(1) 掌握GUI布局管理器用法;
(2) 掌握各类Java Swing组件用途及常用API
一、理论知识
Swing和MVC设计模式
(1)设计模式(Design pattern)是设计者一种流行的 思考设计问题的方法,是一套被反复使用,多数人 知晓的,经过分类编目的,代码设计经验的总结。
(2)模型-视图-控制器设计模式(Model –ViewController )是Java EE平台下创建 Web 应用程序 的重要设计模式。
(3)MVC设计模式 – Model(模型):是程序中用于处理程序数据逻 辑的部分,通常模型负责在数据库中存取数据。
– View(视图):是程序中处理数据显示的部分, 通常视图依据模型存取的数据创建。
– Controller(控制器):是程序中处理用户交互 的部分。通常控制器负责从视图读取数据,控制 用户输入,并向模型发送数据。
(4)Java组件有内容、外观、行为三个主要元素;
布局管理器
(1)布局管理器是一组类。 – 实现 java.awt.LayoutManager 接口 – 决定容器中组件的位置和大小
Java.awt包中定义了5种布局管理类,每一种布 局管理类对应一种布局策略。
每个容器都有与之相关的默认布局管理器。
(2)5种布局管理器:(1)FlowLayout: 流布局(Applet和Panel的默认 布局管理器) (2)BorderLayout:边框布局( Window、Frame和 Dialog的默认布局管理器) (3)GridLayout: 网格布局 (4)GridBagLayout: 网格组布局 (5)CardLayout :卡片布局
3、GridLayout的构造函数如下:1、GridLayout():生成一个单行单列的网格布局
2、GridLayout(int rows,int cols):生成一个设定行数 和列数的网格布局
3、GridLayout(int rows,int columns,int hgap,int vgap): 可以设置组件之间的水平和垂直间隔
文本输入
(1)文本域(JTextField) : 用于获取单行文本输入。
(2)文本区(JTextArea)组件可让用户输入多行文 本。生成JTextArea组件对象时,可以指定文本 区的行数和列数: textArea = new JTextArea(8, 40);
(3)文本区与文本域的异同相同之处: 文本域和文本区组件都可用于获取文本输入。
不同之处: 文本域只能接受单行文本的输入; 文本区能够接受多行文本的输入。
(4)文本区JTextArea的常用API:Java.swing. JTextArea 1.2 – JTextArea(int rows, int cols)
构造一个rows行cols列的文本区对象 – JTextArea(String text,int rows, int cols)
用初始文本构造一个文本区对象 – void setRows(int rows)
设置文本域使用的行数 – void append(String newText)
将给定文本附加到文本区中已有文本的后面 – void setLineWrap(boolean wrap)
打开或关闭换行
(5)标签组件:标签是容纳文本的组件。它们没有任何修饰(如没有边界 ),也不响应用户输入。
标签的常用用途之一就是标识组件,例如标识文本域。其使用步骤如下:
1. 创建一个JLabel组件
2. 将标签组件放置在距离被标识组件足够近的地方。
(6)密码域:密码域是一种特殊类型的文本域。每个输入的字 符都用回显字符实现,典型的回显字符为*。
– JPassWordField(String text, int columns) 构造一个密码域对象
(7)滚动窗格:
Swing中文本区没有滚动条,若需要滚动条。将文 本区放入一个滚动窗格中即可。
常用API—Java.swing. JScrollPane(教材340页) – JScrollPane(Component c) 在组件c上添加滚动条,返回添加后的组件。
选择组件
复选框 单选按钮 边框 组合框 滑动条
(1)复选框构造器 1.bold = new JCheckBox("Bold"); 复选框自动地带有表示标签。
2. JCheckBox(String label,Icon icon); 构造带有标签与图标的复选框,默认初始未被选择。
3.JCheckBox(String label,boolean state); 用指定的标签和初始化选择状态构造一个复选框
(2)单选按钮的构造器(教材492页) 1.JRadioButton(String label,Icon icon); 创建一个带标签和图标的单选按钮
2.JRadioButton(String label,boolean state); 用指定的标签和初始化状态构造单选按钮
(3)按钮组:为单选按钮组构造一个ButtonGroup的对象。 然后,再将JRadioButton类型的对象添加到按钮 组中。按钮组负责在新按钮被按下的时,取消前一 个按钮的选择状态。
(4)如果在一个窗口中 有多组复选框或单选按 钮,就需要可视化的形 式指明哪些按钮属于同 一组。Swing提供了一 组很有用的边框
(5)如果有多个选择项,使用单选按钮占据的屏幕空 间太大时,就可以选择组合框。
faceCombo = new JComboBox(); faceCombo.setEditable(true);
让组合框可编辑 faceCombo.addItem("Serif"); faceCombo.insertItemAt("Monospace",0);
增加组合框选项 faceCombo.removeItem("Monospace");
faceCombo.removeItemAt(0); 删除组合框选项内容
(6)组合框的事件监听:为了判断组合框的哪个选项被选择,可通过 事件参数调用getSource方法来得到发送事件的组 合框引用,接着调用getSelectdeItem方法获取当 前选择的选项。
(7)滑动条:滑动条可以让用户从一组离散值中进行选择 ,并且它还允许进行连续值得选择。
菜单
菜单创建 菜单项中的图标 复选框和单选按钮菜单项 弹出菜单 快捷键和加速器 启用和禁用菜单项 工具栏 工具提示
网格组布局 (GridBagLayout):GridBagLayout与GridLayout有点相似,它也是 将组件排在格子里,但是GridBagLayout在网格 的基础上提供更复杂的布局。
GridBagLayout允许单个组件在一个单元中不填 满整个单元,而只是占用最佳大小,也允许单个 组件扩展成不止一个单元,并且可以用任意顺序 加入组件。
定制布局管理器: 程序员可通过自己设计LayoutManager类来实现 特殊的布局方式。
定制布局管理器需要实现LayoutManager接口, 并覆盖以下方法。
对话框
选项对话框 创建对话框 数据选择 文件对话框 颜色选择器
(1)对话框是一种大小不能变化、不能有菜单的容器窗口; 对话框不能作为一个应用程序的主框架,而必须包含在其 他的容器中。
(2)选项对话框:JOptionPane提供的对话框是模式对话框。当模 式对话框显示时,它不允许用户输入到程序的 其他的窗口。使用JOptionPane,可以创建和自 定义问题、信息、警告和错误等几种类型的对 话框。
(3)数据交换:输入对话框含有供用户输入文本的文本框、一个确认和取 消按钮,是有模式对话框。当输入对话框可见时,要求用户 输入一个字符串。
(4)文件对话框:专门用于对文件(或目录)进行浏览和选择的对 话框,常用的构造方法: – JFileChooser():根据用户的缺省目录创建文件对话框 – JFileChooser(File currentDirectory):根据File型参数 currentDirectory指定的目录创建文件对话框
(5)颜色对话框: javax.swing包中的JColorChooser类的静态方 法: public static Color showDialog(Component component, String title, Color initialColor)创建一个颜色对话框
(6)参数component指定对话框所依赖的组件,title 指定对话框的标题;initialColor 指定对话框返回 的初始颜色,即对话框消失后,返回的默认值。 颜色对话框可根据用户在颜色对话框中选择的颜 色返回一个颜色对象.
二、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第12章示例程序,测试程序并进行组内讨论。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中运行教材479页程序12-1,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种布局管理器的用法;
l 理解GUI界面中事件处理技术的用途。
在布局管理应用代码处添加注释;
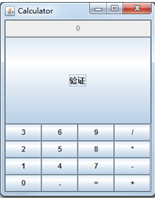
package calculator; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A panel with calculator buttons and a result display. */ public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel { //定义了五个对象 private JButton display; private JPanel panel; private double result; private String lastCommand; private boolean start; public CalculatorPanel() { setLayout(new BorderLayout()); result = 0; lastCommand = "="; start = true; // add the display display = new JButton("0");// display用来显示一个算法的结果 display.setEnabled(false); add(display, BorderLayout.NORTH); //定义了两个监听器对象 ActionListener insert = new InsertAction(); ActionListener command = new CommandAction(); // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid panel = new JPanel();//容器组件 panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4));//四行四列的网格 //调用addButton方法来添加按钮 addButton("3", insert); addButton("6", insert); addButton("9", insert); addButton("/", command); addButton("2", insert); addButton("5", insert); addButton("8", insert); addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert); addButton("4", insert); addButton("7", insert); addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert); addButton(".", insert); addButton("=", command); addButton("+", command); //创建了16个事件源 add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); JButton b1= new JButton("验证"); add(b1, BorderLayout.CENTER); } /** * Adds a button to the center panel. * @param label the button label * @param listener the button listener */ private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener) { JButton button = new JButton(label); button.addActionListener(listener); panel.add(button); } /** * This action inserts the button action string to the end of the display text. */ private class InsertAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String input = event.getActionCommand();//通过事件源来获得动作 if (start) { display.setText("");//用setText方法 来更改 start = false; } display.setText(display.getText() + input); } } /** * This action executes the command that the button action string denotes. */ private class CommandAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start) { if (command.equals("-")) { display.setText(command); start = false; } else lastCommand = command; } else { calculate(Double.parseDouble(display.getText())); //将数字字符串转换成对应的数字,用parseDouble lastCommand = command;//控制变量 start = true; } } } /** * Carries out the pending calculation. * @param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result. */ public void calculate(double x) { if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x; else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x; else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x; display.setText("" + result);//""的意义在于字符串的转换 } }
package calculator; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a calculator panel. */ public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame { public CalculatorFrame() { add(new CalculatorPanel()); pack();//用pack方法 } }
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Calculator { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { CalculatorFrame frame = new CalculatorFrame(); frame.setTitle("Calculator") ; frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);////关闭界面的按钮操作 frame.setVisible(true);//可见的 }); } }
结果如下:
测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材486页程序12-2,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握各种文本组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

