一、前言
从今天你开始我们就开始进行我们的web开发,之前的一篇用SpringBoot起飞系列-使用idea搭建环境(二)已经说明了我们如何进行开发,当然这是搭建起步,接下来我们就开始进行详细的开发,包括springboot中各种starters的使用,真正的使用到的功能都是我们实际项目中能用到的。
这里要提到的时,springboot的开发是分模块化的,每个模块可以对应一个starter,例如:web开发模块就对应spring-boot-starter-web,除此之外还有访问数据库的模块、Redis模块等等,我们需要什么样的功能就去引入什么模块,这样我们的项目管理起来也是十分方便,项目的条理也更加的清晰。
首先我们要搭建一个web项目,所以我们要先选中web模块,这是必须的,之后的模块需要什么我们再逐一引入。
二、SpringBoot的Web开发约定
2.1 配置约定
俗话说,springboot这个框架本身就是用约定大于配置的方式设计的,很多配置都成了我们的约定(默认的配置),我们虽然可以更改,但是还是有必要知道的。下面我们简单介绍一下springboot的自动配置原理,这就是springboot中的约定的实现方法。
首先,springboot会把配置文件中以某个前缀开头的配置映射的bean中去,这样我们的配置就在程序启动的时候成了一个一个bean,使用起来也比较方便,默认情况下springboot会用一个Configuration和一个Properites类来配置,如下:
xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件;xxxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容; 每一个的AutoConfiguration对应一个Properties,springboot中所有的配置都是这么实现的。xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;xxxProperties是接受配置的bean。
我们以
@Configuration //表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpEncodingProperties.class) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中@ConditionalOnWebApplication //Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器;@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = 'spring.http.encoding', value = 'enabled', matchIfMissing = true) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的//即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的;public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final HttpEncodingProperties properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpEncodingProperties properties) { this.properties = properties; } @Bean //给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(CharacterEncodingFilter.class) //判断容器没有这个组件? public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
所以说springboot有很多这样的类,我们默认只关注配置的prefix就行了, 这是我们以后要覆盖修改springboot的默认配置所需要的配置key。
2.2 静态资源映射约定
首先我们可以先看一下静态资源的配置类,和我们上边说的是一样的,前缀使用的是spring.resources:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = 'spring.resources', ignoreUnknownFields = false)public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware { //可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等}
具体代码就不再贴了,直接说结果吧,如果我们用maven管理下载我们的静态资源包时,比如jquery.js什么的,那么我们的默认访问路径是 /webjars/** ,都去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源。
