实验九
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握java异常处理技术;
(2) 了解断言的用法;
(3) 了解日志的用途;
(4) 掌握程序基础调试技巧;
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:
package 异常; //异常示例1 public class ExceptionDemo1 { public static void main(String args[]) { int a=0; if(a==0) { System.out.println("除数不能为零!"); } else { System.out.println(5 / a); } } }
import java.io.*; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; public class ExceptionDemo2 { public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException { try { File file = new File("text.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String b; while((b=in.readLine())!=null) { System.out.print(b); } fis.close(); }catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
实验2:
测试程序1:
package stackTrace; import java.util.*; /** * A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call. * @version 1.01 2004-05-10 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class StackTraceTest { /** * Computes the factorial of a number * @param n a non-negative integer * @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n */ public static int factorial(int n) { System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):"); Throwable t = new Throwable(); StackTraceElement[] frames = t.getStackTrace(); for (StackTraceElement f : frames) System.out.println(f); int r; if (n <= 1) r = 1; else r = n * factorial(n - 1); System.out.println("return " + r); return r; } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter n: "); int n = in.nextInt(); factorial(n); } }

测试程序2:
练习2:
package 计算器;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Random;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Random;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class Exam{
int sum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.sum = 0;
Random r = new Random ();
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("E://text.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Exam exam = new Exam();
exam.sum = 0;
Random r = new Random ();
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("E://text.txt");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) {
exam.score();
}
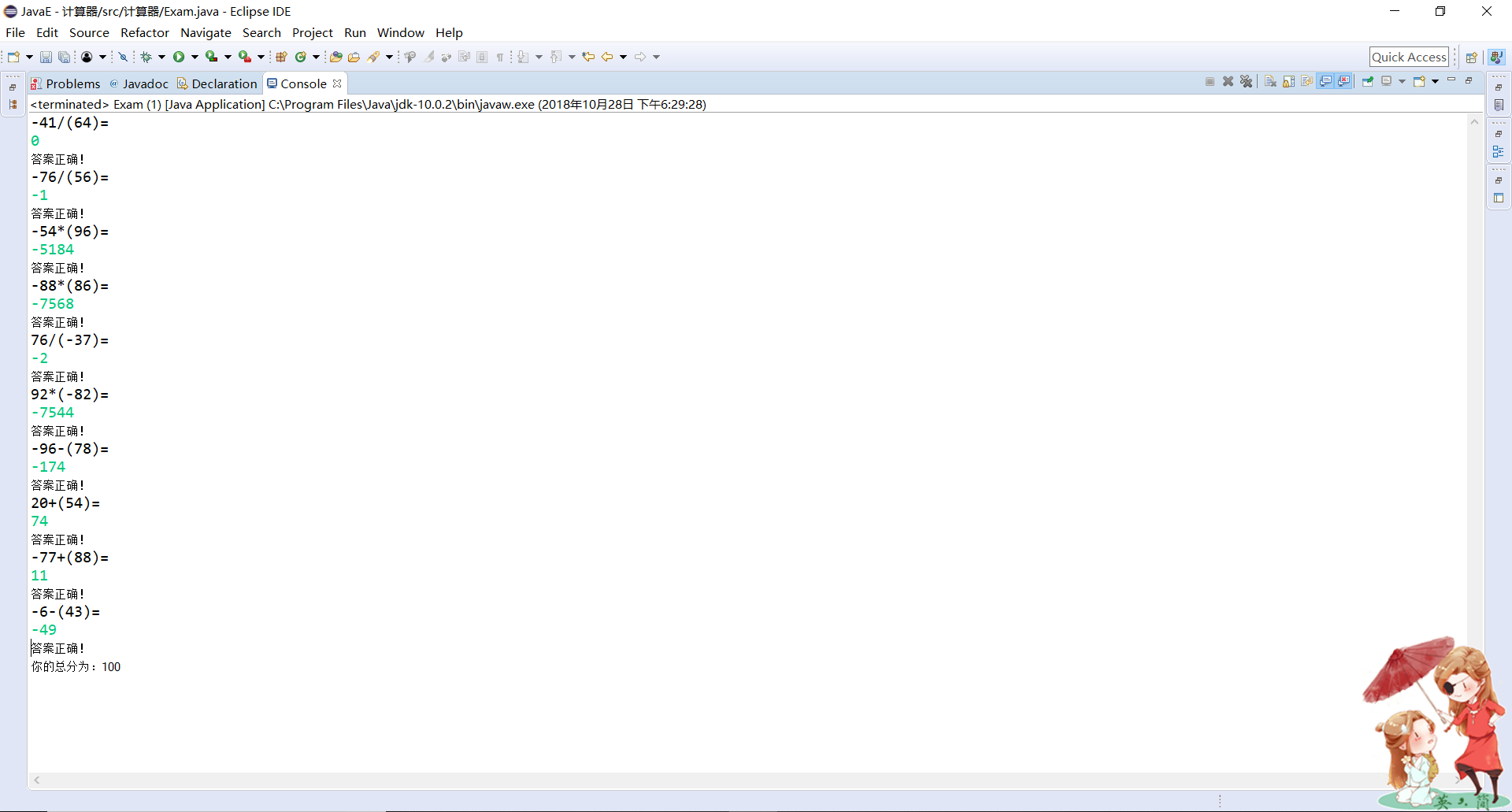
System.out.println("你的总分为:"+exam.sum);
output.println("你的总分为:"+exam.sum);
output.close();
}
private void score() {
Random r = new Random ();
int m;
m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4);
switch(m) {
case 0:
int a,b,c;
a = r.nextInt() % 100;
b = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(a + "+" + "(" + b + ")=");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
c = x.nextInt();
if(c != a+b)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 1:
int o,p,q;
o = r.nextInt() % 100;
p = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(o + "-" + "(" + p + ")=");
Scanner y = new Scanner(System.in);
q = y.nextInt();
if(q != o-p)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 2:
int d,e,f;
d = r.nextInt() % 100;
e = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(d + "*" +"("+ e + ")" + "=");
Scanner z = new Scanner(System.in);
f = z.nextInt();
if(f != d * e)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 3:
int h,i,j;
h = r.nextInt() % 100;
i = r.nextInt() % 100;
if(i == 0)
i++;
System.out.println(h + "/" +"("+ i + ")" + "=");
Scanner u = new Scanner(System.in);
j = u.nextInt();
if(j != h/i)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
}
}
}
exam.score();
}
System.out.println("你的总分为:"+exam.sum);
output.println("你的总分为:"+exam.sum);
output.close();
}
private void score() {
Random r = new Random ();
int m;
m = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4);
switch(m) {
case 0:
int a,b,c;