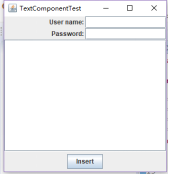
package text; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingConstants; /** * A frame with sample text components. */ public class TextComponentFrame extends JFrame { //定义网格的行数、列数 public static final int TEXTAREA_ROWS = 8; public static final int TEXTAREA_COLUMNS = 20; public TextComponentFrame() { JTextField textField = new JTextField();//创建一个新的文本域 JPasswordField passwordField = new JPasswordField(); JPanel northPanel = new JPanel();//构造一个JPanel组件 northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2));//设置布局管理器 northPanel.add(new JLabel("User name: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT));//指定右对齐标签 northPanel.add(textField); northPanel.add(new JLabel("Password: ", SwingConstants.RIGHT)); northPanel.add(passwordField); add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);//add方法 JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(TEXTAREA_ROWS, TEXTAREA_COLUMNS); JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea); add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER); // add button to append text into the text area JPanel southPanel = new JPanel(); JButton insertButton = new JButton("Insert"); southPanel.add(insertButton); insertButton.addActionListener(event -> textArea.append("User name: " + textField.getText() + " Password: " + new String(passwordField.getPassword()) + " ")); add(southPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }

package text; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.41 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class TextComponentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new TextComponentFrame();//生成 TextComponentFrame类的GUI界面对象 frame.setTitle("TextComponentTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭界面的按钮操作 frame.setVisible(true);//使结果可见的 }); } }
结果如下:
测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材489页程序12-3,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握复选框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

