{
拼接字符串
使用“+”可以对多个字符串进行拼接
语法格式: str1 + str2
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> str1 = "aaa">>> str2 = "bbb">>> print(str1 + str2)aaabbb |
需要注意的是字符串不允许直接与其他类型进行拼接,例如
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> num = 100>>> str1 = "hello">>> print(str1 + num)Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module> print(str1 + num)TypeError: can only concatenate str (not "int") to str |
上面这种情况我们可以将num转换为字符串再进行拼接
|
1
2
3
4
|
>>> num = 100>>> str1 = "hello">>> print(str1 + str(num))hello100 |
这样就不会报错了
计算字符串的长度
在Python中使用len()函数来计算字符串的长度
语法格式: len(string)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> str1 = "hello">>> len(str1)5>>> str2 = "你好">>> len(str2)2>>> str3 = "1111">>> len(str3)4 |
从上面的结果我们可以看出,在默认情况下,len函数在计算字符串的长度时,无论是数字,字母还是多字节的汉字都认为是一个字符。
为什么说是默认情况下呢,因为在实际开发中,可能因为我们采取的编码不同,字符串实际所占的字节数也不同。
- UTF-8编码,汉字占3个字节
- GBK或者GB2312,汉字占2个字节
这时我们可以通过使用encode()方法进行编码后再进行获取长度。
例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> str1 = "你好">>> len(str1)2>>> len(str1.encode('gbk'))4>>> len(str1.encode('utf-8'))6 |
截取字符串
语法格式: string[start : end : step]
参数说明
- string:表示要截取的字符串
- start:表示要截取的第一个字符的索引(包括该字符),如果不指定,则默认为0
- end:表示要截取的最后一个字符的索引(不包括该字符),如果不指定则默认为字符串的长度。
- step:表示切片的步长,如果省略,则默认为1,当省略该步长时,最后一个冒号也可以省略。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
>>> str1 = "hello world!">>> str1[1] #截取第2个字符'e'>>> str1[2:] #从第3个字符开始截取'llo world!'>>> str1[:4]'hell'>>> str1[1:5]'ello'>>> str1[-1] #截取最后一个字符'!'>>> str1[2:-2]'llo worl' |
注意:字符串的索引是从0开始的
分割字符串
python中分割字符串是使用split()方法把字符串分割成列表
语法格式 : str.split(sep, maxsplit)
参数说明:
- str:表示要进行分割的字符串
- sep:用于指定分隔符,可以包含多个字符,默认为None,即所有空字符(包括空格、换行"n”、制表符“t”等)。
- maxsplit:可选参数,用于指定分割的次数,如果不指定或者为-1,则分割次数没有限制,否则返回结果列表的元素个数最多为 maxsplit+1
- 返回值:分隔后的字符串列表。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
>>> str1 = "i am a good boy!">>> str1.split() #采用默认分割符进行分割['i', 'am', 'a', 'good', 'boy!']>>> str1.split(" ") #采用空格进行分割['i', 'am', 'a', 'good', 'boy!']>>> str1.split(" ", 3) #采用空格进行分割,并且只分割前3个['i', 'am', 'a', 'good boy!'] |
注意默认情况下按空格分割
检索字符串
python中字符串的查找方法
1、count()方法
语法格式 : str.count(sub[, start[, end]])
作用:用于检索指定字符串在另一个字符串中出现的次数,如果检索的字符串不存在则返回0,否则返回出现的次数。
参数说明
- str:表示原字符串
- sub:表示要检索的子字符串
- start:可选参数,表示检索范围的起始位置的索引,如果不指定,则从头开始检索
- end:可选参数,表示检索范围的结束位置的索引,如果不指定,则一直检索到结尾
|
1
2
3
|
>>> str1 = "hello world">>> print(str1.count('o'))2 |
2、find()方法
语法格式 : str.find(sub[, start[, end]])
作用:检索是否包含指定的字符串,如果检索的字符串不存在则返回-1,否则返回首次出现该字符串时的索引。
|
1
2
3
|
>>> str1 = "hello world!">>> str1.find('wo')6 |
3、index()方法
