pandas
# pandas 数据结构 # 导入 pandas import pandas as pd from pandas import DataFrame,Series import numpy as np
Series的创建
两种创建方式:
由列表或numpy数组创建 默认索引为0到N-1的整数型索引
还可以通过设置index参数指定索引
Series(data=[1,2,3]) Series(data=[1,2,3],index=['a','b','c']) Series(data=np.random.randint(1,100,size=(3,)))
索引 切片 去重
# Series的索引和切片 s[0:2] # 可以使用s.head(),tail()分别查看前n个和后n个值 s.head(2) s.tail(2)
去空 运算
s1 = Series(data=[1,2,3,4],index=['a','b','c','d']) s2 = Series(data=[1,2,3,4],index=['a','b','e','d']) s = s1 + s2 # 当索引没有对应的值时,可能出现缺失数据显示NaN(not a number)的情况 s # 可以使用pd.isnull(),pd.notnull(),或s.isnull(),notnull()函数检测缺失数据 s.isnull() # s.notnull() s # s[[True,True,False,False,True]] #如果将布尔值作为Serrise的索引,则只保留True对应的元素值 # 去除 为空的 s[s.notnull()] # Series之间的运算 # 在运算中自动对齐不同索引的数据 # 如果索引不对应,则补NaN s1+s2
DataFrame
DataFrame是一个【表格型】的数据结构。DataFrame由按一定顺序排列的多列数据组成。设计初衷是将Series的使用场景从一维拓展到多维。DataFrame既有行索引,也有列索引。
- 行索引:index
- 列索引:columns
- 值:values
1)DataFrame的创建 最常用的方法是传递一个字典来创建。DataFrame以字典的键作为每一【列】的名称,以字典的值(一个数组)作为每一列。 此外,DataFrame会自动加上每一行的索引。 使用字典创建的DataFrame后,则columns参数将不可被使用。 同Series一样,若传入的列与字典的键不匹配,则相应的值为NaN。
DataFrame属性:values、columns、index、shape
DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(1,100,size=(3,4))) df=DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(1,100,size=(3,4)),index=['a','b','c'],columns=['A','B','C','D']) df df.values df.index df.columns df.shape
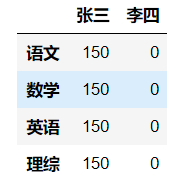
dic = { '张三':[150,150,150,150], '李四':[0,0,0,0] } df = DataFrame(data=dic,index=['语文','数学','英语','理综']) df
索引
对列进行索引
- 通过类似字典的方式 df['q']
- 通过属性的方式 df.q
可以将DataFrame的列获取为一个Series。返回的Series拥有原DataFrame相同的索引,且name属性也已经设置好了,就是相应的列名。
对行进行索引
- 使用.loc[]加index来进行行索引
- 使用.iloc[]加整数来进行行索引
同样返回一个Series,index为原来的columns。
对元素索引的方法
- 使用列索引
- 使用行索引(iloc[3,1] or loc['C','q']) 行索引在前,列索引在后df.iloc[0] df.loc['A'] df.iloc[[0,1]] df.loc[['B','C']] df.iloc[1,1] df.loc['C','d'] df.loc[['A','B'],'c']
切片
【注意】 直接用中括号时:
- 索引表示的是列索引
- 切片表示的是行切片
df[0:2] df.iloc[:,0:2] df.loc['A':"C","b":"d"]
总结:
- 索引:
- 取行:df.loc['A']
- 取列:df['a']
- 取元素:df.iloc[1,2]
- 切片:
- 切行:df[0:2]
- 切列:df.iloc[:,0:2]
DataFrame的运算
DataFrame之间的运算
同Series一样:
- 在运算中自动对齐不同索引的数据
- 如果索引不对应,则补NaN
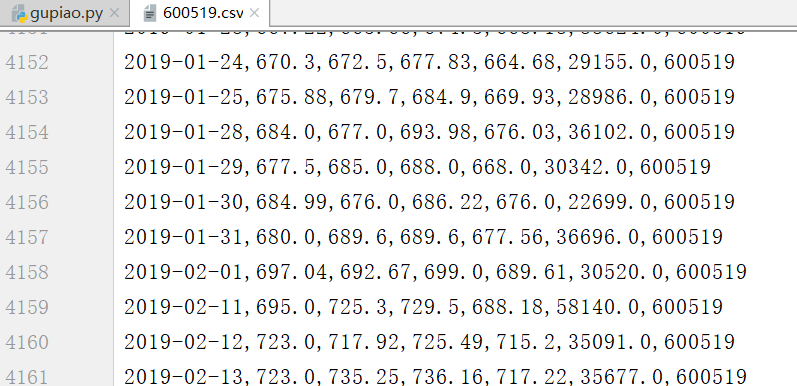
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from pandas import DataFrame,Series import tushare as ts # 使用tushare 包获取某股票的历史行情数据 df=ts.get_k_data(code='600519',start='2000-01-01') # print(df) # 保存 df.to_csv("./600519.csv") # 将date这一列作为源数据的行索引,且将数据类型转换为时间类型 df=pd.read_csv('./600519.csv',index_col='date',parse_dates=['date']) df.drop(labels='Unnamed: 0',axis=1,inplace=True) # 保存 df.to_csv("./600519.csv") # 显示前5行 # print(df.head(5)) #输出该股票所有收盘比开盘上涨3%以上的日期。 #(收盘-开盘)/开盘 >= 0.03 # (df['close']-df['open'])/df['open']>=0.03 # 将上述表达式返回的布尔值作为df 的行索引,取出所有符合要求的数据 # 符合条件的行数据 # print(df.loc[(df['close']-df['open'])/df['open']>=0.03]) # 符合条件的日期 # print(df.loc[(df['close']-df['open'])/df['open']>=0.03].index) #输出该股票所有开盘比前日收盘跌幅超过2%的日期。 #(开盘 - 前日收盘) / 前日收盘 < -0.02 # df['open']-df['close'].shift(1)/df['close'].shift(1) # 符合条件的数据 # print(df.loc[(df['open']-df['close'].shift(1))/df['close'].shift(1)<-0.02]) # print(df.loc[(df['open']-df['close'].shift(1))/df['close'].shift(1)<-0.02].index) #假如我从2010年1月1日开始,每月第一个交易日买入1手股票,每年最后一个交易日卖出所有股票,到今天为止,我的收益如何? # print(df) df=df.loc['2010':'2019'] # print(df) # print(df.head(5)) # 数据重新取样(取样结果 日期有错误,自身的问题) df_monthly=df.resample('M').first() # 最后一个日期的结果去掉 因为还未到年底 df_yearly=df.resample('A').last()[:-1] # print(df_monthly) # print(df_yearly) # 一手 是100股 cost_money=df_monthly['open'].sum()*100 # 还需要加上今年投入的股票 # df_yearly['open'].sum()*12*100 # 现在8月份,所以乘8 recv_money=df_yearly['open'].sum()*12*100+df['open'][-1]*800 final_money=recv_money-cost_money print(final_money) # 结果391697.69999999925 8.12