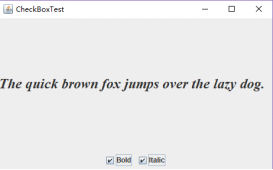
package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and check boxes for selecting font * attributes. */ public class CheckBoxFrame extends JFrame { //定义四个私有属性 private JLabel label; private JCheckBox bold; private JCheckBox italic; private static final int FONTSIZE = 24; public CheckBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label //添加示例文本标签 label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");//创建新标签 label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, FONTSIZE));//设置字体 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // this listener sets the font attribute of // the label to the check box state ActionListener listener = event -> { int mode = 0; if (bold.isSelected()) mode += Font.BOLD; if (italic.isSelected()) mode += Font.ITALIC; label.setFont(new Font("Serif", mode, FONTSIZE));//设置面板中的字体 }; // add the check boxes JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); bold = new JCheckBox("Bold");//在构造器中指定标签文本 bold.addActionListener(listener); bold.setSelected(true);//返回每个复选框的当前状态 buttonPanel.add(bold); italic = new JCheckBox("Italic"); italic.addActionListener(listener); buttonPanel.add(italic); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack();//调整此窗口的大小 } } package checkBox; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class CheckBoxTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new CheckBoxFrame(); frame.setTitle("CheckBoxTest");//设置Title为复选框 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
结果如下:
测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材491页程序12-4,运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握单选按钮组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package radioButton; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample text label and radio buttons for selecting font sizes. */ public class RadioButtonFrame extends JFrame//单选按钮 { //定义四个私有属性 private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; private JLabel label; private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 36; public RadioButtonFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));//设置新字体 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // add the radio buttons buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); //添加单选框按钮 addRadioButton("Small", 8); addRadioButton("Medium", 12); addRadioButton("Large", 18); addRadioButton("Extra large", 36); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack();//调整窗口的大小 } /** * Adds a radio button that sets the font size of the sample text. * @param name the string to appear on the button * @param size the font size that this button sets */ public void addRadioButton(String name, int size) { boolean selected = size == DEFAULT_SIZE;//布尔类型,大小的定义 JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(name, selected); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); // this listener sets the label font size //这个监听器设置标签字体大小 ActionListener listener = event -> label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, size));//表明新的字体,大小 button.addActionListener(listener); } }
结果如下:

测试程序5
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材494页程序12-5,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握边框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; /** * A frame with radio buttons to pick a border style. */ public class BorderFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel demoPanel; private JPanel buttonPanel; private ButtonGroup group; public BorderFrame() { demoPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); group = new ButtonGroup(); addRadioButton("Lowered bevel", BorderFactory.createLoweredBevelBorder()); addRadioButton("Raised bevel", BorderFactory.createRaisedBevelBorder()); addRadioButton("Etched", BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder()); addRadioButton("Line", BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.BLUE)); addRadioButton("Matte", BorderFactory.createMatteBorder(10, 10, 10, 10, Color.BLUE)); addRadioButton("Empty", BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder()); Border etched = BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(); Border titled = BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(etched, "Border types"); buttonPanel.setBorder(titled); setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1)); add(buttonPanel); add(demoPanel); pack(); } public void addRadioButton(String buttonName, Border b) { JRadioButton button = new JRadioButton(buttonName); button.addActionListener(event -> demoPanel.setBorder(b)); group.add(button); buttonPanel.add(button); } } package border; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-13 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class BorderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new BorderFrame(); frame.setTitle("BorderTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

测试程序6
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材498页程序12-6,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握组合框组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package comboBox; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Font; import javax.swing.JComboBox; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A frame with a sample text label and a combo box for selecting font faces. */ public class ComboBoxFrame extends JFrame { private JComboBox<String> faceCombo;//定义组合框面 private JLabel label;//定义标签 private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 24; public ComboBoxFrame() { // add the sample text label label = new JLabel("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog."); label.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE));//设置组件的字体 add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // make a combo box and add face names //调用addItem方法添加选项 faceCombo = new JComboBox<>(); faceCombo.addItem("Serif"); faceCombo.addItem("SansSerif"); faceCombo.addItem("Monospaced"); faceCombo.addItem("Dialog"); faceCombo.addItem("DialogInput"); // the combo box listener changes the label font to the selected face name faceCombo.addActionListener(event ->//组合框产生一个动作事件 label.setFont( new Font(faceCombo.getItemAt(faceCombo.getSelectedIndex()), Font.PLAIN, DEFAULT_SIZE))); // add combo box to a panel at the frame's southern border JPanel comboPanel = new JPanel(); comboPanel.add(faceCombo); add(comboPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }

测试程序7
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材501页程序12-7,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握滑动条组件的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package slider; import java.awt.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.event.*; /** * A frame with many sliders and a text field to show slider values. */ public class SliderFrame extends JFrame { private JPanel sliderPanel; private JTextField textField; private ChangeListener listener; public SliderFrame() { sliderPanel = new JPanel(); sliderPanel.setLayout(new GridBagLayout()); // common listener for all sliders listener = event -> { // update text field when the slider value changes JSlider source = (JSlider) event.getSource(); textField.setText("" + source.getValue()); }; // add a plain slider //添加一个普通滑块 JSlider slider = new JSlider();//构造一个滑动条 addSlider(slider, "Plain"); // add a slider with major and minor ticks //添加一个有大和小刻度的滑块 slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); addSlider(slider, "Ticks"); // add a slider that snaps to ticks slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true);//设置标尺标记 slider.setSnapToTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20);//每20个单位的位置显示一个大标尺标记 slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5);//每5个单位的位置显示一个小标尺标记 addSlider(slider, "Snap to ticks"); // add a slider with no track //添加一个没有轨道的滑块 slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); slider.setPaintTrack(false); addSlider(slider, "No track");//添加滑块“无磁块” // add an inverted slider //添加一个倒滑块 slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); slider.setInverted(true); addSlider(slider, "Inverted"); // add a slider with numeric labels slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setPaintLabels(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); addSlider(slider, "Labels"); // add a slider with alphabetic labels slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintLabels(true); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(5); Dictionary<Integer, Component> labelTable = new Hashtable<>(); labelTable.put(0, new JLabel("A")); labelTable.put(20, new JLabel("B")); labelTable.put(40, new JLabel("C")); labelTable.put(60, new JLabel("D")); labelTable.put(80, new JLabel("E")); labelTable.put(100, new JLabel("F")); slider.setLabelTable(labelTable); addSlider(slider, "Custom labels"); // add a slider with icon labels //添加带有数字标签的滑块 slider = new JSlider(); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setPaintLabels(true);//滑块设置面板标签 slider.setSnapToTicks(true); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(20); slider.setMinorTickSpacing(20); labelTable = new Hashtable<Integer, Component>(); // add card images labelTable.put(0, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("nine.gif"))); labelTable.put(20, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("ten.gif"))); labelTable.put(40, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("jack.gif"))); labelTable.put(60, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("queen.gif"))); labelTable.put(80, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("king.gif"))); labelTable.put(100, new JLabel(new ImageIcon("ace.gif"))); slider.setLabelTable(labelTable); addSlider(slider, "Icon labels"); // add the text field that displays the slider value textField = new JTextField(); add(sliderPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER); add(textField, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * Adds a slider to the slider panel and hooks up the listener * @param s the slider * @param description the slider description */ public void addSlider(JSlider s, String description) { s.addChangeListener(listener); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.add(s); panel.add(new JLabel(description)); panel.setAlignmentX(Component.LEFT_ALIGNMENT);//设置组件 GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints(); gbc.gridy = sliderPanel.getComponentCount(); gbc.anchor = GridBagConstraints.WEST; sliderPanel.add(panel, gbc); } }