语法格式 : str.index(sub[, start[, end]])
作用:和find方法类似,也用于检索是否包含指定的字符串,使用index方法,当指定的字符串不存在时会抛异常。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
>>> str1 = "hello world!">>> str1.index('w')6>>> str1.index('m')Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module> str1.index('m')ValueError: substring not found>>> str1.find('m')-1 |
4、startswith()方法
语法格式 : str.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]])
作用:检索字符串是否以指定的字符串开头,如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
>>> str1 = "hello world!">>> str1.startswith('hello')True>>> str1.startswith('hi')False>>> |
5、endswith()方法
语法格式 : str.endswith(prefix[, start[, end]])
作用:检索字符串是否以指定的字符串结尾,如果是则返回true,否则返回false。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
>>> str1 = "hello world!">>> str1.endswith('world!')True>>> str1.endswith('haha')False |
字符串的大小写转换
1、lower()方法
语法格式 : str.lower()
作用:将字符串中的大写字母转换为小写字母
|
1
2
3
|
>>> str1 = "Hello World!">>> str1.lower()'hello world!' |
2、upper()方法
语法格式 : str.upper()
作用:将字符串中的小写字母转换为大写字母
|
1
2
3
|
>>> str1 = "Hello World!">>> str1.upper()'HELLO WORLD!' |
去除字符串中的空格和特殊字符
开发中,我们会遇到这样的需求,字符串前后(左右侧)不允许出现空格和特殊字符或者将用户输入的字符串中误输入的空格去除掉。这时我们就需要用到strip函数。
1、strip()方法
语法格式 : str.strip([chars])
作用:去除字符串前后(左右侧)的空格或特殊字符
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> str1 = " hello world! ">>> str1.strip()'hello world!'>>> str2 = "#hello world#@#">>> str2.strip('#')'hello world#@'>>> str3 = "@hello world!@.">>> str3.strip('@.')'hello world!' |
2、lstrip()方法
语法格式 : str.lstrip([chars])
作用:去除字符串前面(左侧)的空格或特殊字符
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> str1 = " hello world! ">>> str1.lstrip()'hello world! '>>> str2 = "#hello world#@#">>> str2.lstrip('#')'hello world#@#'>>> str3 = "@.hello world!@.">>> str3.lstrip('@.')'hello world!@.' |
3、rstrip()方法
语法格式 : str.rstrip([chars])
作用:去除字符串后面(右侧)的空格或特殊字符
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
>>> str1 = " hello world! ">>> str1.rstrip()' hello world!'>>> str2 = "#hello world#@#">>> str2.rstrip('#')'#hello world#@'>>> str3 = "@.hello world!@.">>> str3.rstrip('@.')'@.hello world!' |
格式化字符串
所谓格式化字符串就是先制定一个模板,在模板中预留几个空位,然后根据需要填上相应的内容。
使用“%”操作符
语法格式: '%[-][+][0][.n]格式化字符'%exp
参数说明
- -:可选参数,用于指定左对齐,正数前方无符号,负数前面加负号
- +:可选参数,用于指定右对齐,正数前方加正号,负数前方加负号
- 0:可选参数,表示右对齐,正数前方无符号,负数前方加负号,用0填充空白处(一般与m参数一起使用)
- m:可选参数,表示占有宽度
- n:可选参数,表示小数点后保留的位数
- 格式化字符:用于指定类型,其值如下表所示
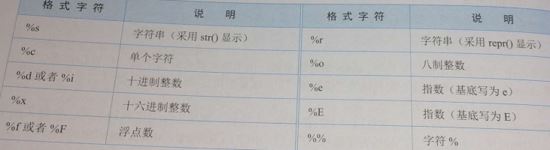
exp:要转换的项,如果要指定的项有多个,需要通过元组的形式进行指定,但不能使用列表。
|
1
2
3
|
>>> template = '学号:%d,姓名:%s,班级:%s'>>> print(template% (123,'张三','一年级'))学号:123,姓名:张三,班级:一年级 |
}