a = r.nextInt() % 100;
b = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(a + "+" + "(" + b + ")=");
Scanner x = new Scanner(System.in);
c = x.nextInt();
if(c != a+b)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 1:
int o,p,q;
o = r.nextInt() % 100;
p = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(o + "-" + "(" + p + ")=");
Scanner y = new Scanner(System.in);
q = y.nextInt();
if(q != o-p)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 2:
int d,e,f;
d = r.nextInt() % 100;
e = r.nextInt() % 100;
System.out.println(d + "*" +"("+ e + ")" + "=");
Scanner z = new Scanner(System.in);
f = z.nextInt();
if(f != d * e)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
case 3:
int h,i,j;
h = r.nextInt() % 100;
i = r.nextInt() % 100;
if(i == 0)
i++;
System.out.println(h + "/" +"("+ i + ")" + "=");
Scanner u = new Scanner(System.in);
j = u.nextInt();
if(j != h/i)
System.out.println("答案错误!");
else {
System.out.println("答案正确!");
sum += 10;
}
break;
}
}
}
实验4:
实验程序1:
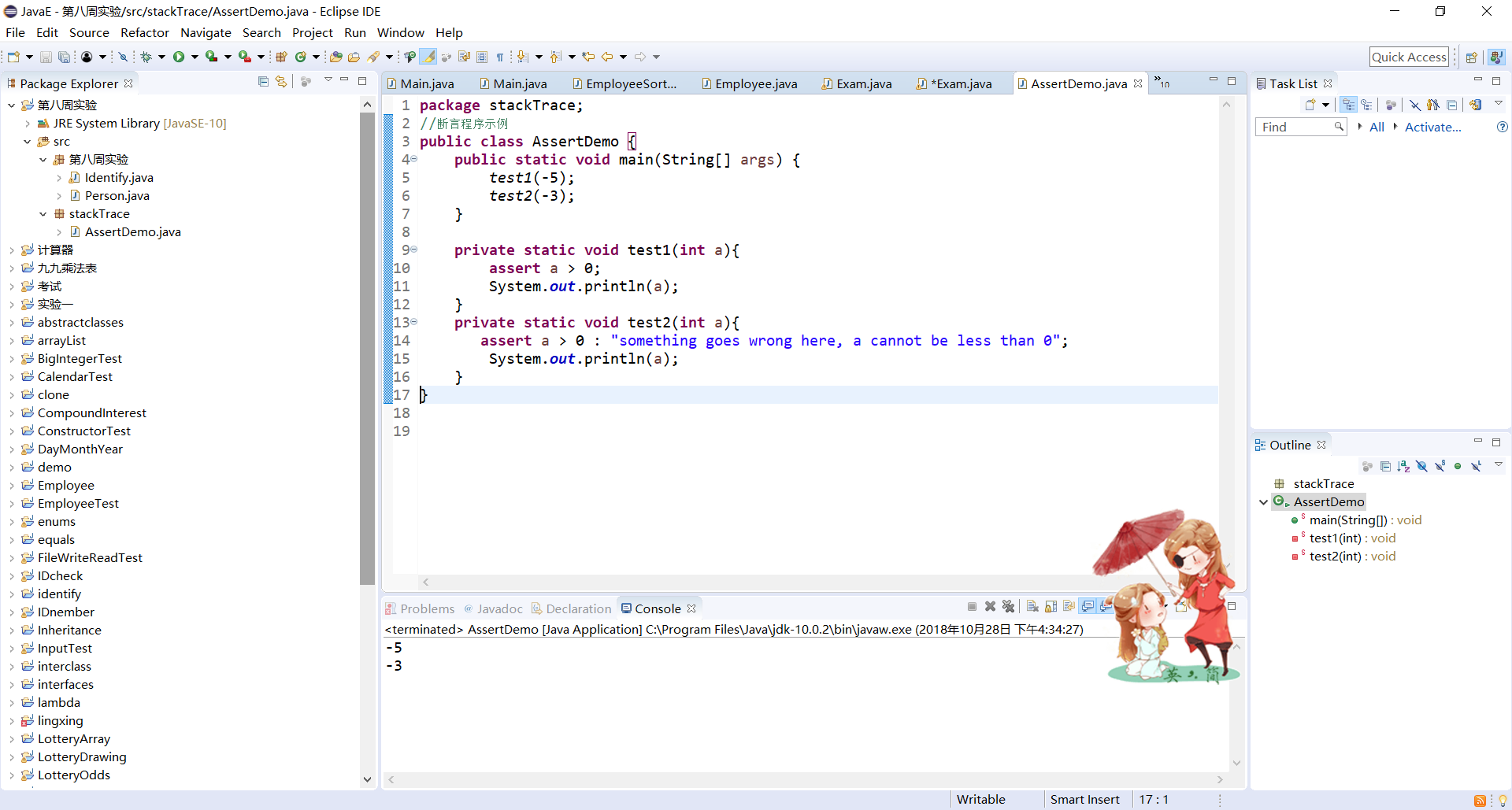
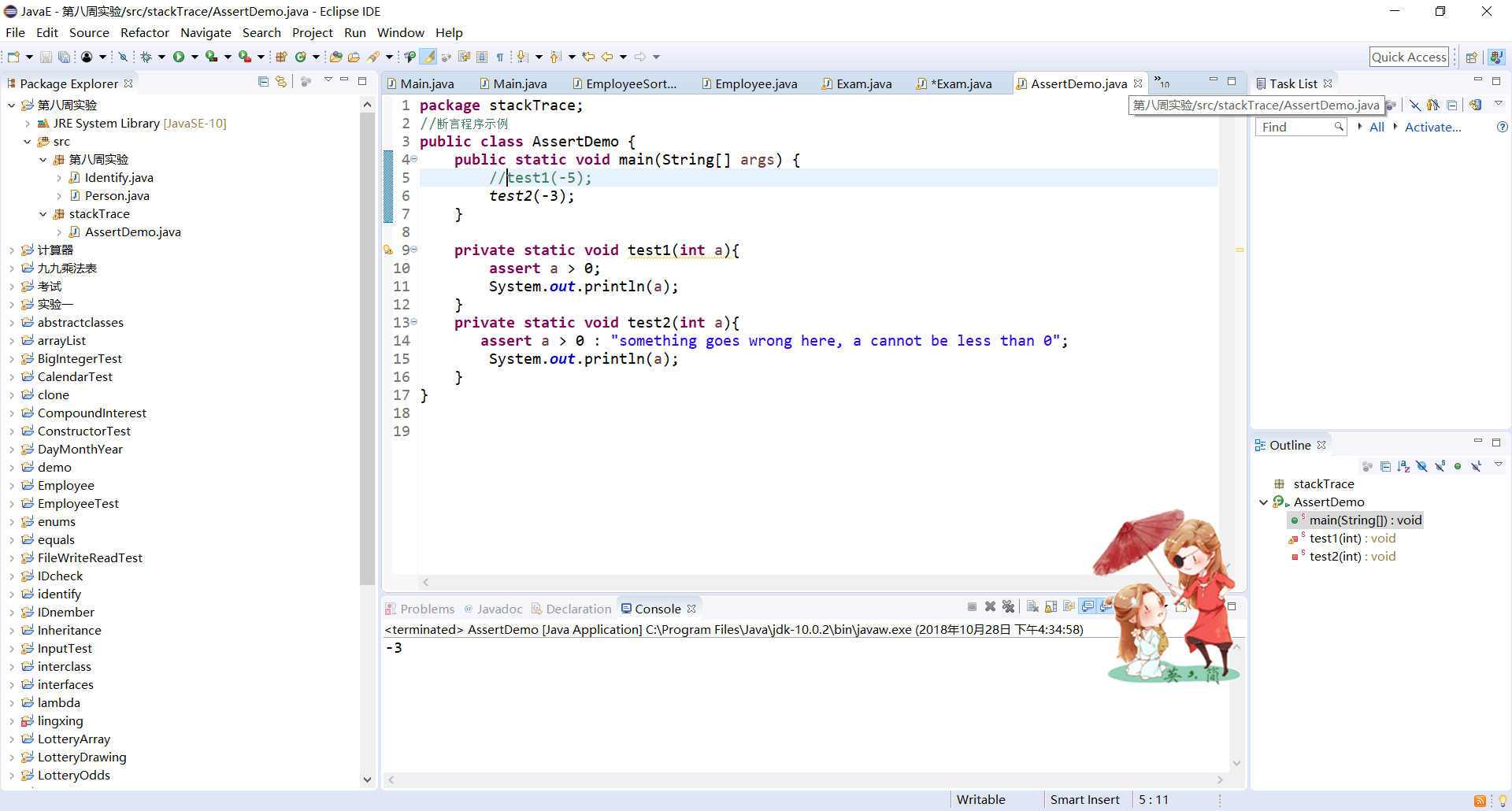
//断言程序示例 public class AssertDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //test1(-5); test2(-3); } private static void test1(int a){ assert a > 0; System.out.println(a); } private static void test2(int a){ assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; System.out.println(a); } }
实验程序2:
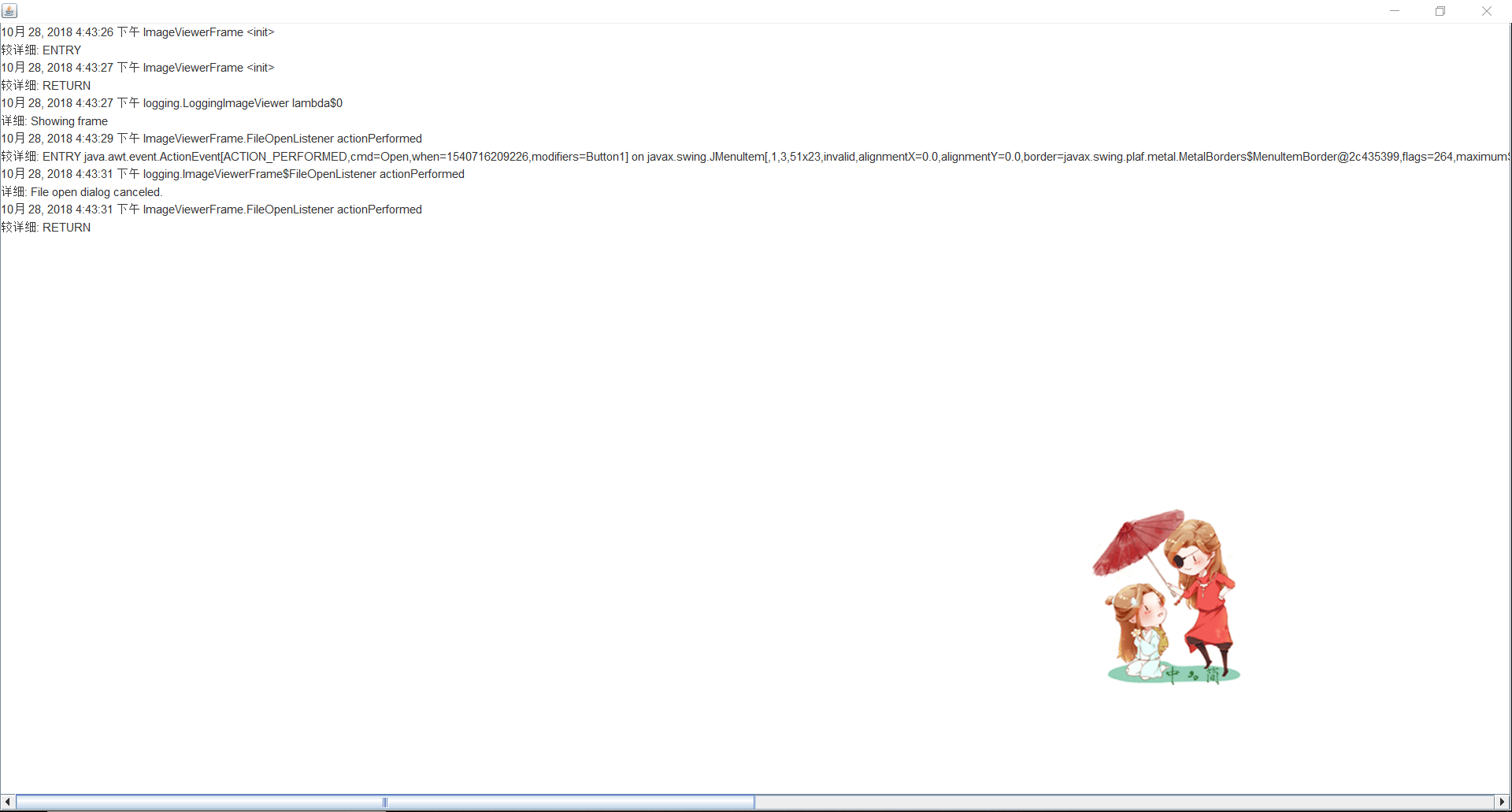
package logging; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.io.*; import java.util.logging.*; import javax.swing.*; /** * A modification of the image viewer program that logs various events. * @version 1.03 2015-08-20 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class LoggingImageViewer { public static void main(String[] args) { if (System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.class") == null && System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.file") == null) { try { Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").setLevel(Level.ALL); final int LOG_ROTATION_COUNT = 10; Handler handler = new FileHandler("%h/LoggingImageViewer.log", 0, LOG_ROTATION_COUNT); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(handler); } catch (IOException e) { Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").log(Level.SEVERE, "Can't create log file handler", e); } } EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { Handler windowHandler = new WindowHandler(); windowHandler.setLevel(Level.ALL); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(windowHandler); JFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); frame.setTitle("LoggingImageViewer"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").fine("Showing frame"); frame.setVisible(true); }); } } /** * The frame that shows the image. */ class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame { private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; private JLabel label; private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava"); public ImageViewerFrame() { logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // set up menu bar JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); menu.add(openItem); openItem.addActionListener(new FileOpenListener()); JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); menu.add(exitItem); exitItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { logger.fine("Exiting."); System.exit(0); } }); // use a label to display the images label = new JLabel(); add(label); logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); } private class FileOpenListener implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed", event); // set up file chooser JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); // accept all files ending with .gif chooser.setFileFilter(new javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter() { public boolean accept(File f) { return f.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif") || f.isDirectory(); } public String getDescription() { return "GIF Images"; } }); // show file chooser dialog int r = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); // if image file accepted, set it as icon of the label if (r == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); logger.log(Level.FINE, "Reading file {0}", name); label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); } else logger.fine("File open dialog canceled."); logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed"); } } } /** * A handler for displaying log records in a window. */ class WindowHandler extends StreamHandler { private JFrame frame; public WindowHandler() { frame = new JFrame(); final JTextArea output = new JTextArea(); output.setEditable(false); frame.setSize(200, 200); frame.add(new JScrollPane(output)); frame.setFocusableWindowState(false); frame.setVisible(true); setOutputStream(new OutputStream() { public void write(int b) { } // not called public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) { output.append(new String(b, off, len)); } }); } public void publish(LogRecord record) { if (!frame.isVisible()) return; super.publish(record); flush(); } }
实验总结:
通过这一章的学习,我重点学习到了什么是异常,异常是在程序的执行过程中所发生的异常事件,它中断指令的正常执行。他分为非致命异常和致命异常。Java中所有的异常类都直接或间接地继承于 Throwable类。Exception类中的RuntimeException为运行时异常类,一般由程序错误产生。派生于Error类或RuntimeException类的所有异常被称为未检查异常,编译器允许不对这些异常进行处理 。捕获异常:try、catch、finally块。
Try语句:括住可能抛出异常的代码段
Catch语句:指明要捕获的异常及相应的处理代码
Finally语句:必须执行的程序块
还有断言以及日志和调试,断言是程序的开发和测试阶段用于插入一些代码错误检测语句的工具。
其次,对于练习二的程序,我还有一点没有完成,就是没有将成绩单输出到TXT文件中。