package slider; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.15 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class SliderTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { SliderFrame frame = new SliderFrame();//生成 SliderFrame类的GUI界面对象 frame.setTitle("SliderTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);////关闭界面的按钮操作 frame.setVisible(true);//使结果可见 }); }
结果:

测试程序8
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材512页程序12-8,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握菜单的创建、菜单事件监听器、复选框和单选按钮菜单项、弹出菜单以及快捷键和加速器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package menu; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a sample menu bar. */ public class MenuFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private Action saveAction; private Action saveAsAction; private JCheckBoxMenuItem readonlyItem; private JPopupMenu popup; /** * A sample action that prints the action name to System.out */ class TestAction extends AbstractAction { public TestAction(String name) { super(name); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.out.println(getValue(Action.NAME) + " selected."); } } public MenuFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); fileMenu.add(new TestAction("New")); // demonstrate accelerators JMenuItem openItem = fileMenu.add(new TestAction("Open")); openItem.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl O")); fileMenu.addSeparator(); saveAction = new TestAction("Save"); JMenuItem saveItem = fileMenu.add(saveAction); saveItem.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl S")); saveAsAction = new TestAction("Save As"); fileMenu.add(saveAsAction); fileMenu.addSeparator(); fileMenu.add(new AbstractAction("Exit") { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.exit(0); } }); // demonstrate checkbox and radio button menus readonlyItem = new JCheckBoxMenuItem("Read-only"); readonlyItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { boolean saveOk = !readonlyItem.isSelected(); saveAction.setEnabled(saveOk); saveAsAction.setEnabled(saveOk); } }); ButtonGroup group = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButtonMenuItem insertItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Insert"); insertItem.setSelected(true); JRadioButtonMenuItem overtypeItem = new JRadioButtonMenuItem("Overtype"); group.add(insertItem); group.add(overtypeItem); // demonstrate icons Action cutAction = new TestAction("Cut"); cutAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("cut.gif")); Action copyAction = new TestAction("Copy"); copyAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("copy.gif")); Action pasteAction = new TestAction("Paste"); pasteAction.putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, new ImageIcon("paste.gif")); JMenu editMenu = new JMenu("Edit"); editMenu.add(cutAction); editMenu.add(copyAction); editMenu.add(pasteAction); // demonstrate nested menus JMenu optionMenu = new JMenu("Options"); optionMenu.add(readonlyItem); optionMenu.addSeparator(); optionMenu.add(insertItem); optionMenu.add(overtypeItem); editMenu.addSeparator(); editMenu.add(optionMenu); // demonstrate mnemonics JMenu helpMenu = new JMenu("Help"); helpMenu.setMnemonic('H'); JMenuItem indexItem = new JMenuItem("Index"); indexItem.setMnemonic('I'); helpMenu.add(indexItem); // you can also add the mnemonic key to an action Action aboutAction = new TestAction("About"); aboutAction.putValue(Action.MNEMONIC_KEY, new Integer('A')); helpMenu.add(aboutAction); // add all top-level menus to menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); menuBar.add(fileMenu); menuBar.add(editMenu); menuBar.add(helpMenu); // demonstrate pop-ups popup = new JPopupMenu(); popup.add(cutAction); popup.add(copyAction); popup.add(pasteAction); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setComponentPopupMenu(popup); add(panel); } }

package menu; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.24 2012-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class MenuTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new MenuFrame(); frame.setTitle("MenuTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

测试程序9(组内实验)
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材517页程序12-9,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握工具栏和工具提示的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package toolBar; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a toolbar and menu for color changes. */ public class ToolBarFrame extends JFrame { //定义两个私有属性 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private JPanel panel; public ToolBarFrame() //定义工具提示类 { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // add a panel for color change panel = new JPanel();//创建新的JPanel add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // set up actions //建立动作 Action blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE); Action yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"), Color.YELLOW); Action redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED); Action exitAction = new AbstractAction("Exit", new ImageIcon("exit.gif")) { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { System.exit(0); } }; exitAction.putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Exit"); // populate toolbar JToolBar bar = new JToolBar(); bar.add(blueAction);//用Action对象填充工具栏 bar.add(yellowAction); bar.add(redAction); bar.addSeparator();//用分隔符将按钮分组 bar.add(exitAction); add(bar, BorderLayout.NORTH); // populate menu JMenu menu = new JMenu("Color");//显示颜色的菜单 menu.add(yellowAction);//在菜单添加颜色动作 menu.add(blueAction); menu.add(redAction); menu.add(exitAction); JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); menuBar.add(menu); setJMenuBar(menuBar); } /** * The color action sets the background of the frame to a given color. */ class ColorAction extends AbstractAction { public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c) { putValue(Action.NAME, name);//动作名称,显示在按钮和菜单 putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon);//存储小图标的地方;显示在按钮、菜单项或工具栏中 putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, name + " background"); putValue("Color", c); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { Color c = (Color) getValue("Color"); panel.setBackground(c); } } }

package toolBar; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.14 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ToolBarTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { ToolBarFrame frame = new ToolBarFrame();//生成新的ToolBarFrame类的GUI界面 frame.setTitle("ToolBarTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭窗口界面 frame.setVisible(true);//使结果可见 }); }