webjars:http://www.webjars.org/,是以jar包的方式引入静态资源。例如我们引入jquery.js库,那么可以再pom.xml中这么写:
<!--引入jquery-webjar-->在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可<dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version></dependency>
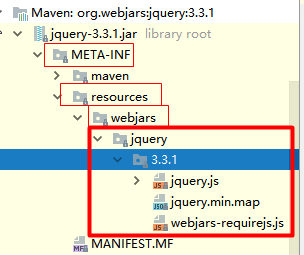
访问地址:localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
如果我们以普通的方式访问我们的静态资源,如html,css,js什么的,所有的访问路径都会从下边的路径里边去找,classpath:指的就是我们的resources文件夹。优先级:/META-INF/resources>resources>static>public。
'classpath:/META-INF/resources/', 'classpath:/resources/','classpath:/static/', 'classpath:/public/' '/':当前项目的根路径
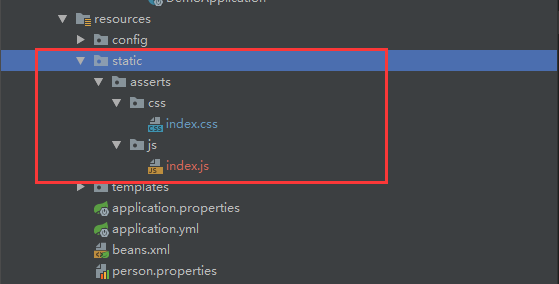
http://localhost:8080/asserts/css/index.css对应static/asserts/css/index.css。
三、模板引擎
3.1 介绍
模板引擎可能这个词听起来很高大上,其实我们之前就接触过,最早的就是jsp,还有现在比较高级的Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf,其实模板引擎这一类的功能大都具有以下特点,我们可以用一张图来解释:
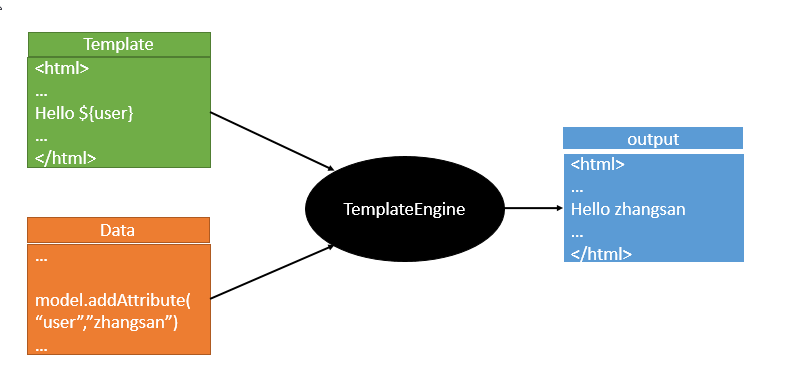
都是数据+表达式,生成html,原理都很简单了,只是我们看哪个写起来比较顺手,功能更加强大了。springboot推荐使用Thymeleaf来作为模板引擎。
3.2 引入Thymeleaf
首先引入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId></dependency>
然后在resources文件夹下添加templates文件夹,下边添加一个index.html,因为默认配置thymeleaf用的前缀是classpath:/templates,后缀是.html。
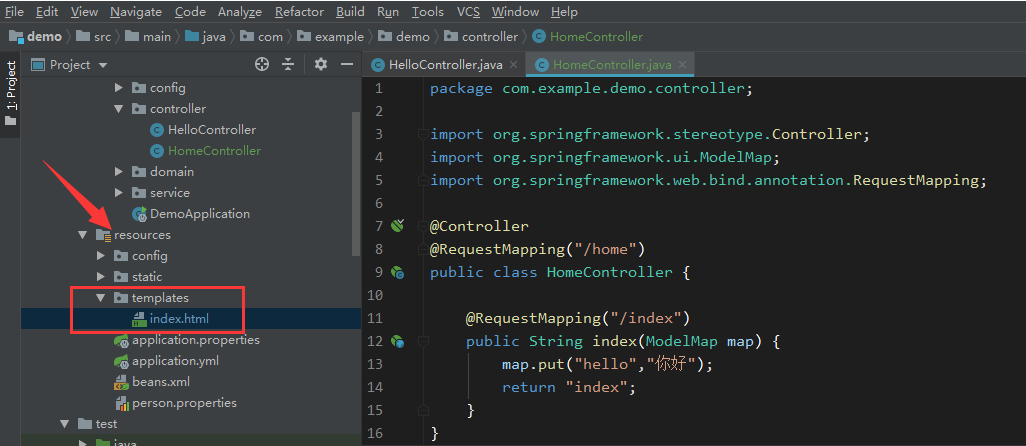
然后我们添加一个HomeController,设置为mvc的控制器,用@Controller注解,如果你用了RestController就直接返回字符串了而不是去找视图了。
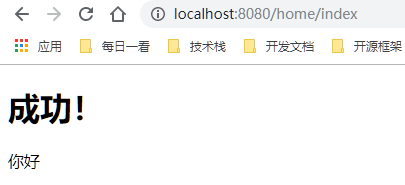
@Controller@RequestMapping('/home')public class HomeController { @RequestMapping('/index') public String index(ModelMap map) { map.put('hello','你好'); return 'index'; }}
然后修改index.html模板,写上thymeleaf语法:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en' xmlns:th='http://www.thymeleaf.org'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <title>Title</title></head><body> <h1>成功!</h1> <!--th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为 --> <div th:text='${hello}'>这是显示欢迎信息</div></body></html>
其中xmlns:th='http://www.thymeleaf.org',是导入名称空间,可以让我们编码的时候有thymeleaf语法提示,不得不说这语法和vue是一样的啊。
我们直接访问http://localhost:8080/home/index就可以看到效果了。
3.3 设置默认启动页
当我们访问一个站点域名的时候,可以默认设置跳转到哪一个页面,这也是许多网站最基本的操作。
下边我们添加一个配置类WebConfig,来设置启动页:
