概述
数据存储是为了可查询,统计。若数据只需存储,不需要查询,这种数据也没有多大价值
本篇介绍Mongodb
- 聚合查询(Aggregation)
- 固定集合(Capped Collections)
准备工作
准备10000条数据
var orders = new Array(); for (var i = 10000; i < 20000; i++) { orders[i] = { orderNo: i + Math.random().toString().substr(3, 3), price: Math.round(Math.random() * 10000) / 100, qty: Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 1, orderTime: new Date(new Date().setSeconds(Math.floor(Math.random() * 10000))) }; } db.order.insert(orders);
聚合查询
Mongodb的聚合函数操作都在db.collection.aggregate,通过定义聚合管道(一组规则),达到分组,统计等功能,下面介绍常用的几种聚合函数
分组管道($group)
格式
{ $group: { _id: <expression>, // Group By Expression <field1>: { <accumulator1> : <expression1> }, ... } }
_id 是分组字段,若指定_id = null 或常量字段,就是将整个结果集分组。
分组统计字段格式{ <accumulator1> : <expression1> }
累计器操作(Accumulator Operator)参考Accumulator Operator
假设现在需要统计每天每个小时的订单总价格,平均价格,最大,最小,总订单数等
db.order.aggregate([ { $group: { //分组字段,这里用到$dateToString格式化,这里按小时统计 _id: { $dateToString: { format: "%Y-%m-%d %H", date: "$orderTime" } }, //总价格 totalPrice: { $sum: "$price" }, //分组第一个订单 firstOrder: { $first: "$orderNo" }, //分组最后一个订单 lastOrder: { $last: "$orderNo" }, //平均价格 averagePrice: { $avg: "$price" }, //最大价格 maxPrice: { $max: "$price" }, //最小价格 minPrice: { $min: "$price" }, //总订单数 totalOrders: { $sum: 1 }, } } ])
返回结果
{ "_id" : "2020-04-12 15", "totalPrice" : 172813.68, "firstOrder" : "10000263", "lastOrder" : "19999275", "averagePrice" : 49.20662870159453, "maxPrice" : 99.94, "minPrice" : 0.01, "totalOrders" : 3512 }
{ "_id" : "2020-04-12 13", "totalPrice" : 80943.98, "firstOrder" : "10004484", "lastOrder" : "19991554", "averagePrice" : 50.780414052697616, "maxPrice" : 99.81, "minPrice" : 0.08, "totalOrders" : 1594 }
{ "_id" : "2020-04-12 14", "totalPrice" : 181710.15, "firstOrder" : "10001745", "lastOrder" : "19998830", "averagePrice" : 49.76996713229252, "maxPrice" : 99.93, "minPrice" : 0.01, "totalOrders" : 3651 }
{ "_id" : "2020-04-12 16", "totalPrice" : 63356.12, "firstOrder" : "10002711", "lastOrder" : "19995793", "averagePrice" : 50.97032984714401, "maxPrice" : 99.95, "minPrice" : 0.01, "totalOrders" : 1243 }
筛选管道($match)
格式
{ $match: { <query> } }
这个比较简单,就是筛选数据
假设我现在需要筛选金额在(10,15)之间的
db.orders.aggregate([ { $match: { "price": { $gt: 10, $lt: 15 } } } ])
排序管道($sort)
格式
{ $sort: { <field1>: <sort order>, <field2>: <sort order> ... } }
指定字段排序,1:升序,-1:倒序
限制条数($limit)
格式
{ $limit: <positive integer> }
Mongodb的聚合管道有很多,具体不一一列出,参考Aggregation Pipeline Stages — MongoDB Manual