测试程序10
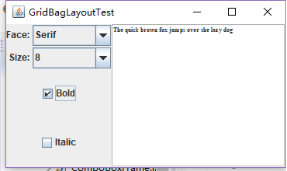
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材524页程序12-10、12-11,结合运行结果理解程序,了解GridbagLayout的用法。
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材533页程序12-12,结合程序运行结果理解程序,了解GroupLayout的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。
测试程序11
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材539页程序12-13、12-14,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握定制布局管理器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package circleLayout; import java.awt.*; /** * A layout manager that lays out components along a circle. */ public class CircleLayout implements LayoutManager {//将布局管理器设置为空 private int minWidth = 0; private int minHeight = 0; private int preferredWidth = 0; private int preferredHeight = 0; private boolean sizesSet = false; private int maxComponentWidth = 0; private int maxComponentHeight = 0; public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)//将组件添加到布局中 { } public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)//从布局中删去一个组件 { } public void setSizes(Container parent) { if (sizesSet) return; int n = parent.getComponentCount(); preferredWidth = 0; preferredHeight = 0; minWidth = 0; minHeight = 0; maxComponentWidth = 0; maxComponentHeight = 0; // compute the maximum component widths and heights // and set the preferred size to the sum of the component sizes. for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Component c = parent.getComponent(i); if (c.isVisible()) { Dimension d = c.getPreferredSize(); maxComponentWidth = Math.max(maxComponentWidth, d.width); maxComponentHeight = Math.max(maxComponentHeight, d.height); preferredWidth += d.width; preferredHeight += d.height;//计算最大组件宽度和高度 } } minWidth = preferredWidth / 2; minHeight = preferredHeight / 2; sizesSet = true; } public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container parent)//返回布局下的容器的首选尺寸 { setSizes(parent); Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int width = preferredWidth + insets.left + insets.right; int height = preferredHeight + insets.top + insets.bottom;//设置长、宽大小 return new Dimension(width, height); } public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container parent)//返回布局下容器的最小尺寸 { setSizes(parent); Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int width = minWidth + insets.left + insets.right; int height = minHeight + insets.top + insets.bottom;//设置最小尺寸 return new Dimension(width, height); } public void layoutContainer(Container parent) { setSizes(parent); // compute center of the circle //计算圆的中心 Insets insets = parent.getInsets(); int containerWidth = parent.getSize().width - insets.left - insets.right; int containerHeight = parent.getSize().height - insets.top - insets.bottom; int xcenter = insets.left + containerWidth / 2; int ycenter = insets.top + containerHeight / 2; // compute radius of the circle //计算圆的半径 int xradius = (containerWidth - maxComponentWidth) / 2; int yradius = (containerHeight - maxComponentHeight) / 2; int radius = Math.min(xradius, yradius);// // lay out components along the circle //在圆周上布置组件 int n = parent.getComponentCount(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { Component c = parent.getComponent(i); if (c.isVisible()) { double angle = 2 * Math.PI * i / n; // center point of component int x = xcenter + (int) (Math.cos(angle) * radius); int y = ycenter + (int) (Math.sin(angle) * radius); // move component so that its center is (x, y) // and its size is its preferred size Dimension d = c.getPreferredSize(); c.setBounds(x - d.width / 2, y - d.height / 2, d.width, d.height); } } } }

package circleLayout; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame that shows buttons arranged along a circle. */ public class CircleLayoutFrame extends JFrame { public CircleLayoutFrame() {//调用add方法来添加各种按钮 setLayout(new CircleLayout()); add(new JButton("Yellow")); add(new JButton("Blue")); add(new JButton("Red")); add(new JButton("Green")); add(new JButton("Orange")); add(new JButton("Fuchsia")); add(new JButton("Indigo")); pack();//调节大小 } }

package optionDialog; import javax.swing.*; /** * A panel with radio buttons inside a titled border. */ public class ButtonPanel extends JPanel { private ButtonGroup group; /** * Constructs a button panel. * @param title the title shown in the border * @param options an array of radio button labels */ public ButtonPanel(String title, String... options) { //设置边框属性 setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder(), title)); setLayout(new BoxLayout(this, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); group = new ButtonGroup(); // make one radio button for each option //为每个选项设置一个单选按钮 for (String option : options) { JRadioButton b = new JRadioButton(option); b.setActionCommand(option); add(b); group.add(b); b.setSelected(option == options[0]); } } /** * Gets the currently selected option. * @return the label of the currently selected radio button. */ public String getSelection() { return group.getSelection().getActionCommand(); } }

package circleLayout; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.33 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class CircleLayoutTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new CircleLayoutFrame(); frame.setTitle("CircleLayoutTest");//设置标题为CircleLayoutTest frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭界面操作 frame.setVisible(true); }); } }

测试程序12
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材544页程序12-15、12-16,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握选项对话框的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