@Configurationpublic class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { //所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用 @Bean //将组件注册在容器 public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController('/').setViewName('forward:/home/index'); registry.addViewController('/index.html').setViewName('forward:/home/index'); } }; return adapter; }}
上边代码的意思是放我们访问/或者/index.html的时候,默认转发到/home/index路径,我们直接设置home/index的页面就行了。
3.4 Thymeleaf语法
3.4.1 标准表达式
使用${},和ognl表达式一样,也是为了照顾我们jsp的开发习惯。
java代码:
@Controller@RequestMapping('/home')public class HomeController { @RequestMapping('/index') public String index(Map<String,Object> map) { map.put('hello','你好啊'); Person person = new Person(); person.setName('zhangsan'); person.setAge(25); map.put('person',person); return 'home/index'; }}
html代码:
<body> <h1>成功!</h1> <!--th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为 --> <div th:text='${hello}'>这是显示欢迎信息</div> <br> <p>姓名:<span th:text='${person.name}'></span></p> <p>年龄:<span th:text='${person.age}'></span></p></body>
3.4.2 选择变量表达式
选择变量表达式,也叫星号变量表达式,使用th:object属性来绑定对象。
html代码:
<p>==========选择变量表达式===========</p><div th:object='${person}'> <div th:text='*{name}'></div> <div th:text='*{age}'></div></div>
选择变量表达式使用th:object来表示要选择的对象,然后使用*来代表这个对象,后边的{}里边写对象中的属性。
也可以直接使用*{person.name}来获取数据,不同的是${}是在上细纹的map中获取数据,而*是在选择的对象上获取数据。
<p>==========选择变量表达式===========</p><div > <div th:text='*{person.name}'></div> <div th:text='*{person.age}'></div></div>
3.4.3 url表达式
生成一个url地址或者一个路径。可用于<script src='..'>、<link href='..'>、<a href='..'>等。
<p>==========Url表达式===========</p><div > <!--相对路径--> <a th:href='@{'person?name='+${person.name}}' >地址1</a> <!--相对于项目的根路径--> <a th:href='@{'/person?name='+${person.name}}' >地址2</a></div><script th:src='@{'/asserts/js/index.js'}'></script>
几乎所有的html属性都能用th:xxx的形式替换,经过thymeleaf解析后会直接替换为原始html属性和值。
3.4.4 内置对象
thymeleaf提供了一些内置对象,可以让我们直接使用,访问一些请求信息。
#request:
${#request.getContextPath()}
${#request.getAttribute('name')}
#session:
{#session.getAttribute('loginUser')}
{#session.id}
3.4.5 工具对象
工具对象可以帮助我们格式化一样数据,简单的处理一数据。
- #dates:java.util.Date对象的实用方法,<span th:text='${#dates.format(curDate,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss')}'></span>
- #calendars:和dates类似,但是是java.util.Calendar对象。
- #numbers:格式化数据对象的实用方法。