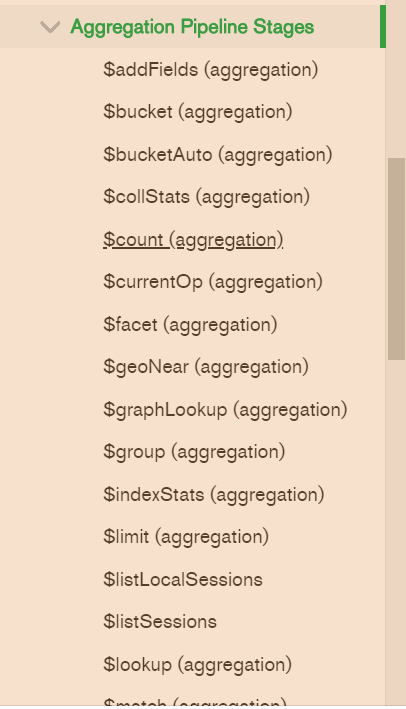
带有(aggregation)就是都可以用于聚合管道
说了那么多,其实都没有使用Mongodb聚合函数最强大的功能,就是组合管道使用,查询我们需要数据,因为Mongodb提供的聚合管道函数非常多,所以组合起来使用是非常强大。
值得注意是管道的顺序,Mongodb是按你定义的顺序,将每一步执行的结果集传给下一个管道处理,输出是最后一个管道的结果集,所以不同的管道顺序会有可能得到不是预期的结果,甚至报错(这种情况报错甚至比得到不是预期的结果可能还好)- 订单金额大于10元 小于 50元 && 数量小于等于5 and
- 去掉金额最小的50条订单 && 去掉金额最大的50条订单 and
- 统计每个小时内订单数量,订单金额
- 按订单金额升序输出

db.order.aggregate([ { $match: { "price": { $gt: 10, $lt: 50 }, "qty": { $lte: 5 } } }, { $sort: { "price": -1 } }, { $skip: 50 }, { $sort: { "price": 1 } }, { $skip: 50 }, { $group: { _id: { $dateToString: { format: "%Y-%m-%d %H", date: "$orderTime" } }, totalPrice: { $sum: "$price" }, totalOrders: { $sum: 1 } } }, { $sort: { "totalPrice": 1 } } ])

解决思路
- 筛选符合条件的记录($match)
- 按金额倒序($sort:-1)
- 跳过金额最大的50条记录($skip:50)
- 按金额升序($sort:1)
- 跳过金额最小的50条记录($skip:50)
- 按每天每小时统计($group)
- 统计结果总金额升序($sort:1)
固定集合
概述
capped-collection are fixed-size collections that support high-throughput operations that insert and retrieve documents based on insertion order. Capped collections work in a way similar to circular buffers: once a collection fills its allocated space, it makes room for new documents by overwriting the oldest documents in the collection.
从上面定义可以看出固定集合具有几个特性
- 固定大小
- 高吞吐量
- 根据插入顺序检索文档
- 超过限制大小覆盖旧的文档
根据固定集合特性,固定集合适合用于以下场景
- 只需保留最近的日志查询系统
- 缓存数据(热点数据)
- 等等
固定集合限制
- 固定集合的大小创建之后不能修改
- 不能删除固定集合里的文档,只能删除集合再重新建固定集合
- 固定集合不能使用固定分区
- 聚合管道$out不能使用在固定集合
固定集合使用
1. 创建固定集合
db.createCollection("log", { capped : true, size : 4096, max : 5000 } )
| 字段 | 必须 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| capped | 是 | 是否创建固定集合 |
| size | 是 | 固定集合大小,单位:字节 |
| max | 否 | 文档数量大小限制 |
size 和 max 是或关系,超出其中一个限制都会覆盖旧文档
2. 检查集合是否固定集合
db.collection.isCapped()
3. 将一个非固定的集合转换固定集合
db.runCommand({"convertToCapped": "mycoll", size: 100000});
测试固定集合
1. 超过限制文档数
// 1. 创建固定集合,大小1M,最大文档数量10 db.createCollection("log", { capped: true, size: 1024 * 1024, max: 10 }); // 2. 插入200条数据 for (var i = 0; i < 200; i++) { db.log.insertOne({ "_id": i + 1, "userId": Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000), "content": "登录" + ("0000" + i).slice(-4), "createTime": new Date(), }); }
再查询现在Mongodb存储情况
db.log.stats()

可以看出每个对象都是占有78个字节,因为字段都是定长的
2. 验证操作存储大小
If the size field is less than or equal to 4096, then the collection will have a cap of 4096 bytes. Otherwise, MongoDB will raise the provided size to make it an integer multiple of 256.