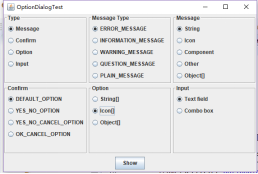
package optionDialog; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.awt.geom.*; import java.util.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame that contains settings for selecting various option dialogs. */ public class OptionDialogFrame extends JFrame//对话框 { //定义属性 private ButtonPanel typePanel; private ButtonPanel messagePanel; private ButtonPanel messageTypePanel; private ButtonPanel optionTypePanel; private ButtonPanel optionsPanel; private ButtonPanel inputPanel; private String messageString = "Message"; private Icon messageIcon = new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"); private Object messageObject = new Date(); private Component messageComponent = new SampleComponent(); public OptionDialogFrame() { JPanel gridPanel = new JPanel(); gridPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 3)); typePanel = new ButtonPanel("Type", "Message", "Confirm", "Option", "Input"); messageTypePanel = new ButtonPanel("Message Type", "ERROR_MESSAGE", "INFORMATION_MESSAGE", "WARNING_MESSAGE", "QUESTION_MESSAGE", "PLAIN_MESSAGE"); messagePanel = new ButtonPanel("Message", "String", "Icon", "Component", "Other", "Object[]"); optionTypePanel = new ButtonPanel("Confirm", "DEFAULT_OPTION", "YES_NO_OPTION", "YES_NO_CANCEL_OPTION", "OK_CANCEL_OPTION"); optionsPanel = new ButtonPanel("Option", "String[]", "Icon[]", "Object[]"); inputPanel = new ButtonPanel("Input", "Text field", "Combo box"); gridPanel.add(typePanel); gridPanel.add(messageTypePanel); gridPanel.add(messagePanel); gridPanel.add(optionTypePanel); gridPanel.add(optionsPanel); gridPanel.add(inputPanel); // add a panel with a Show button JPanel showPanel = new JPanel(); JButton showButton = new JButton("Show"); showButton.addActionListener(new ShowAction()); showPanel.add(showButton); add(gridPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER); add(showPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } /** * Gets the currently selected message. * @return a string, icon, component, or object array, depending on the Message panel selection */ public Object getMessage() { String s = messagePanel.getSelection(); if (s.equals("String")) return messageString; else if (s.equals("Icon")) return messageIcon; else if (s.equals("Component")) return messageComponent; else if (s.equals("Object[]")) return new Object[] { messageString, messageIcon, messageComponent, messageObject }; else if (s.equals("Other")) return messageObject; else return null; } /** * Gets the currently selected options. * @return an array of strings, icons, or objects, depending on the Option panel selection */ public Object[] getOptions() { String s = optionsPanel.getSelection(); if (s.equals("String[]")) return new String[] { "Yellow", "Blue", "Red" }; else if (s.equals("Icon[]")) return new Icon[] { new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"), new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif") }; else if (s.equals("Object[]")) return new Object[] { messageString, messageIcon, messageComponent, messageObject }; else return null; } /** * Gets the selected message or option type * @param panel the Message Type or Confirm panel * @return the selected XXX_MESSAGE or XXX_OPTION constant from the JOptionPane class */ public int getType(ButtonPanel panel) { String s = panel.getSelection(); try { return JOptionPane.class.getField(s).getInt(null); } catch (Exception e) { return -1; } } /** * The action listener for the Show button shows a Confirm, Input, Message, or Option dialog * depending on the Type panel selection. */ private class ShowAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Confirm")) JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog( OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(optionTypePanel), getType(messageTypePanel)); else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Input")) { if (inputPanel.getSelection().equals("Text field")) JOptionPane.showInputDialog( OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel)); else JOptionPane.showInputDialog(OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel), null, new String[] { "Yellow", "Blue", "Red" }, "Blue"); } else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Message")) JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(messageTypePanel)); else if (typePanel.getSelection().equals("Option")) JOptionPane.showOptionDialog( OptionDialogFrame.this, getMessage(), "Title", getType(optionTypePanel), getType(messageTypePanel), null, getOptions(), getOptions()[0]); } } } /** * A component with a painted surface */ class SampleComponent extends JComponent { public void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; Rectangle2D rect = new Rectangle2D.Double(0, 0, getWidth() - 1, getHeight() - 1); g2.setPaint(Color.YELLOW); g2.fill(rect); g2.setPaint(Color.BLUE); g2.draw(rect); } public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(10, 10); } }

package optionDialog; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class OptionDialogTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new OptionDialogFrame(); frame.setTitle("OptionDialogTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); }
测试程序13
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材552页程序12-17、12-18,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的创建方法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package optionDialog; package dialog; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JMenu; import javax.swing.JMenuBar; import javax.swing.JMenuItem; /** * A frame with a menu whose File->About action shows a dialog. */ public class DialogFrame extends JFrame {//定义长和宽的大小 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private AboutDialog dialog; public DialogFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // Construct a File menu. JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(fileMenu); // Add About and Exit menu items. // The About item shows the About dialog. JMenuItem aboutItem = new JMenuItem("About");//建立新的对话框现象 aboutItem.addActionListener(event -> {//并让他可见 if (dialog == null) // first time dialog = new AboutDialog(DialogFrame.this); dialog.setVisible(true); // pop up dialog }); fileMenu.add(aboutItem); // The Exit item exits the program. //按Exit退出程序 JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); fileMenu.add(exitItem); } }

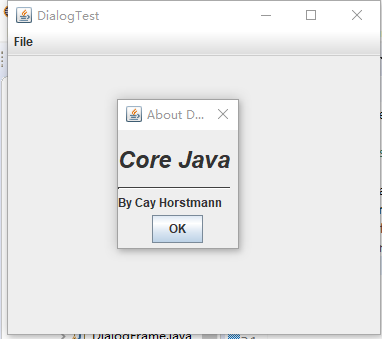
package dialog; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A sample modal dialog that displays a message and waits for the user to click the OK button. */ public class AboutDialog extends JDialog { public AboutDialog(JFrame owner) { super(owner, "About DialogTest", true); // add HTML label to center add( new JLabel( "<html><h1><i>Core Java</i></h1><hr>By Cay Horstmann</html>"), BorderLayout.CENTER);//将HTML标签添加到中心 // OK button closes the dialog //OK按钮关闭对话框 JButton ok = new JButton("OK"); ok.addActionListener(event -> setVisible(false));//监听器对象 // add OK button to southern border JPanel panel = new JPanel();//创建新面板 panel.add(ok); add(panel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); } }