- #strings:字符串对象的实用方法。contains,startsWith,prepending/appending等。
- #objects:对objects操作的实用方法。
- #bools:对布尔值求值的实用方法。
- #arrays:数组的实用方法。
- #lists:list的实用方法.
- #sets:set的实用方法.
- #maps:map的实用方法
- #aggregates:对数组或集合创建聚合的实用方法。
3.4.6 thymeleaf模板片段与布局页
1. 模板片段:可以让我们引入一个写好的html片段,相当于jsp:include功能了,比如头部和尾部我们都一样就可以复用,也可以引入一个页面当做layout布局页,以后的页面都使用这个模板。
我们可以使用th:fragment来定义一个模板,使用th:insert、th:replace、th:include来替换模板。
其中:
- th:insert 3.0+版本新加的。
- th:replace 2.0+ 3.0+都可用。
- th:include 这个在3.0版本已经不建议使用。
这三个命令的语法格式为templatename::[domselector]。
我们先添加模板fragment/footer.html:
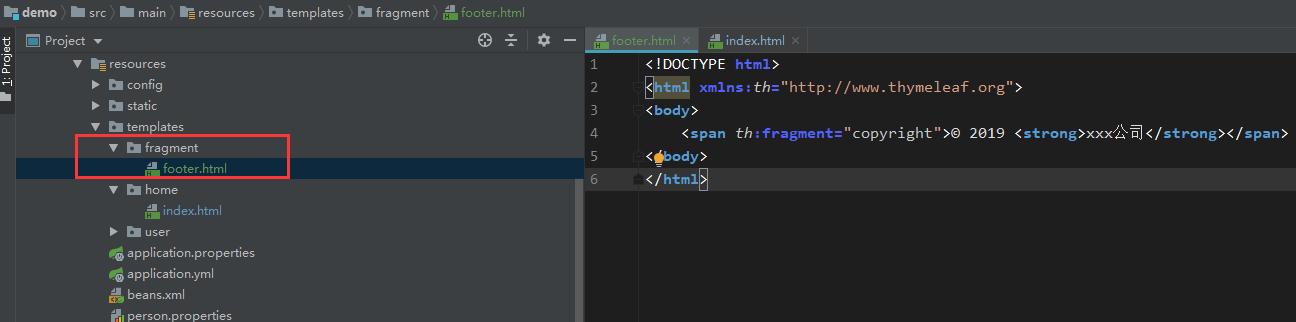
<html xmlns:th='http://www.thymeleaf.org'><body> <span th:fragment='copyright'>© 2019 <strong>xxx公司</strong></span></body></html>
home/index.html引用模板:
<!--th:include--><div th:include='fragment/footer :: copyright'></div><!--th:replace 直接替换--><div th:replace='fragment/footer :: copyright'></div><!--th:insert 把html插入到内部--><div th:insert='fragment/footer :: copyright'></div>
三个命令生成html结构如下,稍微有些不一样:

2. 布局页:设置一个母版页,其他页面以这个页面做为母版,有父类的意思。
首先需要添加布局包依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>nz.net.ultraq.thymeleaf</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-layout-dialect</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version></dependency>
添加一个layout页面(父页面):
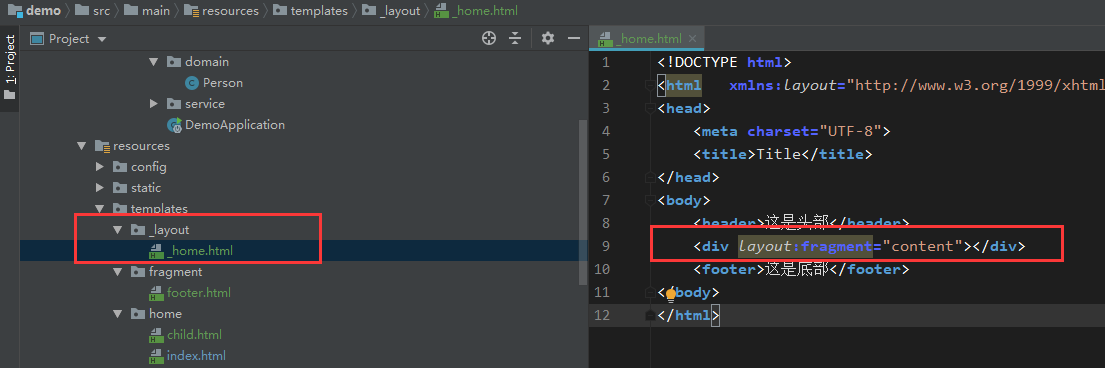
html代码:
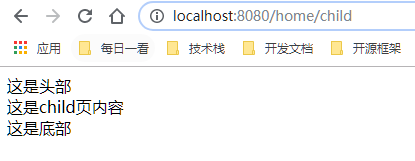
<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns:layout='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <title>Title</title></head><body> <header>这是头部</header> <div layout:fragment='content'></div> <footer>这是底部</footer></body></html>
添加一个子页面,以这个_home.html为父页面:
其中:layout:decorator='_layout/_home' 指明布局页的路径,layout:fragment='content',指明要替换布局页中的位置。
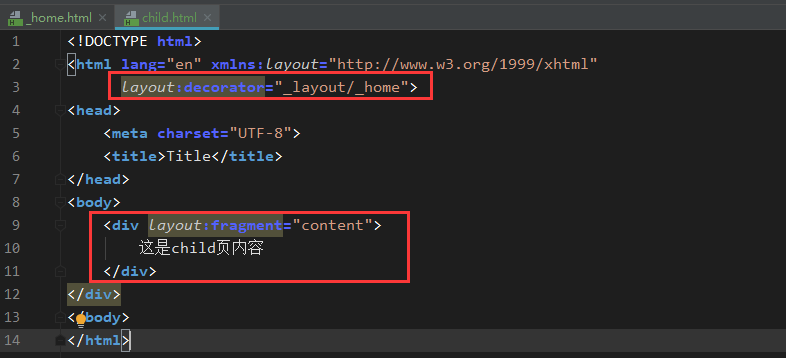
html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en' xmlns:layout='http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml' layout:decorator='_layout/_home'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <title>Title</title></head><body> <div layout:fragment='content'> 这是child页内容 </div></div></body></html>
输出:
四、总结
这次介绍了web开发的基本流程、包括静态文件、模板引擎等,我们现在已经做好了web开发的准备工作,接下来就可以进行业务功能的编写了,接下来我们会做一个简单的CRUD来具体了解一下Web的基本流程。