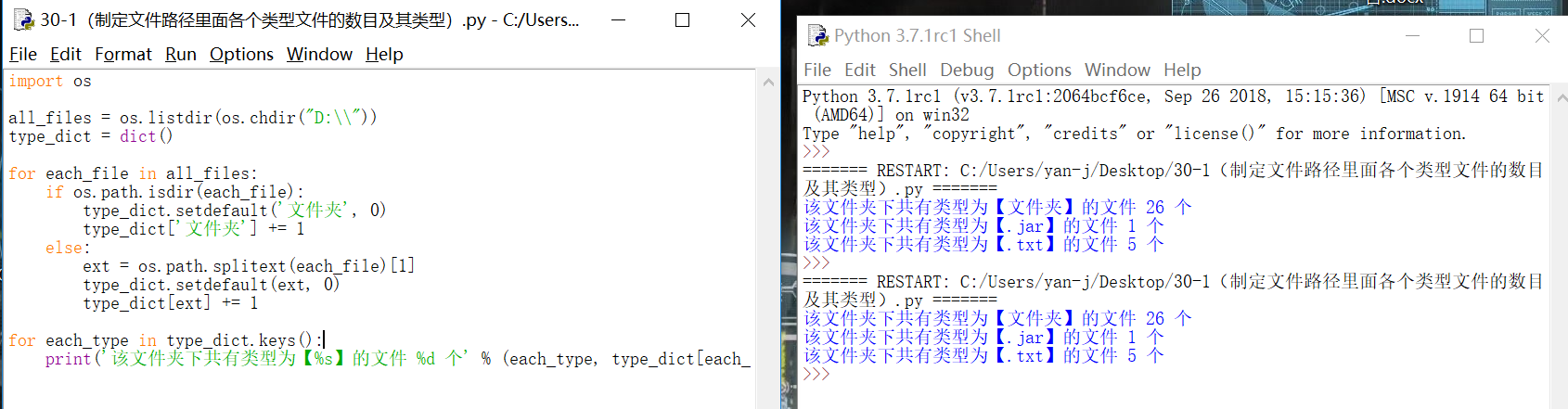
2、编写一个程序,计算当前文件夹下所有文件的大小:
import os
all_files = os.listdir(os.chdir("D:\")) # 使用os.curdir表示当前目录更标准
file_dict = dict()
for each_file in all_files:
if os.path.isfile(each_file):
file_size = os.path.getsize(each_file)
file_dict[each_file] = file_size
for each in file_dict.items():
print('%s【%dBytes】' % (each[0], each[1]))
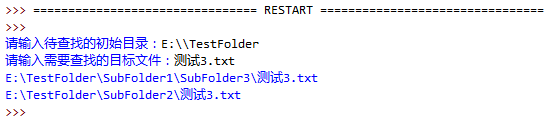
3、编写一个程序,用户输入文件名以及开始搜索的路径,搜索该文件是否存在。如遇到文件夹,则进入文件夹继续搜索:
import os
def search_file(start_dir, target) :
os.chdir(start_dir)
for each_file in os.listdir(os.chdir("C:\")) :
if each_file == target :
print(os.getcwd() + os.sep + each_file) # 使用os.sep是程序更标准
if os.path.isdir(each_file) :
search_file(each_file, target) # 递归调用
os.chdir(os.pardir) # 递归调用后切记返回上一层目录
start_dir = input('请输入待查找的初始目录:')
target = input('请输入需要查找的目标文件:')
search_file(start_dir, target)
4、 编写一个程序,用户输入开始搜索的路径,查找该路径下(包含子文件夹内)所有的视频格式文件(要求查找mp4 rmvb, avi的格式即可),并把创建一个文件(vedioList.txt)存放所有找到的文件的路径,程序实现如图:
import os
def search_file(start_dir, target) :
os.chdir(start_dir)
for each_file in os.listdir(os.curdir) :
ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1]
if ext in target :
vedio_list.append(os.getcwd() + os.sep + each_file + os.linesep) # 使用os.sep是程序更标准
if os.path.isdir(each_file) :
search_file(each_file, target) # 递归调用
os.chdir(os.pardir) # 递归调用后切记返回上一层目录
start_dir = input('请输入待查找的初始目录:')
program_dir = os.getcwd()
target = ['.mp4', '.avi', '.rmvb']
vedio_list = []
search_file(start_dir, target)
f = open(program_dir + os.sep + 'vedioList.txt', 'w')
f.writelines(vedio_list)
f.close()
5、编写一个程序,用户输入关键字,查找当前文件夹内(如果当前文件夹内包含文件夹,则进入文件夹继续搜索)所有含有该关键字的文本文件(.txt后缀),要求显示该文件所在的位置以及关键字在文件中的具体位置(第几行第几个字符)

import os
def print_pos(key_dict):
keys = key_dict.keys()
keys = sorted(keys) # 由于字典是无序的,我们这里对行数进行排序
for each_key in keys:
print('关键字出现在第 %s 行,第 %s 个位置。' % (each_key, str(key_dict[each_key])))
def pos_in_line(line, key):
pos = []
begin = line.find(key)
while begin != -1:
pos.append(begin + 1) # 用户的角度是从1开始数
begin = line.find(key, begin+1) # 从下一个位置继续查找
return pos
def search_in_file(file_name, key):
f = open(file_name)
count = 0 # 记录行数
key_dict = dict() # 字典,用户存放key所在具体行数对应具体位置
for each_line in f:
count += 1
if key in each_line:
pos = pos_in_line(each_line, key) # key在每行对应的位置
key_dict[count] = pos
f.close()
return key_dict
def search_files(key, detail):
all_files = os.walk(os.curdir)
txt_files = []
for i in all_files:
for each_file in i[2]:
if os.path.splitext(each_file)[1] == '.txt': # 根据后缀判断是否文本文件
each_file = os.path.join(i[0], each_file)
txt_files.append(each_file)
for each_txt_file in txt_files:
key_dict = search_in_file(each_txt_file, key)
if key_dict:
print('================================================================')
print('在文件【%s】中找到关键字【%s】' % (each_txt_file, key))
if detail in ['YES', 'Yes', 'yes']:
print_pos(key_dict)
key = input('请将该脚本放于待查找的文件夹内,请输入关键字:')
detail = input('请问是否需要打印关键字【%s】在文件中的具体位置(YES/NO):' % key)
search_files(key, detail)