package dialog; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.34 2012-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class DialogTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new DialogFrame(); frame.setTitle("DialogTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); }
测试程序14
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材556页程序12-19、12-20,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握对话框的数据交换用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package dataExchange; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a menu whose File->Connect action shows a password dialog. */ public class DataExchangeFrame extends JFrame { public static final int TEXT_ROWS = 20; public static final int TEXT_COLUMNS = 40; private PasswordChooser dialog = null; private JTextArea textArea; public DataExchangeFrame() { // construct a File menu JMenuBar mbar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(mbar); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File"); mbar.add(fileMenu); // add Connect and Exit menu items JMenuItem connectItem = new JMenuItem("Connect"); connectItem.addActionListener(new ConnectAction()); fileMenu.add(connectItem); // The Exit item exits the program JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); fileMenu.add(exitItem); textArea = new JTextArea(TEXT_ROWS, TEXT_COLUMNS); add(new JScrollPane(textArea), BorderLayout.CENTER); pack(); } /** * The Connect action pops up the password dialog. */ private class ConnectAction implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { // if first time, construct dialog if (dialog == null) dialog = new PasswordChooser(); // set default values dialog.setUser(new User("yourname", null)); // pop up dialog if (dialog.showDialog(DataExchangeFrame.this, "Connect")) { // if accepted, retrieve user input User u = dialog.getUser(); textArea.append("user name = " + u.getName() + ", password = " + (new String(u.getPassword())) + " "); } } } }

package dataExchange; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Component; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.GridLayout; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JPasswordField; import javax.swing.JTextField; import javax.swing.SwingUtilities; /** * A password chooser that is shown inside a dialog */ public class PasswordChooser extends JPanel { private JTextField username; private JPasswordField password; private JButton okButton; private boolean ok; private JDialog dialog; public PasswordChooser() { setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // construct a panel with user name and password fields JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2)); panel.add(new JLabel("User name:")); panel.add(username = new JTextField("")); panel.add(new JLabel("Password:")); panel.add(password = new JPasswordField("")); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER); // create Ok and Cancel buttons that terminate the dialog okButton = new JButton("Ok"); okButton.addActionListener(event -> { ok = true; dialog.setVisible(false); }); JButton cancelButton = new JButton("Cancel"); cancelButton.addActionListener(event -> dialog.setVisible(false)); // add buttons to southern border JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.add(okButton); buttonPanel.add(cancelButton); add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); } /** * Sets the dialog defaults. * @param u the default user information */ public void setUser(User u) { username.setText(u.getName()); } /** * Gets the dialog entries. * @return a User object whose state represents the dialog entries */ public User getUser() { return new User(username.getText(), password.getPassword()); } /** * Show the chooser panel in a dialog * @param parent a component in the owner frame or null * @param title the dialog window title */ public boolean showDialog(Component parent, String title) { ok = false; // locate the owner frame Frame owner = null; if (parent instanceof Frame) owner = (Frame) parent; else owner = (Frame) SwingUtilities.getAncestorOfClass(Frame.class, parent); // if first time, or if owner has changed, make new dialog if (dialog == null || dialog.getOwner() != owner) { dialog = new JDialog(owner, true); dialog.add(this); dialog.getRootPane().setDefaultButton(okButton); dialog.pack(); } // set title and show dialog dialog.setTitle(title); dialog.setVisible(true); return ok; } }

package dataExchange; /** * A user has a name and password. For security reasons, the password is stored as a char[], not a * String. */ public class User { private String name; private char[] password; public User(String aName, char[] aPassword) { name = aName; password = aPassword; } public String getName() { return name; } public char[] getPassword() { return password; } public void setName(String aName) { name = aName; } public void setPassword(char[] aPassword) { password = aPassword; } }

测试程序15
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材556页程序12-21、12-2212-23,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握文件对话框的用法;
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

package fileChooser; import java.awt.*; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A file chooser accessory that previews images. */ public class ImagePreviewer extends JLabel { /** * Constructs an ImagePreviewer. * @param chooser the file chooser whose property changes trigger an image * change in this previewer */ public ImagePreviewer(JFileChooser chooser) { setPreferredSize(new Dimension(100, 100));//设置此组件的首选大小 setBorder(BorderFactory.createEtchedBorder());//设置此组件的边框 chooser.addPropertyChangeListener(event -> { if (event.getPropertyName() == JFileChooser.SELECTED_FILE_CHANGED_PROPERTY) { // the user has selected a new file File f = (File) event.getNewValue();//创建一个新的文件对话框 if (f == null) { setIcon(null); return; } // read the image into an icon //将图像读成图标 ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(f.getPath()); // if the icon is too large to fit, scale it //如果图标太大而无法容纳,将其缩放 if (icon.getIconWidth() > getWidth()) icon = new ImageIcon(icon.getImage().getScaledInstance( getWidth(), -1, Image.SCALE_DEFAULT)); setIcon(icon);//图标 } }); } }