如果size的字段设置小于4096,Mongodb将会提供一个256的倍数的数据存储大小
假设256的大小,256 / 78 = 3.282051282051282,应该能存3个文档
// 1. 删除之前固定集合 db.log.drop(); // 2. 创建固定集合,size < 78 , 验证是否创建一个256的大小 db.createCollection("log", { capped: true, size: 78 }); // 2. 插入200条数据 for (var i = 0; i < 200; i++) { db.log.insertOne({ "_id": i + 1, "userId": Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000), "content": "登录" + ("0000" + i).slice(-4), "createTime": new Date(), }); }
查看集合统计
db.log.stats()
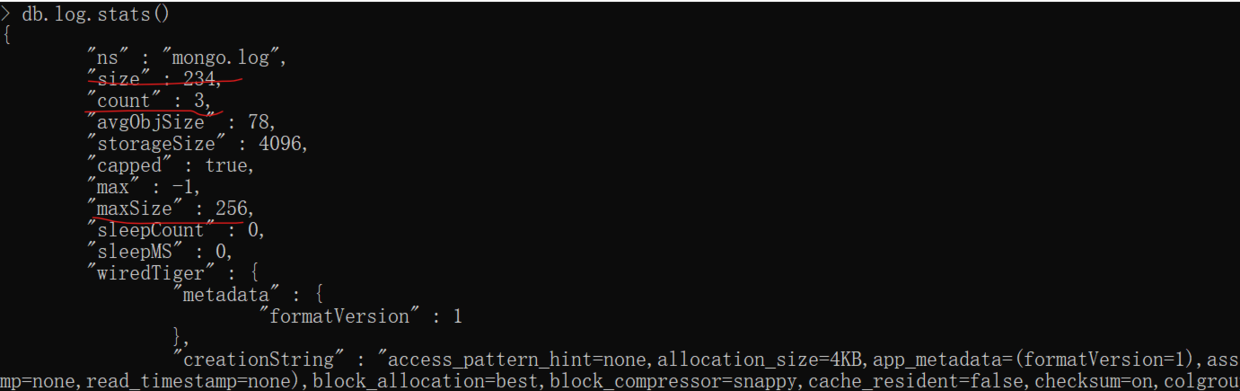
可以看出log集合使用了234个字节(78 * 3),也即3个文档的大小,最大能使用大小是256
3. 查询固定集合
Mongodb若没指定排序字段,是按存入顺序检索,可以使用.sort( { $natural: -1 } )改变输出顺序
db.log.find({}).sort( { $natural: -1 } )
4. 将非固定集合转换固定集合
将order转换试试
db.runCommand({"convertToCapped": "order", size: 8096});
查看order集合统计
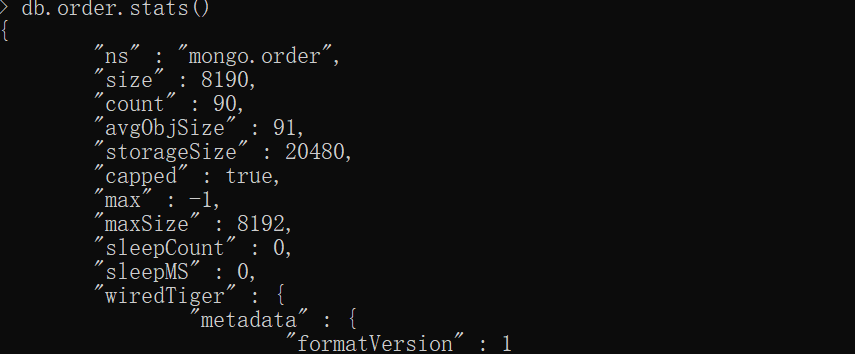
只剩下90条数据
转发请标明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/WilsonPan/p/12692642.html