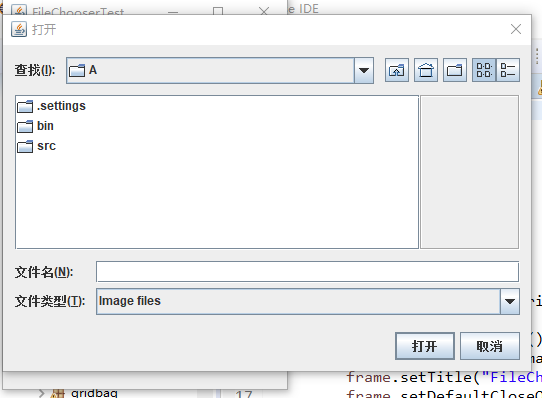
package fileChooser; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter; /** * A frame that has a menu for loading an image and a display area for the * loaded image. */ public class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; private JLabel label; private JFileChooser chooser; public ImageViewerFrame() { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // set up menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); menu.add(openItem); openItem.addActionListener(event -> { chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); // show file chooser dialog int result = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); // if image file accepted, set it as icon of the label if (result == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); pack(); } }); JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); menu.add(exitItem); exitItem.addActionListener(event -> System.exit(0)); // use a label to display the images //使用一个标签来显示图像标签 label = new JLabel(); add(label); // set up file chooser //设置文件选择器 chooser = new JFileChooser(); // accept all image files ending with .jpg, .jpeg, .gif FileFilter filter = new FileNameExtensionFilter( "Image files", "jpg", "jpeg", "gif");//接受各种形式 chooser.setFileFilter(filter); chooser.setAccessory(new ImagePreviewer(chooser)); //设置过滤器 chooser.setFileView(new FileIconView(filter, new ImageIcon("palette.gif"))); } }

package fileChooser; import java.io.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.*; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter; /** * A file view that displays an icon for all files that match a file filter. */ public class FileIconView extends FileView { private FileFilter filter; private Icon icon; /** * Constructs a FileIconView. * @param aFilter a file filter--all files that this filter accepts will be shown * with the icon. * @param anIcon--the icon shown with all accepted files. */ public FileIconView(FileFilter aFilter, Icon anIcon) { filter = aFilter; icon = anIcon; } public Icon getIcon(File f) { if (!f.isDirectory() && filter.accept(f)) return icon; else return null; } }

package fileChooser; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.25 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class FileChooserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); frame.setTitle("FileChooserTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
测试程序16
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材570页程序12-24,结合运行结果理解程序;
l 了解颜色选择器的用法。
l 记录示例代码阅读理解中存在的问题与疑惑。

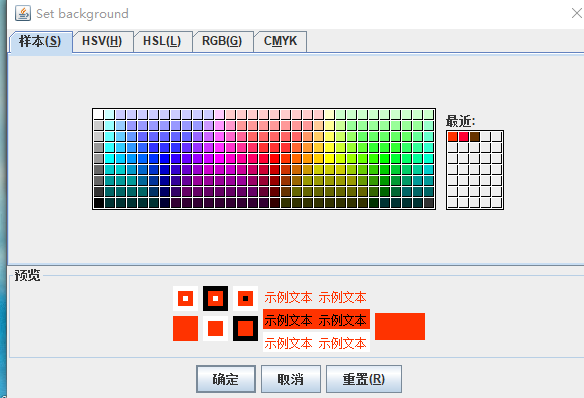
package colorChooser; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.Frame; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JColorChooser; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JPanel; /** * A panel with buttons to pop up three types of color choosers */ public class ColorChooserPanel extends JPanel { public ColorChooserPanel()//狗仔一个初始颜色的颜色选择器 { JButton modalButton = new JButton("Modal"); modalButton.addActionListener(new ModalListener()); add(modalButton); JButton modelessButton = new JButton("Modeless"); modelessButton.addActionListener(new ModelessListener()); add(modelessButton); JButton immediateButton = new JButton("Immediate"); immediateButton.addActionListener(new ImmediateListener()); add(immediateButton); } /** * This listener pops up a modal color chooser */ private class ModalListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { Color defaultColor = getBackground(); Color selected = JColorChooser.showDialog(ColorChooserPanel.this, "Set background", defaultColor); if (selected != null) setBackground(selected); } } /** * This listener pops up a modeless color chooser. The panel color is changed when the user * clicks the OK button. */ private class ModelessListener implements ActionListener { private JDialog dialog; private JColorChooser chooser; public ModelessListener() { chooser = new JColorChooser(); dialog = JColorChooser.createDialog(ColorChooserPanel.this, "Background Color", false /* not modal */, chooser, event -> setBackground(chooser.getColor()), null /* no Cancel button listener */); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { chooser.setColor(getBackground()); dialog.setVisible(true); } } /** * This listener pops up a modeless color chooser. The panel color is changed immediately when * the user picks a new color. */ private class ImmediateListener implements ActionListener { private JDialog dialog; private JColorChooser chooser; public ImmediateListener() { chooser = new JColorChooser(); chooser.getSelectionModel().addChangeListener( event -> setBackground(chooser.getColor())); dialog = new JDialog((Frame) null, false /* not modal */); dialog.add(chooser); dialog.pack(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { chooser.setColor(getBackground()); dialog.setVisible(true); } } }

package colorChooser; import javax.swing.*; /** * A frame with a color chooser panel */ public class ColorChooserFrame extends JFrame {//设置两个私有属性 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public ColorChooserFrame()//颜色选择器 { setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // add color chooser panel to frame ColorChooserPanel panel = new ColorChooserPanel(); add(panel); } }

package colorChooser; import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * @version 1.04 2015-06-12 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ColorChooserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new ColorChooserFrame();//生成ColorChooserFrame类 frame.setTitle("ColorChooserTest"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//关闭界面操作 frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
实验2:组内讨论反思本组负责程序,理解程序总体结构,梳理程序GUI设计中应用的相关组件,整理相关组件的API,对程序中组件应用的相关代码添加注释。
总结:我们组这次所分析的是工具栏和工具提示的用法方面的知识,工具栏(Toolbar Test)是在程序中提供的快速访问常用命令的按纽栏,它可以随意的移动安放,可以用JToolBar bar=new JToolBar();来创建工具栏。但工具栏有缺点,为了便利用户能快速明白小按钮的含义,用户界面设计者发明了工具提示toooltips,示例程序说明了如何将一个Action对象添加到菜单和工具栏中。通过代码解读和注释,我们可以明白如何去构建一个工具栏,将组建添加到工具栏中,因此实现工具栏的功能。
实验3:组间协同学习:在本班课程QQ群内,各位同学对实验1中存在的问题进行提问,提问时注明实验1中的测试程序编号,负责对应程序的小组需及时对群内提问进行回答。
具体见QQ群
